* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Taking Control of Advanced Threats
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Security Essentials wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
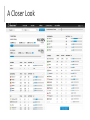
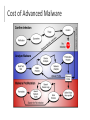
Taking Control of the Advanced Threat Problem Adam Hogan, Security Engineer, Sourcefire @adamwhogan [email protected] Agenda Frame the Advanced Threat Problem Define “Next-Gen Security” Traditional Network-Based Solutions: NG-IPS and NGFW Endpoint Approach to Advanced Malware (Cloud Supported) IT Environments are Changing Rapidly Devices Networks Application s VoIP Virtualization Mobilization Consumerization Threats are Increasingly Complex Targeted | Organized Relentless | Innovative Client-side Attacks Malware Droppers Advanced Persistent Threats 2010 Ponemon Institute Study Published in March 2011 51 U.S. companies interviewed with breaches that occurred in 2010 ▸ 4,200 to 105,000 records stolen ▸ Breach costs ranged from $780,000 to $35.3 million Report highlights: ▸ Average data breach cost: $7.2 million ▸ Average cost per stolen record: $214 ▸ 31% of breaches were criminal attacks ▸ Breaches related to criminal attacks are the most expensive ▸ Customer turnover remains the main driver of data breach costs Professionalization of Hacking “Once a deviant industry is professionalized, crackdowns merely promote innovation.” Nils Gilman, 4th European Futurists Conference “The criminal breaks the monotony and humdrum security of bourgeois life, he thereby insures it against stagnation, and he arouses that excitement and restlessness without which even the spur of competition would be blunted” Karl Marx A Closer Look Hacktivism Targeted Attacks Threats Change — Traditional Security Products Do Not Static | Inflexible Closed/Blind | Labor Intensive “Begin the transformation to context-aware and adaptive security infrastructure now as you replace legacy static security infrastructure.” - Neil MacDonald VP & Gartner Fellow Source: Gartner, Inc., “The Future of Information Security is Context Aware and Adaptive,” May 14, 2010 Next Gen Security is… Agile Security …a continuous process to respond to continuous change. You Can’t Protect What You Can’t See Breadth: who, what, where, when Depth: as much detail as you need Real-time data See everything in one place Threat s Device s Applications Network Agile Security Vulnerabilities OS Users Files “Seeing” provides information superiority Gain insight into the reality of your IT and security posture Get smarter by applying intelligence Automatically optimize defenses Lock down your network to policy Leverage open architecture Block, alert, log modify, quarantine, remediate Respond via automation Reduce the ‘noise’ Configure custom Correlate, prioritize, decide fit security Key: intelligence & automation Security Before, During & After the Attack Before During After Policy & Control Identification & Block Analysis & Remediation Discover environment Detect Determine Scope Prevent Contain Implement access policy Remediate Harden assets What is needed is a new approach to protect your organization What Can You Do? Assess your vendors by assuming you will be hacked ▸p.s., you will be have been. Your security tools are tools. ▸Forget about set-and-forget tech and think about how each process, program or product helps your analysts keep you safe. Exploring Detection There are some really useful rules not on by default ▸INDICATOR-OBFUSCATION ▸Javascript obfuscation fromCharCode, non alphanumeric ▸Hidden iFrames ▸Excessive queries for .cn/.ru ▸HTTP POST to a JPG/GIF/PNG/BMP ? Java 0-Day SIDs 25301, 25302 Largely used by exploit kits (Blackhole, Cool Kit, Nuclear, Redkit) - covered ▸Why is java.exe downloading calc.exe? BTW, User Agents are telling No, really: ▸User-Agent: Malware ▸(RFC 3514 anybody?) Unless your proxy rewrites them all... What can we do? Communication Watch hackers. Many aren’t that sneaky. (L|H)OIC source code is public, for crying out loud. ▸LOIC packet contains: “U dun goofed” ▸HOIC botched protocol, used two spaces where one is allowed. They recruit! Publicly. Get on twitter. Watch pastebin.org. Scrape it. Use google alerts if you can’t script. What Can You Do? Hire analysts ▸It’s going to cost you. ▸And if they aren’t trained they depreciate. Example: “Agile Security” Fuels Automation in an IDS/IPS IT Insight Impact Assessment Spot rogue hosts, anomalies, policy violations, and more Threat correlation reduces actionable events by up to 