* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 投影片 1
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
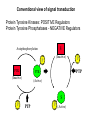
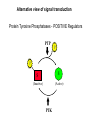
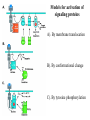
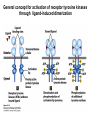
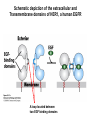
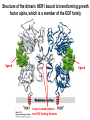
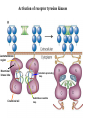
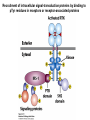
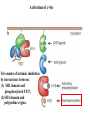
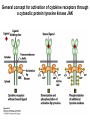
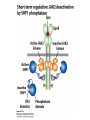
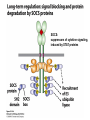
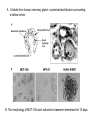
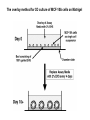
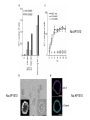
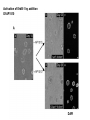
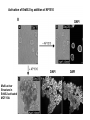
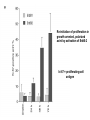
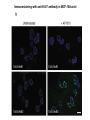
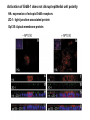
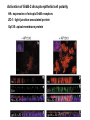
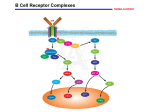
Lecture II Protein kinases and cancers December 18, 2008 Tyr kinases and phosphatases Amino acid specificity of protein kinases: (1) Ser/Thr-specific protein kinases (2) Tyr-specific protein kinases (3) His-specific protein kinases (4) Asp/Glu-specific protein kinases Classification of protein phosphatases: (1) Ser/Thr-specific phosphatases (2) Tyr-specific phosphatases (3) Dual specificity phosphatases (4) Acidic phosphatases (5) Basic phosphatases Conventional view of signal transduction Protein Tyrosine Kinases: POSITIVE Regulators Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases - NEGATIVE Regulators S Autophosphorylation P PTK (Inactive) PTP PTK (Inactive) (Active) S P PTP P P (Active) Alternative view of signal transduction Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases - POSITIVE Regulators PTP P P S S (Inactive) (Active) PTK General concept – Classification and basic function of protein tyrosine kinases Important references 1. Hunter (2000) Signaling-2000 and beyond. Cell, 100: 113-127 2. Schlessinger (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell, 103: 211-225 3. Schlessinger (2002) Ligand-Induced, Receptor-Mediated Dimerization and Activation of EGF Receptor, Cell, 110: 669-672 4. Garrett et al., (2002) Crystal Structure of a Truncated Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Extracellular Domain Bound to Transforming Growth Factor. Cell, 110: 763-773 Classification of human receptor tyrosine kinases (RPTKs) Models for activation of signaling proteins A). By membrane translocation B). By conformational change C). By tyrosine phosphorylation General concept for activation of receptor tyrosine kinases through ligand-induced dimerization Schematic depiction of the extracellular and Transmembrane domains of HER1, a human EGFR A loop located between two EGF binding domains Structure of the dimeric HER1 bound to transforming growth factor alpha, which is a member of the EGF family ligand ligand A loop located between two EGF binding domains Activation of receptor tyrosine kinases Juxtamembrane region N-terminal kinase lobe C-terminal tail Substrate precluding loop Substrate accessible loop Recruitment of intracellular signal-transduction proteins by binding to pTyr residues in receptors or receptor-associated proteins Classification of human cytoplasmic protine tyrosine kinases Activation of c-Src Two modes of intrinsic inhibition by interactions between: (1) SH2 domain and phosphorylated Y527; (2) SH3 domain and polyproline region. Surface model of a SH2 domain bound to a pTyr-containing peptide Four-residue core sequence: pTyr (0)-Glu1-Glu2-Ile3 Two pronged “plug”: Side chain of pTyr and Ile Homework: Structural basis for a PTB domain bound to a pTyr peptide (Src PTK) General concept for activation of cytokine receptors through a cytosolic protein tyrosine kinase JAK Activation of STAT (Signal Transduction and Activation of Transcription) protein through phosphorylation and dimerization ? SOCS: suppressors of cytokine signaling, induced by STAT proteins Deregulation of pTyr signaling and development of human cancers * * * * * * Blume-Jensen and Hunter, Nature, 411: 355-365, 2001. In most cases of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the leukemic cells share a chromosome abnormality not found in any nonleukemic white blood cells, nor in any other cells of the patient's body. This abnormality is a reciprocal translocation between one chromosome 9 and one chromosome 22. This translocation is designated t(9;22). It results in one chromosome 9 longer than normal and one chromosome 22 shorter than normal. The latter is called the Philadelphia chromosome and designated Ph1. Expression of a fusion PTK p210 Brc-Abl References: * 1. Nat Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;3(9):785-92. ErbB2, but not ErbB1, reinitiates proliferation and induces luminal repopulation in epithelial acini. Muthuswamy SK, Li D, Lelievre S, Bissell MJ, Brugge JS. Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, 240 Longwood Ave, Boston, MA 02115, USA. 2. Methods. 2003 Jul;30(3):256-68. Morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini grown in three-dimensional basement membrane cultures. Debnath J, Muthuswamy SK, Brugge JS. Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, 240 Longwood Avenue, Boston, MA 02115, USA. [email protected] ErbB-2 is amplified and overexpressed in 20-80% cases of early stage of breast cancer. Overexpression of ErbB-2 is correlated with a poor clinical prognosis of breast tumors. Overexpression of ErbB-2 in cultured cells induces both ligand-independent receptor phosphorylation and cell transformation. The Her (ErbB) family of receptors and their ligands To study the effect of ErbB-2 in morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini -----Using MCF-10A cells grown in threedimensional basement membrane cultures as a model system A. A lobule from human mammary gland– a polarized architecture surrounding a hollow lumen. B. The morphology of MCF-10A acini cultured on basement membrane for 10 days. The overlay method for 3D culture of MCF-10A cells on Matrigel The Biological events during MCF-10A acinar morphogenesis Expression of synthetic, ligand-inducible activation of ErbB receptors (ErbB-1 or ErbB-2) in MCF10A cells No AP1510 No AP1510 No AP1510 Activation of ErbB-1 by addition Of AP1510 DAPI Activation of ErbB-2 by addition of AP1510 DAPI DAPI Multi-acinar Structure in ErbB-2-activated MCF-10A DAPI Re-initiation of proliferation in growth-arrested, polarized acini by activation of ErbB-2 ki-67 = proliferating-cell antigen Immunostaining with anti-Ki-67 antibody in MCF-10A acini Activation of ErbB-1 does not disrupt epithelial cell polarity HA: expression of ectopic ErbB receptors ZO-1: tight-junction-associated protein Gp135: Apical-membrane protein Activation of ErbB-2 disrupts epithelial cell polarity HA: expression of ectopic ErbB receptors ZO-1: tight-junction-associated protein Gp135: apical-membrane protein Assigned reading