* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Optional HW Assignments SUN-EARTH
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
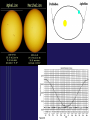
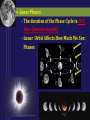
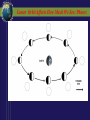
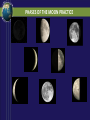
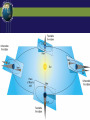
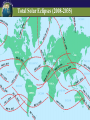
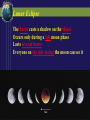
SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM Tools of Astronomy The Moon The Sun-Earth-Moon System TEST DATE: OPT. HW DUE: Optional HW Assignments III. SUN-EARTH-MOON A. Motions of Earth • Rotation – spinning of a body on an imaginary axis. Explains day/night cycles. Sun rise, Moon rise, Constellations moving across sky • Day Length - Solar day – noon to noon. 24 hrs - Siderial day – 1 complete rotation on axis in reference to a distant star. 23h. 56 m Due to Earth’s motion in its orbit. B Annual Motions Plane of Earth’s orbit called the ecliptic plane As viewed from a rotating Earth, the Sun & planets appear to move across the sky along a line. This line or path is called the ecliptic. Revolution –one body orbits around another body. - Siderial period – time it takes a planet to orbit the sun in reference to a distant star. - Earth’s sidereal period is 365.25 days. The most reasonable explanation is that Earth is tilted 23.5 o. This is the cause of Earth’s seasons Some have suggested that distance is the cause, but this was shown not to be true by the results of the Apparent Size of the Sun activity. According to the data from the activity, Earth is closest to the sun in January and furthest from the sun in July. The distance difference is relatively small, only about 3 million miles. Seasonal Cycle - Due to Earth’s Tilt 23.5 degrees on its axis Axis has a fixed orientation in space. Result: As it orbits, Earth’s N hemisphere is angled toward sun and then away. Same for the S. Hemisphere. Part of year neither is angled toward sun. Earth experience seasons. Summer Solstice – June. 21 Begins the summer season in northern hemisphere Earth’s northern hemisphere is tilted toward the sun. Sun appears higher in the sky for most of northern hemisphere and cause the time between rise and set to be longer. At our latitude we experience: about 14 .5 hrs of daylight & 9.5 hrs of night People north of 66.5o experience 24 hr of daylight. Opposite conditions in the southern hemisphere. - AutumnEquinox (northern hemisphere)Sept. 22 or 23 Begins the fall season in the northern hemisphere. Opposite season in southern hemisphere. Earth’s axial tilt is neither toward or away from sun. It is as if Earth has no tilt. Sun noon altitude of 90o (directly overhead) occurs at the equator (0o latitude) Everyone on Earth experiences about 12 hrs of daylight & 12 hrs of night. •Winter Solstice Dec. 21/22 -Winter Solstice Dec. 21/22 Begins the winter season in northern hemisphere Earth’s northern hemisphere is tilted away from the sun. Receives less direct rays from sun. Everyone north of this latitude experiences shorter daylight hours At our latitude we experience: about 9 .5 hrs of daylight & 14.5 hrs of night People north of 66.5o experience 24 hr of night. Opposite conditions in the southern hemisphere. -Vernal (spring) Equinox Mar. 22 or 23 Begins the spring season in norther hemisphere. Same conditions as autumn equinox Test Essay Question You are at a social gathering and overhear someone announce that the Earth experiences season because its distance from the sun varies. He adamantly asserts that winter occurs because we are further from the sun than during summer. Please explain to him that he is incorrect and that you can provide very convincing quantitative evidence against his assertion. Not only that but you can provide quantitative evidence for what the real cause of our winter and summer. You can give 3 strong pieces of evidence that strongly suggests Earth’s Axis Is Tilted. 1. The Sun’s noon altitude changes cyclically during the year. Highest during summer to lowest during winter and back to highest in summer. 2. Earth’s poles experience 24 hours of either daylight or darkness during their respective summer and winter. Only explanation is that Earth axis is tilted. 3. The opposite conditions occur at the same latitude in the southern hemisphere Assignment Finish Apparent Size of Sun Questions & turn in. Assgn. Packet Vocab. 12-17 Sec. III. Sun-Earth Moon 1-14 Will Check Assgn. Packet on Block Day Lunar Phases - The duration of the Phase Cycle is 29.5 days (synodic month) - Lunar Orbit Affects How Much We See: Phases Lunar Orbit Affects How Much We See: Phases PHASES OF THE MOON PRACTICE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kgbK2FZFFdw Eclipses - one object passing between two other objects - Overview Eclipses create 2 shadow Umbra – darker, inner shadow Penumbra – lighter, outer shadow Usually no more than 4-7 solar & lunar eclipses each year. Why? Because the Moon orbits Earth on a different orbital plane than the Earth-Sun plane. - Solar Eclipse The Moon casts a shadow on the Earth Occurs only during a new moon phase Last about 7.5 minutes Sketch of Solar Eclipse Only those within the umbra experience total eclipses. Shadow path is no more than 150 miles wide People in penumbra see a partial solar eclipse Total Solar Eclipses (2008-2035) Lunar Eclipse The Earth casts a shadow on the Moon Occurs only during a full moon phase Lasts several hours Everyone on the side facing the moon can see it Sketch of Lunar Eclipse ASSIGNMENT FINISH ASSIGNMENT PACKET – Don’t forget the vocabulary on p. 2 Work on Opt. HW – some easy points. Study for Phases Mastery on Monday. Work on your Test Essay about the seasons.