* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 – Biology – Cells PowerPoint
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
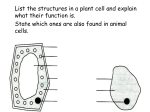
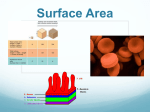
Cell biology Revision B2 REVISION – CHAPTER 1 – Cells F Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Animal & Plant Cells Where is the genetic material in a bacteria cell? Structure Purpose Where is the genetic material in a plant cell? Controls the cells activities Where is the genetic material in an animal cell? What type of cell is shown to the right? Plant/Animal/ Bacteria/all Cytoplasm What is a prokaryotic cell? Both What is a eukaryotic cell? Mitochondria Specialised Cells Cells are specialised to carry out a specific function. The structure gives a clue to its function. How is a root hair cell adapted to absorb water and minerals? Ribosomes Protein synthesis takes place Plant Contain chlorophyll, absorb light energy to make food How is a sperm cell adapted to swim to the egg? Vacuole If a cell has many chloroplasts what would its job be? Where would it be found? If a cell has many mitochondria it is making a lot of energy, which type of cell might it be? KEY WORDS: Gland cells Nucleus Algal cell Cellulose Chloroplast ASSESSMENT: B2 REVISION – CHAPTER 1 – Cells H Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Animal & Plant Cells Where is the genetic material in a bacteria cell? Where is the genetic material in a plant and animal cell? Structure Purpose Plant/Animal/ Bacteria/all Controls the cells activities Describe the structure of a bacteria cell (pictured right) Cytoplasm Both Specialised Cells Say how each are specialised to carry out their function function Adaptations to carry out function 1. sperm cells 2. nerve cells 3. muscle cells 4. root hair cells 5. xylem 6. phloem If a cell has many chloroplasts what would its job be? Where would it be found? If a cell has many mitochondria it is making a lot of energy, which type of cell might it be? Mitochondria Ribosomes Protein synthesis takes place Plant Contain chlorophyll, absorb light energy to make food Vacuole ASSESSMENT: KEY WORDS: Gland cells Nucleus Algal cell Cellulose Chloroplast Exam Questions Practical: Growing Bacteria Growing micro-organisms Method Questions 1. Why did you flame the loop? 2. Why did you allow the loop to cool? 3. Why is the Petri dish only opened a little? 4. Why do we incubate the bacteria at 25 C? 5. Why do we seal the Petri dish before incubation? 6. What do you call a bacteria that causes disease ? Disinfectant = Antibiotic = Uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms are required for investigating the action of disinfectants and antibiotics. To prepare an uncontaminated culture: • Petri dishes and agar must be ________ before use to kill unwanted microorganisms • inoculating loops used to transfer microorganisms to the media must be sterilised by passing them through a _________ • the lid of the Petri dish should be secured with adhesive tape to prevent __________________ from the air contaminating the culture, and stored _________ _________to stop condensation drops falling onto the agar surface. Missing words: flame, sterilised, microorganisms, upside down Chromosomes Learning Outcomes R A G Know that chromosomes are found in the nucleus and carry genes. Know that genes control characteristics of the body. Keywords Cell Nucleus Chromosome DNA characteristics Gene Inherited Gametes Questions Where in the cell is the genetic information found? What are the X shaped structures in the nucleus? What molecule are chromosomes made of? What do chromosomes carry that control characteristics of the body? Use the key words to fill in the spaces… Sexual reproduction Information that results in plants and animals having similar characteristics to their parents is carried by ________________, which are passed on in the __________________________ from which the offspring develop. Male and female ________________ join. The Different _______________ control the development of different _______________________ of an organism. mixture of genetic information from two parents means that offspring are genetically different from their parents. Mitosis and the cell cycle H Cell division & Growth What cell division results in two identical cells being produced from an original cell? Cell division in sexual reproduction By which process are gametes(sex cells) produced? What is the difference between gametes and body cells? In body cells, what are found in pairs? What is so special about stem cells? How could stem cells be used to cure some disorders? What are the gametes in plants called? What are the gametes in animals called? What are unspecialised cells called? Stem Cells More on Mitosis…. Cells divide in a series of stages called the cell ________. One of these stages is __________ where the DNA, which has already been copied, divides. During the cell cycle the ______________ material is doubled and then divided into two ______________ cells. Before a cell can divide it needs to ________ and increase the number of sub-cellular structures such as ribosomes and ____________. The DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome. One set of ______________ is pulled to each end of the cell and the nucleus divides. Finally the cytoplasm and cell membranes divide to form two identical cells. Cell division by mitosis is important in the growth, __________, replacement of worn out ________ and _____________ Missing words reproduction, identical, mitosis, genetic, repair, cycle, grow, chromosomes, cells, asexual, mitochondria, KEY WORDS: Meiosis Ova DNA fingerprint ASSESSMENT: Mitosis and the cell cycle H Cell division & Growth What cell division results in two identical cells being produced from an original