* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
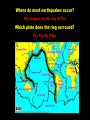
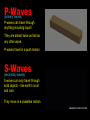
EARTHQUAKES! Part 3 Quick review: Where do most earthquakes occur? 90% happen on the ring of Fire Which plate does the ring surround? The Pacific Plate Where did the four that we studied occur? Chile, California, Alaska and Japan Which was the largest of all time? Valdivia – 1960 How big was it? 9.2 to 9.6 on the Richter Scale What two things did the Valdivia quake cause? Tsunamis up to 82 feet tall And It caused volcano to blow! How do we measure earthquakes? We use the Richter magnitude scales and the Mercalli intensity scale. What is the difference? The Richter scale measures how much energy is released in an earthquake The Mercalli intensity scale measures how much damage was done Scientists use the Richter scale to compare earthquakes while studying plate tectonics Insurance companies use the Mercalli scale to help them decide how much your damaged house is worth. What is the scale for the Richter scale? 1-10 - each number is 10x larger than the last What is the scale for the Mercalli scale? 1-12 and is measured by the damage done Can a quake have more than one number? On the Richter scale – no On the Mercalli scale – yes – it depends upon where you are. What is a focus? It is the exact spot where an earthquake occurred – usually deep below ground What is the epicenter? It is the spot directly above the focus – on land How big was it? 9.2 to 9.6 on the Richter Scale What two things did the Valdivia quake cause? Tsunamis up to 82 feet tall And It caused volcano to blow! The focus of an earthquake the actual spot where the quake started it is usually deep under ground When the plates get stuck they build up pressure until one of them snaps. The exact spot that the rock snapped is the focus. The spot on the ground above the focus is called the epicenter. The shaking that we feel is called a seismic wave. Seismic waves travel through earth. So what exactly is a seismic wave? Seismic Seismic waves waves are are energy energy that travels on on waves waves like like sound sound and and light. There are two different types of seismic waves: Body waves travel through the interior of the earth. The two types of body waves are P-waves and S-waves Surface waves – these travel through the rock that we are standing on – the crust P-Waves (primary waves) P-waves can travel through anything including liquid! They are almost twice as fast as any other wave. P-waves travel in a push motion S-Waves (secondary waves) S-waves can only travel through solid objects – like earth’s crust and core. They move in a snakelike motion Surface waves Surface waves move in both directions at once! They are responsible for most of the damage that earthquakes do – mostly because the surface waves run through the rock that we build on top of.