* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download rep_ and dev
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
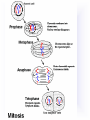
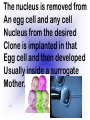
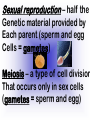
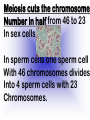
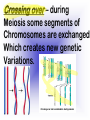
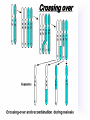
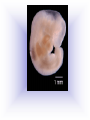
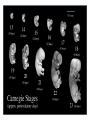
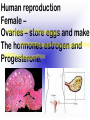
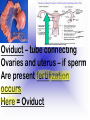
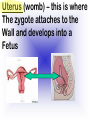
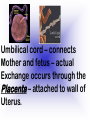
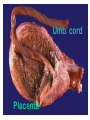
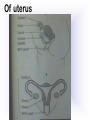
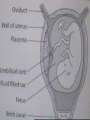
Reproduction and Development – ensures that The species lives on – passes On genetic info.(DNA) Genetic material = DNA - made of genes, are Located in the nucleus of all cells On x shaped structures called Chromosomes. Humans have 46 Chromosomes in a normal cell. Asexual reproduction – One parent, offspring are Exact copies (clones), same DNA. Mitosis – most common form Of asexual reproduction. In Mitosis the cell simply Makes an exact copy of Itself by dividing. All living things depend on Mitosis to create new cells And to grow – Very important We make new skin, hair etc. MITOSIS In mitosis the genetic Material, DNA doubles then The cell splits and each half Gets a set of DNA. This is DNA replication =It Copies itself exactly. . Mitosis is AKA Mitotic Cell division All individual cells reproduce By mitosis, a very important Process. Examples = paramecium, Algae, all of our individual Body cells except gametes. Cloning – produces identical Offspring by inserting a Nucleus into an egg cell. Cloning – produces identical Offspring by inserting a Nucleus into an egg cell. The nucleus is removed from An egg cell and any cell Nucleus from the desired Clone is implanted in that Egg cell and then developed Usually inside a surrogate Mother. Dolly The $155,000 CLONED PUPPY 2 major types of cloning Therapeutic vs reproductive Therapeutic – embryo not put In a “mother” – can develop Into stem cells. Reproductive – develops Into exact copy of organism Stem cells can be used to develop / grow Specialized tissues , organs . This could save lives – prevent/reverse Diseases – disorders but has GREAT Moral issues. – Is it right to do ??? Brain Buster Question!!! Dolly died of lung cancer. Would the birth mother of Dolly be at the same, an increased, or decreased risk of getting the same cancer? ………..Explain your answer. Technically cutting a piece From a plant and potting it Is also cloning. An amoeba Dividing by mitosis is also Cloning. Sexual reproduction – half the Genetic material provided by Each parent (sperm and egg Cells = gametes) Meiosis – a type of cell division That occurs only in sex cells (gametes = sperm and egg) Meiosis cuts the chromosome Number in half from 46 to 23 In sex cells In sperm cells one sperm cell With 46 chromosomes divides Into 4 sperm cells with 23 Chromosomes. In egg cell meiosis one egg Cell with 46 chromosomes Divides into one functional Egg with 23 chromo. And 3 Nonfunctional cells. How Many Chromosomes Should be on each line? Mother _____ Father _____ Meiosis ↓ Meiosis ↓ egg _____ sperm _____ » Fertilization Zygote _____ Mitosis ↓ Embryo _____ Mitosis ↓ baby ______ In meiosis the chromosomes Randomly mix and line up in Many different patterns which Causes great genetic variation Meiosis is responsible for Great genetic variation. Crossing over – during Meiosis some segments of Chromosomes are exchanged Which creates new genetic Variations. Crossing over Fertilization – egg meets Sperm – fertilized egg is Known as a ZYGOTE Zygote contains genes from Both parents that have Recombined, this is known As recombination. Differentiation – after fertilization the Zygote copies itself repeatedly by Mitosis. Zygote --- Cell divides, but gets no Larger = differentiation (develops) Zygote Zygote goes through many Divisions by mitosis known As differentiation. Embryo – early stages of Development , after zygote About 28 days Fetus = after 2 months ????? ???????? Zygote goes through many Divisions by mitosis known As differentiation. Embryo – early stages of Development , after zygote About 28 days Fetus = after 2 months Gene expression -if gene is Actively producing its Proteins , trait is present. Can be influenced by the Environment. Ex = plant grown in dark is White, sun needed to Stimulate chlorophyll Human reproduction Female – Ovaries – store eggs and make The hormones estrogen and Progesterone. Oviduct – tube connecting Ovaries and uterus – if sperm Are present fertilization occurs Here = Oviduct Uterus (womb) – this is where The zygote attaches to the Wall and develops into a Fetus Umbilical cord – connects Mother and fetus – actual Exchange occurs through the Placenta – attached to wall of Uterus. Umb. cord Placenta Of uterus Fetus may be harmed by moms Actions such as drug use, Smoking, alcohol, poor diet, Mom having measles, AIDS or Other illnesses as fetus is connected To moms blood stream. Placenta – actual site of Exchange with fetus & mom Sonogram Male reproductive stuff Testes – produce sperm, And hormone testosterone, Which influences sexual Development. Meiosis Happens here. Scrotum – maintains proper Temp for sperm production ( a few degrees cooler) Cowpers glands Prostrate Other reproductive glands And structures (prostate and Cowpers) Produce fluids for sperm to Swim in (semen) Penis – deposits sperm Hormonal regulation – Females – 28 day egg release Cycle controlled by hormones (estrogen & progesterone – Thicken uterus lining). = Menstrual cycle Males – testosterone – sperm Production & 2ndary sex characteristics Twins Identical = zygote splits into 2 zygotes during first stages Of differentiation – both then Divide on their own. Fraternal – 2 or more eggs are Released and fertilized.




































![Mutations—1 [1] Mutations [2] To understand what mutations are](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002828601_1-86318c7047d168e9c4500928cbbe6885-150x150.png)
