* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1- Matter and Energy 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
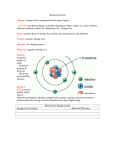
ATOM – Notes Outline for Review Atom: • • • The smallest component of an ______________. So if there are103 different elements there are 103 _____________ __________ of atoms. Subatomic Particles • Protons o Mass = _____ AMU o Charge = _________ • Neutrons o Mass = _____ AMU o Charge = _________ • Nucleons are all of the particles in the _____________ (_____________ and _____________) • Electrons o Mass = _____ AMU o Charge = _________ Atomic Theories • • • • • • Dalton • Elements are composed of extremely small particles called ________________. • All atoms of a given element have ______________ properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with one another in ________ _______ numbers. • The relative numbers and kinds of atoms are _______________ in a given compound. JJ Thompson • Atom can be divided into parts. One of which is an ____________. • These are _________________ charged particles ______________ in a positively charged atom. • Raisins embedded in plum pudding Rutherford • An atom contains a ___________ ______________ charged nucleus accounting for the majority of its mass. • The rest of the atom is mostly _____________ _____________ where the electrons are. • Determined this theory after performing the gold-foil experiment. o Rutherford directed __________ particles (radioactive source) which are ____________ charged and smaller than atoms at a thin piece of gold foil. o He expected all the alpha particles to pass through (detected by the fluorescent screen) with just a few being slightly defected. o _____________ of the particles did go straight through proving that atoms are mostly empty space. o A few were slightly deflected. BUT, some were greatly deflected. They were strongly _____________ by a dense, positive, central core and bounced back Bohr • • Electrons are located in specific ___________ around the nucleus. Each electron must contain a certain amount of energy to stay in its orbit. The ________________ the electron is from the nucleus, ______________ _____________ it contains. Wave-Mechanical Model • Previously matter was considered a particle and energy was considered a wave. • This current model predicts that matter and energy can act like ________ or _________ – Dual Nature Concept • In this model (aka - the electron cloud model), the electrons are in ____________, which are defined as regions of ___________ ______________ _______________ ______________. Bohr’s Model versus the Wave – Mechanical Model • The difference is in the description of _____________ _________________ around the nucleus. • Bohr suggested well ___________, ______________ orbits. • The wave-mechanical model shows electrons located around the nucleus in orbitals. • An orbital is a region in which an electron with a certain amount of energy is most likely to be located (like a _____________). Atomic Number • • • Equals the number of ______________ in an atoms nucleus. It identifies the element. It _______________ changes unless the element has changed. • All atoms of Lithium will have ________ Protons. Mass Number • • • • • Equals the number of ________ + _________ in the _____________. Can be determined by ______________ the decimal (atomic mass) to the nearest whole number. Does NOT _____________ the element. Li : mass # = 7 The # of neutrons in the nucleus can change thus ________ # can change. Atomic Mass • • • • • Decimal Average of all the ______________ that occur in ___________. Atoms with the same protons but with a different number of neutrons. C-12, C-13, C-14 - All carbon atoms have 6 _____________ and 6,7, or 8 ______________. Steps required to calculate atomic mass o Convert _____________ into _______________ o Calculate the contribution of each isotope to the atomic mass by multiplying the decimal percentage by the ________ # for each isotope. o Add them together to get the ______________ average for the atomic mass. Electrons • • • • • • • • Found in energy levels around the nucleus (orbitals according to the wave-mechanical model) Negatively charged Very, Very, Very small When atoms are neutral (no charge), protons _________________electrons, Na________. Can be gained or lost from the outer most energy level. This is called the ______________ ______________ ________________ electrons are found in the valence shell. o These are responsible for most _____________ _____________ and in the formation of __________________. o Every atom wants __________ valence electrons (unless it has only 1 energy level, then it wants only _______). o In general, the number of valence electrons affects the _______________ properties of an element. o Valence electron # = ___________ # on the ___________ ___________. Each electron in an atom has its own distinct amount of _______________ which depends on their orbital or how far they are from the nucleus. o Electrons in orbitals closer to the nucleus have ___________ energy and are __________ stable o Electrons in orbitals further from the nucleus have ____________ energy and are ________ stable o When all electrons in an atom are in their lowest possible energy level, the atom is at its ________ state. The number of electrons found in each orbital when an atom is at the ground state can be found on the periodic table. This is the atoms _____________ ____________________. Ions • • Cations • Sodium has _____________ orbits (Bohr Model) • The third orbit has ___________ electron. • To be more ______________, sodium will give away the one electron it has in the third orbit or it could receive 7 more electrons from another atom in order for it to have ___________ electrons on the outer orbit. • Both processes would have sodium ending up with 8 electrons on its outer orbit. • Giving away 1 electron is _________________ than receiving 7 electrons. • Sodium will lose 1 electron which means that it now has 10 electrons and 11 protons. • It has 1 less electron than proton so it’s charge is _____________. The charge is also referred to as its oxidation number. • The equation showing the lose of an electron is _____________________________________ • Cations are _______________ in size than atoms. Anions • Oxygen has ____________ orbits (Bohr Model). • The second orbit has ________________ electrons. • To be more stable, oxygen will give away all the 6 electrons in the second orbit or receive 2 more electrons from another atom. • • • • • • Both processes will lead to oxygen having _______________ electrons on its outer orbit. Receiving 2 more electrons from another atom is easier than giving away all its 6 electrons. Oxygen will receive 2 more electrons which means it now has ____________ electrons and _________ protons. It has 2 more electrons than protons so it’s charge is _______________. The charge is also referred to as its _______________ _________________. The equation showing the gaining of electrons is _____________________________________ Anions are __________________ in size than atoms. Lewis Dot Diagrams • • • • Shows only __________________ ______________ for the element. Steps for drawing them o Write the elemental symbols for the atoms o Fill in the electrons If more than 2, place 1 electrons at each side of the element symbol and then double up as needed. If there are 2 valence electrons, place both of them on the ________ __________ of the element symbol. Cations have ____________ electrons in the outermost orbital. Anions have ___________ in the outermost orbital. Atomic Spectra • Electrons ______________ energy to become EXCITED • When an electron in an atom gains a specific amount of energy, the electron becomes ____________ and jumps to a ________________ energy level (orbital). • The energy can come from outside sources like _____________, ___________, ______________. • Copper is absorbing energy from a Bunsen burner flame and the flame turns _____________. • The _________________ state configuration changes. • But the ______________ number of electrons stays the same. • The wavelengths of energy that are absorbed can be seen in an _______________ spectra as black lines in a colorful background. • Electrons _____________ energy to go back to the Ground State • After jumping to a higher level, the electron will very quickly return to its ______________ level. • The energy they previously absorbed is now released as infrared, ultraviolet, or visible ___________. • This ______________ energy can be used to ____________ an element. • Copper emits blue light as its electrons return to the ground state. • The wavelengths of energy that are emitted can be seen in an _______________ spectra as colorful lines in a black background.