* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06_prughNS2
Survey
Document related concepts
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sex-limited genes wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
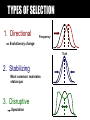
One last time: haplodiploidy Leafcutter ant queen + workers Male leafcutter ant reproduction 0.5 of genome from dad X 1.0 = 0.5 + 0.5 of genome from mom X 0.5 = 0.25 r = 0.75 SEXUAL SELECTION A type of natural selection that acts differently on males and females of the same species Traits that increase mating success are selected for Pheasants SEXUAL SELECTION Damselflies SEXUAL SELECTION Sexual dimorphism: male and female have different forms Elephant seals SEXUAL SELECTION Why aren’t all species dimorphic? SEXUAL SELECTION Dimorphism arises from competition for mates Males produce sperm: cheap Females produce eggs: expensive BATEMAN PRINCIPLE # kids # mates BATEMAN PRINCIPLE The sex that invests most in reproduction is a limiting resource that opposite sex competes for Female is usually limiting sex (expecially in mammals), but not always SEXUAL SELECTION Role reversal Greater Painted Snipe SEXUAL SELECTION Which is the limiting sex? Seahorse Sea dragon Pipefish SEXUAL SELECTION Parental care Male may be needed to care for young SEXUAL SELECTION Sage grouse Peacock SEXUAL SELECTION 1. Runaway selection: trait initially useful for survival is exaggerated by sexual selection Long-tailed Widowbird SEXUAL SELECTION 1. Runaway selection: trait initially useful for survival is exaggerated by sexual selection SEXUAL SELECTION 2. Handicap principle: ornaments show that males are high-quality Ornaments expensive to produce, only males in good condition can have them Ornamental males less likely to have disease SEXUAL SELECTION Satin bowerbird OPTIMIZING FITNESS Every trait has costs and benefits Natural selection should favor strategies that lead to higher fitness OPTIMIZING FITNESS Gulls “mob” predators that approach nest sites OPTIMIZING FITNESS How daring should the gull be? Daring mobber Benefits of action Units of Fitness Cautious mobber Cost of action 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 Distance from predator (m) OPTIMIZING FITNESS Optimal strategy: Benefits - Costs = Maximum Natural selection should favor optimal strategy GENE FLOW the movement of genes from one population to another “Hide” allele “Run” allele TYPES OF SELECTION 1. Directional Frequency Evolutionary change Trait 2. Stabilizing Most common: maintains status quo 3. Disruptive Speciation DIRECTIONAL SELECTION Darwin’s finches Geospiza fortis Severe drought 1976-1977 Killed plants with small seeds: birds with larger beaks survived better Boag and Grant 1981 10.5 mm 11 mm STABILIZING SELECTION Human birth weight Extreme light weight and extreme heavy weight both selected against 8 lbs DISRUPTIVE SELECTION Three-spined sticklebacks Dolph Schluter benthic limnetic Descended from common ancestor Selection favored large fish near shore and small fish in open water Assortative mating led to speciation Assortative mating: Like mates with like; nonrandom mating