* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download reasons for seasons
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
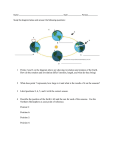
Name _______________________________ Date ________ Period ____ REASONS FOR SEASONS (Review Part 1) day year solstice summer Sun Polaris orbit tilt winter winter summer Northern 23.5 365 24 axis colder warmer Southern Hemisphere circle rotates Planet Earth _________________ once around its axis every ________ hours. We call this period of time a __________. There are _________ days in a ________. It takes one year for Earth to ______________ once around the ________. If I am _________ years old (enter your own age), then I have made _________ trips around the Sun during my life. Earth’s orbit around the Sun traces out an almost perfect _____________. Thus the distance between the Sun and Earth does not change very much over the course of a year. So the reason that temperatures are _______________ in the summer and _____________ in the winter is the tilt of Earth’s axis. The Earth being closer or farther from the Sun does NOT cause Earth’s seasons. Earth’s axis is tilted __________ degrees toward a distant star called _____________ (the North Star). As Earth moves around the Sun, Earth’s ________ remains tilted toward this star, but how Earth is tilted relative to the Sun changes as Earth moves in its orbit around the Sun. When Earth is located on one side of the Sun, the tilt causes the Northern Hemisphere to be tilted toward the Sun. When Earth is on the opposite side of the Sun, this same __________ toward Polaris causes the Northern Hemisphere to be leaning away from the Sun. When the ________________ Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, the season is ___________________ in the Northern Hemisphere and______________ in the Southern Hemisphere. When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, the season is _____________ in the Northern __________________ and summer in the _________________ Hemisphere.