* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Macromolecules
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
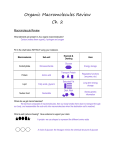
Bell Ringer • After swabbing the floor and culturing the plate for 48hrs at 37 C, you notice that there was not any growth. Explain why this may have occurred. Objectives • By the end of the lesson, students will be able to – Describe basic chemistry principles including different organic molecules – By understanding basic chemistry concepts, you will be able to grasp the various interactions between a microorganism and its environment Organic Macromolecules • Contain carbon and hydrogen atoms – Macromolecules – large molecules used by all organisms – Lipids – Carbohydrates – Proteins – Nucleic acids – Monomers – basic building blocks of macromolecules © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Functional Groups – specific chemical arrangement of atoms – NH2 amino functional group – Found in amino acids – OH hydroxyl functional group – Found in alcohols – R (residue) stands for atoms in a compound that change from one molecule to another © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Lipids – Hydrophobic – Afraid of, or insoluble in water • Four groups – Fats – Phospholipids – Waxes – Steroids © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Fats –Energy stored in covalent bonds © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Phospholipids –The fatty acid tail is nonpolar –Phospholipid head is polar –Forms phospholipid bilayer © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Waxes – Contain one long-chain fatty acid – Insoluble in water – Mycobacterium tuberculosis is surrounded by a waxy wall – Resistant to drying © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Steroids – Four rings fused – Hormones – Chemical messengers – Part of phospholipid membrane – Keeps membrane fluid and flexible at low temperatures © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Carbohydrates – Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen – Functions – Long and short energy reserve – Make up DNA and RNA – Form cell wall – Cell to cell communication © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • 1) Monosaccharides – Simplest sugars – Deoxyribose – Glucose • 2) Disaccharides – Two monosaccharides linked together – sucrose (table sugar) © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Figure 2.18 Monosaccharides-overview Organic Macromolecules • 3) Polysaccharide – More than two monosaccharides – Cellular structure or store energy – Peptidoglycan – long polymer composing bacterial cell walls – Cellulose – cell walls of plants – Glycogen – energy storage in animal cells © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Figure 2.20 Polysaccharides-overview Organic Macromolecules • Proteins – Mostly composed of C, H, O, N, S – Functions – Structure – Enzymatic catalysis – Regulation – Transportation – Defense and offense © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Amino Acids – – – – Monomers 21 amino acids Side groups differ (R) among A.A Peptide bond links amino acids via dehydration reaction © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Figure 2.21 Amino acids-overview Figure 2.23 Linkage of amino acids by peptide bonds Dehydration synthesis Carboxyl Amino group group Amino acid 1 Amino acid 2 Peptide bond Dipeptide Organic Macromolecules • Protein Structure – Structure = function – 1) Primary structure – Amino acid sequence – Combination unique to each protein – A single change in ONE amino acid can disrupt function – 136th amino acid valine replaced with alanine causes formation of prions – Proteins spread, causing mad cow disease © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Protein Structure – 2) Secondary structure – Polypeptide chain folds into α-helices and β-pleated sheets – Held together by hydrogen bonds – 3) Tertiary structure – folds into 3D shapes – Held together by ionic bonds, hydrophobic hydrophilic forces, and disulfide bridges – 4) Quaternary structure – Two or more tertiary structures coming together – Same as tertiary structure forces © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Figure 2.24 Levels of protein structure-overview Organic Macromolecules • Protein Structure –Physical and chemical factors cause loss of shape = loss of function – pH changes, extreme hearting, changes in salt concentrations – Denaturation – disruption in the 3D structure of proteins – temporary or permanent © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Nucleic Acids – DNA and RNA: the genetic material of organisms – RNA also acts as enzyme, binds amino acids, and helps form polypeptides © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Organic Macromolecules • Nucleic Acids – Nucleotides are monomers that make up nucleic acids – Composed of three parts – Phosphate – Pentose sugar – Nitrogenous bases (A,T,C,G) © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Figure 2.25 Nucleotides-overview Figure 2.26 General nucleic acid structure-overview Organic Macromolecules • Nucleic Acids – Nucleic acid function – DNA is genetic material of all organisms and of many viruses – Cells replicate and pass on DNA to their descendants – RNA helps synthesize proteins © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. Practice with Proteins • With your partners, complete the handouts over protein structure. Exit Slip • 1) List the four main categories of organic molecules and identify one function for each molecule. Friday • • • • Aseptic Technique Lab Review safety with Bunsen burner Purpose of aseptic technique Aseptic Technique Demonstration