cell? Cell division in sexual reproduction By which process are gametes(sex cells) produced? What are the gametes in plants called? Stem Cells A stem cell is an _______________ cell of an organism which is capable of giving rise to ______ other cells type. Stem cells from human ________ and adult ______ marrow can be cloned and made to differentiate into many different types of human cells. Scientific research is trying to find ways that stem cells can be used to cure many _____________. Missing words undifferentiated illnesses bone any embryos What are the gametes in animals called? What is the difference between gametes and body cells? What are unspecialised cells called? In body cells, what are found in pairs? More on Mitosis…. Cells divide in a series of stages called the cell ________. One of these stages is __________ where the DNA, which has already been copied, divides. During the cell cycle the ______________ material is doubled and then divided into two ______________ cells. Before a cell can divide it needs to ________ and increase the number of sub-cellular structures such as ribosomes and ____________. The DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome. One set of ______________ is pulled to each end of the cell and the nucleus divides. Finally the cytoplasm and cell membranes divide to form two identical cells. Cell division by mitosis is important in the growth, __________, replacement of worn out ________ and _____________ Missing words reproduction, identical, mitosis, genetic, repair, cycle, grow, chromosomes, cells, asexual, mitochondria, KEY WORDS: Meiosis Ova DNA fingerprint ASSESSMENT: Stem Cells F and H Keywords Sexual reproduction Asexual reproduction Gametes Cuttings Tissue culture Embryo transplant Adult cell cloning Clone Plant Cloning There are two methods of plant cloning… Use the space provided to describe how each method works. Cuttings Tissue culture ___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Tick the statements that are true ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Only one parent is needed ____________________________________________________ __________________________ ____________________________________________________ __________________________ Asexual reproduction Male and female gametes join No joining of gametes Offspring are genetically identical Offspring are clones of their parents Offspring are genetically different to their parents Stem cells from meristems in plants can be used to produce clones of plants quickly and economically. • Rare species can be cloned to protect from extinction. • Large numbers of identical crop plants with special features such as disease resistance. In therapeutic cloning an embryo is produced with the same genes as the patient. Stem cells from the embryo are not rejected by the patient’s body so they may be used for medical treatment. Animal Cloning Embryo transplants An embryo is split up into several groups of cells and each group of cells is put into a host mother. Questions: Is cow A genetically identical to cow B? A Is cow B genetically identical to cow C? C Adult cell cloning Questions: How do they get the egg cell to begin to divide into an embryo? The lamb is genetically identical to which sheep, A, B or C? Explain your answer. B Place the following units in order of size, starting with the largest first Microscopy Match the unit with the correct symbol Micrometer nm Millimeter cm Centimeter mm Nanometer µm • ______________ = material placed under a microscope. • ______________ = the appearance of material when viewed under the microscope. • The __________________ of an object is how many times bigger the image is when compared to the object. An electron microscope has much higher ______________ and resolving __________ than a light microscope. This means that it can be used to study cells in much _____________ detail. This has enabled biologists to see and understand many more sub-cellular structures. Missing words Image, magnification, finer, object, power, magnification Use the triangle to complete the following equations: Magnification = Real/actual size = Light microscope Image size = Electron microscope Can see images in colour Small field of view Resolution The resolution or resolving power of a microscope is the minimum distance apart two objects can be in order for them to appear as separate items. The greater the resolution the greater the clarity. The image produced is clearer and more precise. Top tip – to help you remember the equation I AM Slides are cheap and easy to prepare Can only view dead objects Magnification is 600x bigger than the object. OSMOSIS - definition Osmosis is the movement of ___________ molecules from a _____________ solution to a ______________ solution through a __________ permeable membrane. Surrounding solution Where are there more water molecules? Does water enter or leave the cell. Weak salt concentration Pure water water Strong salt concentration concentrated Partially Dilue 2 Diffusion and definitions.. 