* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 2 - VCOMcc
Sonic hedgehog wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
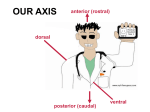
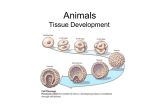
Lecture 30-32 Pre-embryo = 0-2 weeks o Increase cell number o NOT susceptible to teratogens (but highest mortality rate) o Bilaminar disc (2 layers) Embryo = 3-8 weeks o Morphological development o **key period for development o Greatest sensitivity to teratogens (but not high mortality) o Week 3 = gastrulation initiation trilaminar disc Fetus = 9 weeks – birth o Functional development Teratogenesis o = an agent (virus, drug, radiation) that causes malformation o “monster-forming”; congenital malformation of anatomical structures. o Occur prenatally and can be casued by genetic factors, environmental factors of a combination. Sacrococcygeal teratomas o Cellular remnants of the primitive streak o most common congenital tumor found in newborns Primitive Streak o Forms at end of week 2 o 3 components Primitive node – Nodal is a protein that is secreted at the primitive node and this helps to form and maintain the primitive streak (proliferation and differentiation) Primitive pit Primitive groove – cells move towards groove Gastrulation o Initiated at week 3 (trilaminar disc (3 layers) seen in the 3rd week) o = process by which epiblast cells of bilaminar disc migrate through the primitive streak to form 3 cell layers Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm o Mesenchymal cell = any cell that loses adhesion to neighboring cell and is migratory o (*all cells from our body come from epiblast) Oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes o = forms immediately after gastrulation o o Regions of fused ectoderm and endoderm Depression on either end of the embryo = area where there is no mesoderm and the endoderm and ectoderm form together 1. Oropharyngeal membrane – will form mouth and located where the primitive node is pointing to 2. Cloacal membrane – will form anus 2 1 Notochord Formation o = rod-like structure derived from mesoderm o Plays critical role in formation of CNS o Differentiate into core of the intervertebral discs (nucleus pulposus) o Development: Prenotochordal cells = invaginate at the primitive node and migrate cranially toward the prechordal plate Folding – provides basic body form (cylinder) Occurs during 4th week Folding occurs in 2 planes Lateral fold Cranial-caudal folding Fate Maps o Fate mapping = technique used to determine embryonic origin of adult tissues o Tracer/dye is injected into a specific region of the embryo and those cells are followed to adulthood Differentiated Adult Tissues o Epithelium = lines body cavities and body surfaces; comprises glands and organs; derived from all 3 germ layers o Connective Tissue = comprises skeletal system, blood, fat and derived mainly from mesoderm o Muscle = skeletal, smooth and cardiac; derived mostly from mesoderm o Nerve = neurons and glia; derived mostly from ectoderm Organ o = comprised of 2 or more tissues o Develop via organogenesis which occurs during week 4-8 (embryo) Germ Layer derivatives o The primary/ functional cell type of an organ is derived from a single specific germ layer Ectodermal Derivatives o Neural Tube Brain Spinal Cord o Neural Crest PNS Medulla of adrenal Bones of head Septum of heart Melanocytes Odontoblast o Surface Ectoderm Epidermis Epidermal derivatives Hair Nails Sebaceous (oil) glands Sudoriferous (sweat) glands Arrector pili muscle Mammary glands Ectodermal – Neurulation o Neurulation = process by which rain and spinal cord form Notochord secretes protein to stimulate ectoderm to invaginate Neural plate Neural groove Invaination continues until lateral margins meet Neural folds Non-neural surface (surface ectoderm) fuses and gives rise to epidermis of the back Cells of neural folds detach Neural crest Neural plate fuses = precursor to brain and spinal cord Neural tube Failure of neuroposes to close results in neural tube defects (day 24 for cranial and day 26 for caudal) anencephaly and spina bifida o Anencephaly = failure of the anterior neuropore to close There is no brain, but brainstem persists o Maternal intake of folate reduces the likelihood of this happening Spina Bifida = failure of the posterior neuropore to close Rachischisis = “split spine” Infant will be paralyzed completely from the point of deficit Endodermal Derivatives o Endodermal Tube Epithelial lining of GI tract o Endodermal Bud Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Epithelial lining of respiratory system Epithelial lining of urinary bladder Epithelial lining of urethra Liver Gall bladder Pancreas Mesodermal Derivatives o 4 types Axial Located on the midline Forms notochord Induce formation of neural tube Differentiate into nucleus pulposus of IV disc Paraxial Forms somites initially 42-44 pairs but some degenerate leaving 36 functional pairs Somatic cells differentiate into 3 cell populations o Scleratome axial skeleton o Dermatome dermis of dorsal and lateral body o Myotome skeletal muscle Intermediate Forms much of urinary system and contributes to gonad development Failure of cells to proliferation/ differentiate can cause kidney problems and caudal dysgenesis ( lack of limbs due to not enough mesoderm) Lateral plate Somatic (body/ superficial) o Forms the dermis of the ventral body wall, hypodermis, and all skeletal components of limbs (bones, ligaments, tendonds etc.) Splanchnic (viscera/ deep) o Forms the smooth muscle and connective tissue of endoermally-derived organs and all of the heart BOTH somatic and splanchnic forms blood vessel, serous membranes of heat, lungs, and abdominal organ Formation of the Body Cavity (coelom) o Result of lateral folding = the extraembryonic coelom is incorporated into the ventral aspect of the embryo and is now the intraembryonic coelom o 3 ventral cavities form Pericardial (thorax) Pleural (thorax) Peritoneal (abdomen) o Initial step in this process is the movement of the septum transversum to its final placement separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities Formation of the Diaphragm o 1st step begins during cranial folding result = relocation of the septum transversum caudally o Septum transversum seperates the intraembryonic cavity into the thoracic and peritoneal cavities (not completely separate) o 2 channels (pericardioperitoneal canals) will persist, allowing the cavities to remain continuous o Pleuroperitoneal membrane grow over the pericardioperitoneal canals o Myoblasts form cervical somites muscular part o Septum transversum central tendon ** Diaphragm is a smooth muscle, it is voluntary, it is derived from MYOTOME from the somites!!! (somites myotome myoblast) General Info on Extraembryonic Membranes o Allantois = hindgut diverticulum lined with endoderm; fuses with umbilical cord and removes waste from fetus o Amniotic membrane = derived from epiblast o Amniotic cavity = fluid-filled space initially between the amniotic membrane and epiblast; increases in size to surround and support embryo/fetus o Chorion = gives rise to chorionic villi that invade the endometrium and promote transfer of nutrients from maternal blood to fetal blood o Yolk sac = functions as circulatory system for first few weeks; observed in prenatal ultrasound; later attaches to the hindgut via vitelline duct External Morphology of Embryo o 4th Week Pharyngeal arches form craniocaudally Pharyngeal clefts begin to form craniocaudally Eye, ear, nasal primordial begin to form (placodes) Cardiac prominence Limb buds emerge (upper first) th o 5 Week Hepatic prominence All pharyngeal arches and clefts formed o 6 Week Paddle-shaped hands Facial tissue is beginning to converge th o 7 Week Eyelids Philtrum (not formed in FAS babies; above upper lip) Digits begin to form th o 8 Week External genitalia is recognizable Digits completely formed** **end of embryo period! Limb Rotation o Elbows point back o Knees forward Syn- and Poly- Dactyly Carnegie Stages = standardized system of 23 stages used to provide unified developmental chronology of the vertebrate embryo. o Base on morphological features and independent of chronological age or size o Not definitive steps, rather a series of events that must be completed during development o The description of each stage is based on the “average” embryo th