* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Luggage security system - Kaushik Science Projects
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Antique radio wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
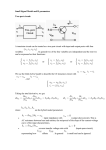
index S.NO. CONTENT 1. Introduction 2. Circuit diagram 3. Part list 4. Circuit description 5. Components used 6. IC 3561 8. Transistor 9. Capaciters 10. Battery 11. Speaker 12 13 PCB references PAGENO. Luggage security system: While travelling by a train or bus, we generally lock our luggage using a chain and lock arrangement but still we are under tension apprehending that somebody may cut the chain and steal our luggage. Here is a simple circuit to alarm you when somebody tries to cut the chain. Circuit diagram: Parts List: Resistor: R1 ----------------------- 10 K R2 ----------------------- 560 ohm R3 ----------------------- 220 K Transistor: T1 ------------------------ BC558 T2 ------------------------ BC548 T3 ------------------------ BC548 Integrated circuit: IC ------------------------- UM3561 Speaker ---------------- 8 ohm, 250mW Battry ------------------- 3V Circuit description: Transistor T1 enables supply to the sound generator chip when the base current starts flowing through it. When the wire (thin enameled copper wire of 30 to 40 SWG, used for winding transformers) loop around the chain is broken by somebody the base of transistor T1 which was earlier tied to positive transistor t1 gets forward biased to extend the positive supply to the alarm circuit . in the idle mode the power consumption of the circuit is minimum and thus it can be used for hundreds of travel hours. To enable generation of different alarm sounds connections to pin 1 and 6 may be made as per the table. Select 1 X Vdd siren select 2 X X sound effect police siren fire enegine X ambulance Vdd machine gun siren sound Note:X=no connection; = do not care Components: UM3561 Features ••• Four sounds can be selected • Power on reset. • Typical 3V operating voltage • A magnetic speaker can be driven by connecting • 8-pin DIP package form an NPN transistor General Description UM3561 is a low-cost, low-power CMOS LSI designed for use in alarm and toy applications. Since the integrated circuit includes oscillator and selector circuits, a compact sound module can be constructed with only a few additional components. The M3561 contains a programmed mask ROM to simulate siren sound. Absolute Maximum Ratings DC Supply Voltage .......................................... -0.3V to +5.0V Input Voltage Range ...................................... Vss-0.3V to Vdd+0.3V Operating Ambient Temperature .................... -10°C to +60°C Storage Temperature ...................................... -55°C to +125°C Resistors : Example: Circuit symbol: Function Resistors restrict the flow of electric current, for example a resistor is placed in series with a lightemitting diode (LED) to limit the current passing through the LED. Connecting and soldering Resistors may be connected either way round. They are not damaged by heat when soldering. The Resistor Colour Code Colour Number Resistor values - the resistor colour code Resistance is measured in ohms, the symbol for ohm is an omega . 1 is quite small so resistor values are often given in k and M . 1 k = 1000 1 M = 1000000 . Black 0 Brown 1 Red 2 Orange 3 Yellow 4 Resistor values are normally shown using Green 5 coloured bands. Blue 6 Each colour represents a number as shown Violet 7 in the table. Grey 8 Most resistors have 4 bands: White 9 The first band gives the first digit. The second band gives the second digit. The third band indicates the number of zeros. The fourth band is used to shows the tolerance (precision) of the resistor, this may be ignored for almost all circuits but further details are given below. This resistor has red (2), violet (7), yellow (4 zeros) and gold bands. So its value is 270000 = 270 k . On circuit diagrams the is usually omitted and the value is written 270K. Small value resistors (less than 10 ohm) The standard colour code cannot show values of less than 10 . To show these small values two special colours are used for the third band: gold which means × 0.1 and silver which means × 0.01. The first and second bands represent the digits as normal. TRANSISTOR The name is transistor derived from ‘transfer resistors’ indicating a solid state Semiconductor device. In addition to conductor and insulators, there is a third class of material that exhibits proportion of both. Under some conditions, it acts as an insulator, and under other conditions it’s a conductor. This phenomenon is called Semi-conducting and allows a variable control over electron flow. So, the transistor is semi conductor device used in electronics for amplitude. Transistor has three terminals, one is the collector, one is the base and other is the emitter, (each lead must be connected in the circuit correctly and only then the transistor will function). Electrons are emitted via one terminal and collected on another terminal, while the third terminal acts as a control element. Each transistor has a number marked on its body. Every number has its own specifications. There are mainly two types of transistor (i) NPN & (ii) PNP NPN Transistors: When a positive