1. . Substances may move into and out of cells across the cell Complete the equation for respiration Glucose + ___________ water + ___________ _________ + energy What gas is needed for respiration? Where does respiration occur? What is the useful product of respiration? What is the waste product of respiration? How do these gases enter and leave the cell? 4. In multicellular organisms the smaller surface area to volume ratio means surfaces and organ systems are specialised for exchanging materials. This is to allow sufficient molecules to be transported into and out of cells for the organism’s needs. The effectiveness of an exchange surface is increased by 4 things: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. Surface area to volume ratios.. Single cells have a _________ surface area to volume ratio. This means their surface is large enough to be able to exchange essential substances. Multicellular organisms have a ___________ surface area to volume ratio. This means their surface is not large enough to be able to exchange essential substances. They overcome tis by having organs specialised for exchange. E.g. humans have ________ and the ___________ ______________. membranes via diffusion. Diffusion is the ____________ of the particles of any substance in ______________, or particles of a gas, resulting in a net movement from an area of ___________ concentration to an area of _____________ concentration ( __________ a concentration gradient). Some of the substances transported in and out of cells by diffusion are _____________ and ____________ ________in gas exchange, and of the waste product _______ from cells into the blood plasma for excretion in the kidney. 3 Factors which affect the rate of diffusion are: 1. 2. 3. Missing words Oxygen, solution, spreading, lower, carbon dioxide, higher, down, urea Examples of specialised exchange surfaces Fish use gills for gas exchange. Gills allow oxygen to enter the blood and carbon dioxide to leave. 1. Gills have numerous folds and fine gill filaments that give them a very large surface area. 2. The folds are kept supported and moist by the water that is continually pumped through the mouth and over the gills, so water is constantly refreshed 3. The walls are thin. 4. The gills have a very good blood supply 5. The oxygenated blood is pumped away to maintain a concentration gradient.. Humans have the small intestine to absorb small soluble food (such as glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol) The small intestine has villi…. 1. The villi INCREASE THE OVERALL SURFACE AREA of the small intestine, thus increasing the volume of substances which can be absorbed by diffusion. 2. The villi have a very GOOD BLOOD SUPPLY as each contains a capillary, which leads to the main blood supply, so when substances diffuse, they can go straight to the bloodstream. 3. Villi have very thin walls to allow faster diffusion. 4. Villi are covered in cells that have thousands and thousands of MICROVILLI. These are exactly the same as the villi, except a lot smaller. They further increase the surface area. Humans have lungs for gaseous exchange Lungs allow oxygen to enter the blood and carbon dioxide to leave. Lungs have numerous alveoli. Alveoli 1. Are very thin – only one cell thick. 2. Have a very good blood supply 3. Are numerous and so create a very large surface area 4. Are ventilated so a concentration gradient is maintained. Plants have leaves for gaseous exchange. This is so oxygen and carbon dioxide can be exchanged for photosynthesis and respiration. During the day photosynthesis needs carbon dioxide to enter the leaves and oxygen to leave. Leaves 1. Are flattened to increase the surface area so more gases can enter and leave (and more sunlight can be absorbed. 2. Are thin so there is a shorter distance for the gases to diffuse in and out. 3. Have numerous stomata. These are holes mainly on the underside of the leaves. They can open (usually in daylight) to allow gases to enter and leave. Create a revision table using the previous slide.. Organism Exchange surface Substances that are exchanged How the surface is adapted for exchange Active Transport Describe active transport in the root hair cell: Describe the effects of osmosis in animal cells: Give the definition of active transport: How is it different to diffusion: Describe the how glucose is absorbed in the gut, place the sentencess in the correct order The molecules are then released into the cell This increases the concentration inside the cell A carrier protein is used to transport molecules across the cell membrane The concentration of glucose is higher inside the cell than outside Molecules need to be taken into the cell against the concentration gradient Active transport occurs when glucose is being moved from a low concentration to a high concentration Energy is required to make the carrier protein work. This energy comes from respiration How is the root hair cell adapted for active transport? Active transport moves substances from a more ___________ solution to a more ______________ solution (against a concentration gradient). This requires _____________ from ___________. Active transport allows ____________ ions to be absorbed into plant root hairs from very dilute solutions in the soil. Plants require ions for healthy growth. It also allows ___________ molecules to be absorbed from ____________ concentrations in the gut into the blood which has a __________ sugar concentration. Sugar molecules are used for cell respiration. Missing words: lower, respiration, dilute, mineral, energy, concentrated, sugar higher. Describe the effects of osmosis in plant cells: Which type of solution would an animal cell burst in? Why wouldn’t a plant cell burst if also placed in this solution? What would happen if root hair cells absorbed mineral ions by diffusion? What would happen if intestinal cells absorbed glucose by diffusion? Comparing the 3 modes of transport – rearrange the mixed up table below Active transport Osmosis Diffusion Does it require energy? No Yes No Does it require a membrane? yes yes No An example… Does it go down a concentration gradient? Carbon dioxide diffuses into a Absorption of glucose in the leaf through stomata for small intestine and mineral ions photosynthesis by root hair cells Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli to the blood. Substances move along a concentration gradient Substances move against the concentration gradient Absorption of water by root hair cells Reabsorption of water in the kidneys Water moves along its concentration gradient