* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Internal Structure of the Earth
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
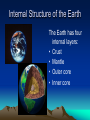
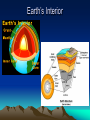
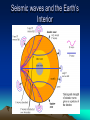
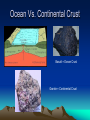
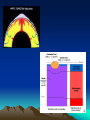
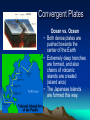
Internal Structure of the Earth Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading Internal Structure of the Earth The Earth has four internal layers: • Crust • Mantle • Outer core • Inner core Earth’s Interior How do we know there are four layers? • We don’t, it’s a theory! • Using earthquake waves, they can tell whether an object is a liquid or a solid, so by using that information, they theorized about the interior layers of the Earth Seismic waves and the Earth’s Interior Layers of the Earth • Crust – Made out of ocean crust or continental crust – Thinnest layer – The one we live on – We have never dug through this layer • Ocean crust: Dark, dense, and thin • Continental crust: Light, less dense, and thicker Ocean Vs. Continental Crust Basalt = Ocean Crust Granite = Continental Crust Mantle • The mantle is the thickest layer • The material is similar to Jello—not quite a solid, but not a liquid either • The elasticity of the substance allows the plates to move around the planet • The mantle is broken into two parts – Lithosphere: upper mantle and crust – Asthenosphere: lower mantle Outer Core/Inner Core • The outer core is made out of liquid Iron and Nickel • The inner core is a solid layer made out of Iron and Nickel • Both layers make up the majority of the weight of the planet Theory of Continental Drift • The theory that continents drifted across the ocean to get their current spots on the globe. • First suggested by Alfred Wegner • First used the idea of one super giant continent called Pangaea. Evidence? • What was the evidence behind Wegner’s idea? • The continents fit together like puzzle pieces. • The fossils and rocks on separate continents being identical. • Climate regions (found by looking at fossils) that did not match up with the positions the continents are located today. What made it go? • Wegner believed that the continents floated on the waters of the ocean to get to their current locations. Theory of Seafloor Spreading • Molten material rises at the Mid-Ocean Ridge. • The material flows away from the ridge, carrying the land that was once together, further apart. Theory of PLATE TECTONICS • First accepted in 1968 by a man named Hess. • Combined the ideas of seafloor spreading and continental drift. • States that the Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates. Why do the plates move? • Hot magma from within the Earth rises to the surface then cools down and sinks back into the Earth. What makes the plates move? 1. New seafloor is created and spreads out. 2. The continents on either side begin to move away from each other. What makes the plates move? 3. Dense seafloor hits continental land. 4. Denser floor goes into the mantle and melts. How do the plates move? • The plates move in three different ways: • Collide • Separate • Slide past each other Convergent Plates Continent vs. Ocean • The more dense ocean plate slides under the less dense continental plate (Subduction) • Chains of volcanoes are formed along the edge of continents. Also trenches are formed off the coast of the continent. • The Cascade Mountain chain is formed this way. Convergent Plates Ocean vs. Ocean • Both dense plates are pushed towards the center of the Earth • Extremely deep trenches are formed, and also chains of volcanic islands are created (island arcs) • The Japanese Islands are formed this way. Convergent Plates Continent vs. Continent • When two continental plates hit both plates are forced up. No subduction occurs. • Mountains are formed, not volcanoes. • The Himalayan Mountains in India are formed this way. Transform Boundary • When one plate slides past another. • The most famous is the San Andreas fault in California. • No creation of anything, just destruction. Divergent Boundary • When two plates separate from each other. • The Mid-Atlantic ridge is the best example. • This is what caused Europe and the United States to separate. Plate Video