99% Automated Tuning User Identification Adjust IPS policies automatically based on network change Associate users with security and compliance events Reduce Risk with: Application Control – on the IPS! Control access to Web-enabled apps and devices ▸ “Employees may view Facebook, but only Marketing may post to it” ▸ “No one may use peer-to-peer file sharing apps” Over 1,000 apps, devices, and more! Reduce Risk with: IP Reputation Block and Alert on: ▸Botnet C&C Traffic ▸Known Attackers ▸Malware, Phishing, and Spam Sources ▸Open Proxies and Relays Create Your Own Lists Download from Sourcefire or Third Parties So, what is the difference between NG-IPS and NGFW? Gartner Defines NGIPS & NGFW Next-Gen IPS (NGIPS) Next-Gen Firewall (NGFW) Standard first-gen IPS Standard first-gen firewall Application awareness and Application awareness and full-stack visibility full-stack visibility Context awareness Integrated network IPS Content awareness Extrafirewall intelligence Agile engine “Next-generation network IPS will be incorporated within a next-generation firewall, but most nextgeneration firewall products currently include firstgeneration IPS capabilities.“ Source: “Defining Next-Generation Network Intrusion Prevention,” Gartner, October 7, 2011. “Defining the Next-Generation Firewall,” Gartner, October 12, 2009 Next-Generation IPS Comparison What is a Next-Generation Firewall? Stateful First-Generation Firewall ▸ Stateful protocol inspection ▸ Switching, routing and NAT Integrated Network Intrusion Prevention ▸ Not merely “co-located” ▸ Includes vulnerability- and threat-facing signatures Application Awareness with Full-Stack Visibility ▸ Example: Allow Skype, but disable Skype file sharing ▸ Make Facebook “read-only” Extrafirewall Intelligence ▸ User directory integration ▸ Automated threat prevention policy updates Gartner on Next-Generation IPS “Next-generation network IPS will be incorporated within a next-generation firewall, but most next-generation firewall products currently include firstgeneration IPS capabilities.” Source: “Defining Next-Generation Network Intrusion Prevention,” Gartner, October 7, 2011 ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ Application awareness Contextual awareness Content awareness Agile engine Available now on Sourcefire.com Ponemon NGFW Survey Highlights Survey conducted in October 2011 2,561 responses Key Results: ▸Most NGFWs augment (not replace) existing firewalls ▸IPS component rated “most important” for securing data What about an Endpoint Approach to the Advanced Threat Problem? Threats Continue to Evolve The likelihood that you will be attacked by advanced malware has never been greater. 75% Of attacks are seen on only one computer “Nearly 60% of respondents were at least ‘fairly certain’ their company had been a target.” – Network World (11/2011) Cost of Advanced Malware Solve the Problem at the Endpoint Action at point of entry ▸Best place to stop client-side attacks is on the client Awareness at source ▸Focus where files are executed ▸Do not miss threats due to encryption Secure Endpoints - Wherever They Are. What is needed to fight advance malware at the Endpoint? Clients need better visibility to detect and assess advanced malware. Visibility answers questions like: ▸ ▸ ▸ ▸ Do we have an advanced malware problem? Which endpoint was infected first? How extensive is the outbreak? What does the malware do? Clients also need help regaining control after the inevitable attack. Control answers questions like: ▸ What is needed to recover? ▸ How can we stop other attacks? Cloud-Based Advanced Malware Protection – Sample Architecture Lightweight Agent • Watches for move/copy/execute • Traps fingerprint & attributes Cloud Analytics & Processing • Transaction Processing • Analytics • Intelligence Web-based Manager Agile Security for Advanced Malware – Endpoint Benefits SEE ▸ Advanced malware at the source ▸ Patient 0 + propagation paths ▸ APT reporting LEARN ▸ Real-time root cause analysis of threats ▸ Collective immunity & comparative reporting ▸ Data mining & machine learning ADAPT ▸ Custom detections/signatures ▸ Application control ▸ Whitelisting ACT ▸ Immediate & retrospective remediation ▸ Action at the point of entry ▸ Continuous scans in cloud Regain Control of Your Environment Outbreak control ▸Custom Signatures for immediate response ▸Whitelisting ▸Application Control Immediate & retrospective remediation ▸Automatic remediation of damaged endpoints with Cloud Recall ▸Collective Immunity Arm YOU to fight advanced malware Thank You.