* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics - Northwest ISD Moodle
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
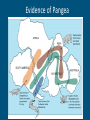
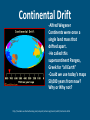
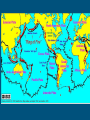
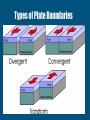
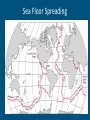
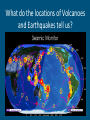
Plate Tectonics The Crust • This is where we live! • The Earth’s crust is made of: Continental Crust Oceanic Crust - thick (10-70km) - buoyant (less dense than oceanic crust) - mostly old - thin (~7 km) - dense (sinks under continental crust) - young Plate Tectonics • Pieces of the lithosphere that move around • Each plate has a name based on the name of the continents and oceans nearby. • Fit together like jigsaw puzzles • Float on top of mantle Evidence of Pangea Evidence of Pangaea 1.Fossils of animals and plants living on separate continents 2.Rock deposits 3.Ancient mountain ranges 4.Glacial deposits 5.Continental drift Continental Drift -Alfred Wegener Continents were once a single land mass that drifted apart. -He called this supercontinent Pangea, Greek for “all Earth” -Could we use today’s maps 50,000 years from now? Why or Why not? http://members.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/planets/earth/Continents.shtml Names & Locations of the tectonic plates Tectonic Plates Types of Plate Boundaries Ocean-Ocean Plate Collision • When two oceanic plates collide, one runs over the other which causes it to sink into the mantle forming a subduction zone→ trench. • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. • The worlds deepest parts of the ocean are found along trenches. – Ex: The Mariana Trench is 11 km deep! Continent-Oceanic Crust Collision • Causes SUBDUCTION → volcanoes Volcanoes are formed by: - Subduction - Rifting - Hotspots Ring of Fire -An area in the Pacific Ocean (Pacific Plate) where many Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur. California Continent-Continent Collision • Forms folding of crust →mountains, • Ex: European Alps, Himalayas Divergent Boundaries • Spreading ridges, rift valleys – As plates move apart new material is erupted to fill the gap Sea Floor Spreading Sea Floor Spreading • Mid Ocean Ridges – underwater mountain chains that run through the Earth’s Basins • Magma rises to the surface and solidifies and new crust forms • Older Crust is pushed farther away from the ridge Transform Boundaries • Where plates slide past each other • Causes a fault → earthquakes Above: View of the San Andreas transform fault in California. It is caused by the Pacific Plate sliding on the North American Plate. Where do earthquakes from? Figure showing the tectonic setting of earthquakes What do the locations of Volcanoes and Earthquakes tell us?