voltage is applied to the base, the transistor begins to conduct by allowing current to flow through the collector to emitter circuit. The relatively small current flowing through the base circuit causes a much greater current to pass through the emitter / collector circuit. The phenomenon is called current gain and it is measure in beta. PNP Transistor: It also does exactly same thing as above except that it has a negative voltage on its collector and a positive voltage on its emitter. Transistor is a combination of semi-conductor elements allowing a controlled current flow. Germanium and Silicon is the two semiconductor elements used for making it. There are two types of transistors such as POINT CONTACT and JUNCTION TRANSISTORS. Point contact construction is defective so is now out of use. Junction triode transistors are in many respects analogous to triode electron tube. A junction transistor can function as an amplifier or oscillator as can a triode tube, but has the additional advantage of long life, small size, ruggedness and absence of cathode heating power. 3volt battery: This long-running 3 volt lithium battery has tested as strong as brand name batteries that cost 3 times as much. These are great for our stun guns or compact police flashlights that require CR123A power sources. The only 3 volt cells that are stronger are the "E Cells" which cost about 5 times as much but do not last 5 times as long, so the best buy for your money is a couple sets of our 3 volt lithium batteries. Available to power all your needs. Battery brand may vary. Features: Voltage: 3.00 V Dia.: 0.6690 in Height: 1.358 in Batt. Cap.: 1.400 A-h Applications: Photographic Type: Non-Rechargeable Dry Cell Quantity: 1 Weight: 0.60 oz Speaker: SPEAKER, 8OHM, 66MM; Transducer Function:Speaker; Power Rating RMS:2W; Impedance:8ohm; Resonant Frequency:255Hz; Frequency Response Min:255Hz; Frequency Response Max:15kHz; External Diameter:61mm; External Depth:26mm; External Diameter:61mm; Fixing Hole Diameter:4mm; Sound Level Distance:1m; Sound Level SPL:88dB; Weight:133g PCb designing &fabrication 1. INTRODUCTION: A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically components using conductive pathways, traces etched from copper connect electronic tracks sheets laminated onto or a signal non- conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board (PWB) or etched wiring board. Printed circuit boards are used in virtually all but the simplest commercially produced electronic devices. A PCB populated with electronic components is called a printed circuit assembly (PCA), printed circuit board assembly or PCB Assembly (PCBA). In informal use the term "PCB" is used both for bare and assembled boards, the context clarifying the meaning. Alternatives to PCBs include wire wrap and point-to-point construction. PCBs must initially be designed and laid out, but become cheaper, faster to make, and potentially more reliable for high-volume production since production and soldering of PCBs can be automated. Much of the electronics industry's PCB design, assembly, and quality control needs are set by standards published by the IPC organization. PCBs are inexpensive, and can be highly reliable. They require much more layout effort and higher initial cost than either wire-wrapped or point-to-point constructed circuits, but are much cheaper and faster for high-volume production. Much of the electronics industry's PCB design, assembly, and quality control needs are set by standards that are published by the IPC organization. Printed Circuit Boards are primarily an insulating material used as base, into which conductive strips are printed. The base material is generally fiberglass, and the conductive connections are e generally copper and are made through an etching process. The main PCB board is called the motherboard; the smaller attachment PCB boards are called daughter boards or daughter cards What is PCB Board Design? PCB board design defines the electrical pathways between components. It is derived from a schematic representation of the circuit. When it is derived, or imported from a schematic design, it translates the schematic symbols and libraries into physical components and connections Units: PCB Boards are primarily designed in imperial units (inches) as opposed to metric units (mm). A thousands of an inch is called mil (not to be confused with mm), where: 100 mils = 0.1 inch = 2.54 mm. The reason for using imperial units in a PCB document is because most of the components were manufactured according to imperial pin spacing. The practice continues even today Why this particular circuit: A very low cost circuit. The circuit uses low cost components which are easily available in market. Working to easy to understand. The circuit is very simple and no alighment is required. The circuit operates on 9 volt DC. This circuit is simplified by using FND counter as display, this reduces complexity of the circuit and cost as well. Tool and equipments required: The used tools and equipments requipments for making project are as follows: Soldering iron Desoldering pump Drill machine Multi meter File Tweezer Screw driver Flux Desoldering wick Brush Petrol Soldering wire PCB kit References: www.google.com www.wikipedia.com www.electronicsclub.com