* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Team composition wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Vested interest (communication theory) wikipedia , lookup
Implicit attitude wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Attribution bias wikipedia , lookup
Self-perception theory wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
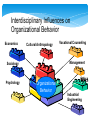
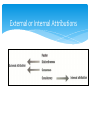
HUBERT KAIRUKI MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF BEHAVIOURAL SCIENCES TOPIC; DYNAMICS OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOUR FACILITATOR; MR LEMA 2 PRESENTERS RAYYAN SAID FATMA SAID BAESH ASHA SALUM HAMAD ENOCK RAPHAEL RAMADHAN IDDY GAMBUNA DAVID VALENTINE JUVINILE TUMENYE AMBAKISYE MARTIN JOSHUA 3 OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION ATTITUDE PERSONALITY PERCEPTION LEARNING STRESS MANAGEMENT SUMMARY CONCLUSION RECOMMENDATION 4 OVERVIEW Employees and managers bring their individual differences to work each day Differences in attitudes, values, personality, and behavior influence how people interpret an assignment, whether they like to be told what to do how they handle challenges how they interact with others Manager’s Challenge: Quick Eagle Networks 5 Organizational Behavior • Interdisciplinary field dedicated to the study of attitudes behavior performance 6 Interdisciplinary Influences on Organizational Behavior Economics Cultural Anthropology Management Sociology Psychology Vocational Counseling Ethics Organizational Behavior 33 Industrial Engineering Organizational Citizenship Work behavior that goes beyond job requirements and contributes as needed to the organization’s success ● Being helpful to coworkers and customers ● Doing extra work when necessary ● Looking for ways to improve products & procedures 8 Attitudes Cognitive and affective evaluation that predisposes a person to act in a certain way Attitudes determine how people Perceive the work environment Interact with others Behave on the job 9 Components of an Attitude 10 Components of Attitudes Particularly important when attempting to change attitudes Cognitive component includes the beliefs, opinions, and information the person has about the object of the attitude Affective component is the person’s emotions or feelings about the object of the attitude Behavioral component of an attitude is the person’s intention to behave toward the object of the attitude in a certain way 11 High-Performance Work Attitudes Two attitudes that might relate to high performance Job Satisfaction Organizational Commitment Managers of today’s knowledge workers often rely on job satisfaction to keep motivation and enthusiasm for the organization high 12 High-Performance Work Attitudes Job Satisfaction = positive attitude toward one’s job Organizational Commitment = loyalty to and heavy involvement in one’s organization 13 Conflicts Among Attitudes Cognitive Dissonance = condition in which two attitudes or a behavior and an attitude conflict Leon Festinger – 1950s People want to behave in accordance with their attitudes Usually will take corrective action 14 Perception Cognitive process people use to make sense out of the environment by ● Selecting ● Organizing ● Interpreting information 15 Perception Perception Process: Cognitive process used to make sense out of the environment (3 steps) Observe information via senses Screen information & select what to process Organize selected data into patterns Perceptual Selectivity: process by which individuals screen and select various stimuli that vie for their attention Primacy (toward beginning) Recency (toward end of event) Perceptual Distortions: errors in perceptual judgment arising from inaccuracies in any part of the perceptual process Common Errors: Stereotyping Halo effect Projection 16 Common Perceptual Distortions Stereotyping Tendency to assign an individual to a group or broad category and then attribute generalizations about the group to the individual 17 Common Perceptual Distortions Halo Effect Overall impression of a person or situation based on one characteristic, either favorable or unfavorable 18 Common Perceptual Distortions Tendency to see one’s own personal traits in other people 19 Projection Common Perceptual Distortions Perceptual Defense Tendency of perceivers to protect themselves by disregarding ideas objects, or people that are threatening to them 20 Attributions Judgments about what caused a person’s behavior— either characteristics of the person or of the situation As people organize what they perceive, they often draw conclusions 21 External or Internal Attributions 22 Attribution Biases Fundamental Attribution Error = tendency to underestimate the influence of external factors on another’s behavior and to overestimate the influence of internal factors Self-serving Bias = tendency to overestimate the contribution of internal factors to one’s sucesses and the contribution of external factors to one’s failures 23 Personality Set of characteristics that underlie a relatively stable pattern of behavior in response to ideas, objects, or people in the environment Big Five Personality Factors Extroversion Agreeableness Conscientiousness Emotional Stability Openness to Experience 24 Big Five Personality Factors 25 Emotional Intelligence (EQ) Basic Components Self-awareness: basis for all other components, being aware of what you are feeling Self-management: control disruptive or harmful emotions and balance one’s moods so they do not cloud thinking Social awareness: understand others and practice empathy Relationship awareness: connect to others, build positive relationships, respond to emotions of others, and influence others 26 Behaviors Influenced by Personality Authoritarianism = belief that power and status differences should exist within the organization Stick to conventional values Obey recognized authority above them Critically judge others Oppose the use of subjective feelings Concerned with power and toughness 27 Behaviors Influenced by Personality cont… Machiavellianism = tendency to direct much of one’s behavior toward the acquisition of power and the manipulation of other people for personal gain 28 Problem Solving Styles Individuals differ in the way they solve problems and make decisions Gathering and evaluating information are separate activities ● Gather information ● Sensation ● Intuition ● Evaluate information ● Thinking ● Feeling 29 Learning and Learning Styles Learning = change in behavior or performance that occurs as the result of experience Learning Styles Diverger Assimilator Converger Accommodator 30 Stress and Stress Management Stress = physiological and emotional response to stimuli that place physical or psychological demands on an individual Type A Behavior = pattern characterized by extreme competitiveness, impatience, aggressiveness, and devotion to work Type B Behavior = pattern that lacks Type A and includes a more balanced, relaxed lifestyle 31 Work Stress Four Categories Job Tasks Demands Physical Demands Role Demand (Sets of expected behaviors) Interpersonal Demands 32 Recommendation People conducting organisations like managers and directors should be fully aware of different kinds of their employees and costermars so as to have a highly effective and productive organisations. 35 Conclusion Organizations should make sure that they catch people’s interests and attention for them to love their jobs and be committed with them. 34 REFFERENCES WIKIPEDIA FREE ENCYCLOPEDIA OXFORD DICTIONARY 35








































![[Product Name] Marketing Plan](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008637503_1-871502ddbf1d19bd696476716a3494d6-150x150.png)



