* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CLICK HERE! Ecology PowerPoint
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
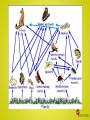
Ecology Ecology: study of how living things interact with each other & with their environment. Ecosystem: a community of interacting organisms and their environment Biotic factors: The living or once-living parts of an ecosystem. Ex:animals, decayed remains, animal waste, plants, bacteria, fungi, etc. Abiotic factors: The nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Ex:H2O, soil, sunlight, temperature, etc. aquatic: living in H2O (fresh or marine) terrestrial: living on land Habitat- a natural place for an organism to live, the place within an ecosystem that provides the biotic and abiotic factors an organism needs to survive and reproduce, a single ecosystem can contain many habitats This wetland ecosystem contains several habitats. How many can you see? Population- all the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same time. Community- all the populations living in an ecosystem at the same time Niche- the way a species interacts with abiotic and biotic factors to obtain food, find shelter and fulfill other needs The Wolf and the Moose https://youtu.be/PdwnfPurXcs Biosphere Biome ECOSYSTEM ↑ COMMUNITY ↑ Population ↑ organism Biosphere- World Biomes Predation: interaction in which one organism kills & eats another •Predator = killer •Prey = killed Competition: struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat w/ limited resources . Anything that restricts the number of individuals in a population is a limiting factor. Symbiosis- a close, long-term relationship between two species that usually involves an exchange of food or energy. Mutualism- both species benefit from the relationship Ex: ● Bees & flowers pollinate flowers and collect nectar ● Oxpeckers and rhinos - In this relationship, the oxpecker (a bird) lives on the zebra or rhino, sustaining itself by eating all of the bugs and parasites on the animal. The Acacia and the Ant https://youtu.be/Xm2qdxVVRm 4 Commensalism- one species benefits from the relationship. The other species is neither harmed nor benefited. Ex: ● Cattle egret and Livestock- The cattle egret benefits because it eats insects that are stirred up when the livestock move through the grass. ● Barnacles and Whales- Barnacles are a type of crustacean that attach to whales. Barnacles cannot move on their own, so they use the whale to move around and find locations with food. ● Clownfish and Sea Anemone https://youtu.be/jbExPtTEBYM Parasitism- one species (the parasite) benefits and the other species (the host) is harmed. Ex: ● Fleas or ticks that live on dogs and cats are parasites. They are living off of the blood of the host animal. ● Lice are another type of parasite. They live off of the blood of the host animal ● Most species of cockatoos will lay their eggs in the nests of other birds, in the hopes that the other bird will raise the babies. Cockatoos often remove an egg (or more) from the nest to decrease suspicion over the additional eggs. Producer: makes its own food Consumer: feeds on other organisms •Herbivore: eats plants (rabbit, cow, elephant) •Carnivore: eats meat (wolf, cat, snake) • Scavenger: feeds on already dead organisms (vulture, crab) •Omnivore: eats both plants & animals (human, bear, crow) Decomposer: also called detritivores • break down wastes & dead organisms • return raw materials to the environment (fungi, insects, worms) Food Chain: series of events in which one organism eats another & obtains energy • 1st in series = the producer • Next = first level consumer (which eats a producer) • Next = second level consumer (which eats a 1st level consumer, etc.) Predator and Prey https://youtu.be/CsfJL-IIVz4 Food Web: consists of many overlapping food chains • Most animals eat or are eaten by more than one thing Energy Flow in Ecosystems The flow of energy can be represented by an energy pyramid. An energy pyramid shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web. It loses energy as it goes up. Only 10% of energy goes to next level. Amoeba Sisters: Food Webs and Energy Pyramids: Bedrocks of Biodiversity https://youtu.be/-oVavgmveyY Biomes Biomes are a large group of ecosystems determined by temperature and amount of precipitation. These abiotic factors largely determine what kinds of plants grow in an area which, in turn, provides niches for different animals. Organisms in that biome are adapted to that environment.