* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STOCKS
Currency intervention wikipedia , lookup
Algorithmic trading wikipedia , lookup
Market sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis wikipedia , lookup
Securities fraud wikipedia , lookup
Day trading wikipedia , lookup
Short (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Efficient-market hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
2010 Flash Crash wikipedia , lookup
Stock market wikipedia , lookup
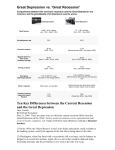
STOCKS Finance: the management of money Stock: ownership of a small piece (share) of a company Advantage The company selling stock is able to raise money needed for the business The person buying the stock makes money as long as the stock’s value goes up Dividend: profits made by stockholders - - Disadvantage The Company is selling off pieces of ownership to other people This ownership gives stockholders a part in the major decision making about the company Stockholders loose money if the company is not doing well Stock Prices Affect on the Economy….. 1. Consumption: --Increase means shareholders are making money --Increased wealth leads to increased consumption --Decrease in prices means people have less money and buy less 2. Investments --Increase in price means the value of the corporation has increased --When the corporation is more valuable, more people invest and business expands --Decrease in price means the value of the company decreases --Could lead to lost jobs and possible the company might close 3. Expectations --When prices increase, investors feel optimistic about the future of the economy --Optimism may lead to more spending and production --When prices fall, pessimism can lead to not spending and slow down in production 4. Prices = Indicator of Economic Activity --Increases in prices = rise in GDP and economic expansion --Decreases = declining GDP and recession Recession: a temporary depression in economic activity or prosperity 1. loss of jobs 2. businesses close 3. less money being spent New York Stock Exchange Stock Market Crash Sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a significant cross-section of the stock market resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth Stock Market Crash of 1921 The 1920’s was a “technological golden age” Radio, automobiles, aviation, telephone and the power grid 1929, 2 out of every 5 dollars a bank loaned were used to purchase stocks Dow Jones Industrial Average rose from a value of 63.9 in 1921 to 381.2 in 1929 Then the market began experiencing a series of price declines The declines fed investor anxiety In the last hour of trading on Thursday, Oct. 23, 1929, stock prices suddenly plummeted Dramatic Drop in Prices “Black Tuesday” 10/29/1929 Dow Jones fell 38 points in 1 day Because of the time period and information was not easily available, this led to more fear and panic Thirteen million shares changed hands — the highest daily volume in the exchange's history at that point — and As the story goes, the opening bell was never heard on Black Tuesday because the shouts of "Sell! Sell! Sell!" drowned it out. In the first thirty minutes, 3 million shares changed hands and with them, another $2 million disappeared into thin air. Phone lines clogged. The volume of Western Union telegrams traveling across the country tripled. Stock Brokers of the 1920s Because of limited information like rumors of investors jumping out of buildings spread through Wall Street; although they weren't true, they drove the prices down further When the market closed at 3 p.m., more than 16.4 million shares had changed hands, using 15,000 miles of ticker tape paper. In total, $25 billion — some $319 billion in today's dollars — was lost in the 1929 crash World War II helped pull the country out of a Depression by the early 1940s, the stock market wouldn't recover to its pre-crash numbers until 1954 By July of 1932, the Dow Jones had lost 89% of its value which resulted in the Great Depression The Great Depression is recognized as the worst economic crisis of modern times The Great Recession…. The late-2000s is considered by many economists to be the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression It resulted in: 1. Collapse of large financial institutions 2. Bailout of banks by the federal government 3. Downturns in stock markets around the world Job seekers line up to register at a City of Miami job fair in Miami, Tuesday, Jan. 26, 2010. Florida's unemployment rate hit 11.8 percent, the highest in Florida in almost 35 years. Nearly 1,087,000 workers were searching for a paycheck in Florida Levin-Coburn Report: Causes of Recession High risk, complex financial products Undisclosed conflicts of interest (you scratch my back, I will scratch yours) Failure of regulators, the credit rating agencies, and the Market itself to rein in the excesses of Wall Street Triggers for the Recession 1. Housing Market- the combination of easy credit and increased purchasing 2. Increased Lending- loans of various types (mortgage, credit card, auto) were easy to obtain and consumer assumed an unprecedented debt load 3. Deregulation by the Government- failure to stem toxic mortgages, financial firms taking on too much risk U.S. Stock Market peaked in October 2007 when the Dow Jones exceeded 14,000 points By March 2009, the Dow had dropped averaging 6,600 points It has since recovered most of the decline, exceeding 12,000 points for most of the 1st half of 2011 Great Recession Mirror Great Depression? While the decline of March 2009 is similar, the rate of decline was not as steady and there have been stages of growth