* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry Review - Petal School District
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
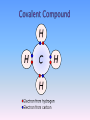
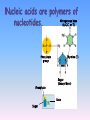
Review Atom—the building block of matter; the smallest unit of an element; Made up of 3 subatomic particles: Nucleus—which contains: 1. protons—positive charge 2. neutrons—no charge (neutral) Energy levels—which contain: 3. electrons—negative charge Element—pure substance made up of only ONE kind of atom; found on periodic table Compound—atoms of two or more different elements combined chemically *Elements in a compound do NOT retain their properties. Chemical bonds—hold atoms together chemically Types of Chemical Bonds: 1. Ionic bond—formed by TRANSFER of electrons Example of Ionic compound: NaCl (table salt) 2. Covalent bond—formed by SHARING of electrons; these are found in most life substances Examples of covalent compounds: Organic compounds—such as C6H12O6 (glucose) Water 3. Hydrogen bond—ex: connect water molecules to one another 4. Peptide bond—hold amino acids together in a protein Chemical Reactions—are represented by a chemical equation Ex: 2Na + Cl2→ 2NaCl Reactants → Products Acid—A compound that produces hydrogen ions (H+) or hydronium ions (H3O+) in solution pH of an acid = less than 7 The more hydrogen ions an acid has, the stronger the acid is. Base—A compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) pH of a base = greater than 7 The more hydroxide ions a base has, the stronger the base is. Neutral—Not an acid or a base neutral = 7 The farther an acid or base’s pH is from 7, the stronger the acid or base. pH Scale: 0 acids 7 neutral 14 bases Buffers—substances that have the ability to neutralize acids Ex: blood Water is the universal solvent. Most chemical reactions in organisms require water. Most organisms consist of 70-95% water. Water is a polar molecule —has + pole and - pole! Water resists temperature change. Water expands as it freezes. Adhesion—water’s attraction for certain other substances Capillary action is related to adhesion. Cohesion—water’s strong attraction for water Surface tension, high heat of vaporization (high specific heat) are results of cohesion. 1. What are atoms with an electric charge called? A. molecules B. electrons C. polar D. ions 2. Molecules that have an uneven pattern of electric charge (more positive in one area; more negative in another) are said to be ________. A. nucleic B. polar C. non-polar D. ionic Organic means made of carbon(C), hydrogen(H), and oxygen(O). Inorganic means NOT made of C, H, and O! Water is inorganic!!! 1. 2. 3. 4. Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins Building blocks → monosaccharides Function → to store and release energy Building blocks→ glycerol and fatty acids Functions→ *Main component of the cell membrane (phospholipids) *Long-term energy storage *Padding, insulation, waterproofing, flotation Building blocks→ nucleotides, each made of: sugar phosphate nitrogen base Function → DNA-contains genetic information RNA-used in protein synthesis ATP-provides energy! Nitrogenous base (A,G,C, or T) Phosphate group Phosphate Thymine (T) Sugar (deoxyribose) Base Sugar Building blocks→amino acids Functions → *Build structure in organisms *Speed up (CATALYZE) chemical reactions as enzymes *Is a component of the cell membrane Substrate—the reactant (substance) on which the enzyme works The enzyme can only work on a specific substrate! Enzymes remain completely unchanged by the reaction. Enzymes work through the Lock and Key method. 3. NO other kind of atom can form the number and variety of molecules that ___________________ can because it can bond to 4 other atoms at the same time to make carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. A. hydrogen B. oxygen C. carbon D. sodium 4. A ____________________ is made up of a sugar, a nitrogen base, and a phosphate group. A. amino acid B. nucleotide C. phospholipid D. glycoprotein 5. Glycogen, cellulose, and starch are all __________________. A. proteins B. polysaccharides C. nucleic acids D. lipids E. phospholipids 6. Reactants in an enzymecatalyzed chemical reaction are called __________________ A. polymers B. products C. substrates D. organics