* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography of Judaism
Haredim and Zionism wikipedia , lookup
Jonathan Sacks wikipedia , lookup
Who is a Jew? wikipedia , lookup
Supersessionism wikipedia , lookup
The Invention of the Jewish People wikipedia , lookup
Conservative Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Ritual washing in Judaism wikipedia , lookup
The Reform Jewish cantorate during the 19th century wikipedia , lookup
Orthodox Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Homosexuality and Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Sephardic law and customs wikipedia , lookup
Conversion to Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hamburg Temple disputes wikipedia , lookup
Conservative halakha wikipedia , lookup
Interfaith marriage in Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Origins of Rabbinic Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on religious pluralism wikipedia , lookup
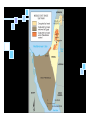
Geography of Judaism Vignesh Murali Haley Gordon Tucker Hill TEST QUESTIONS: 1. What conflicts are connected to the religion of Judaism? What are the major denominations of Judaism? 2. Origin Eastern region of Canaan Present day Israel 1st century C.E. God made a Covenant with Abraham Natural Environment Influence Separation between Jewish holiday of Passover: (no bread, Ashkenazi and Sephardic grains or risen have growth 2 dialects of product) Sephardic Hebrew: Jews may eat rice on Yiddish is a dialect Passover between German and Service on Rosh Hebrew Hashana: bread Ladino is a dialect using crumbs into moving Spanish and Hebrew body of water, different groups wave chicken around head 3 times Di-jew-sion 722 B.C.- The Assyrians conquered Israel. Forced migration into various parts of empire 597 and 586 B.C.Nebuchadnezzar of Babylon deported Jews. Babylon and other parts of the Middle East Judaea Egypt. Di-jew-sion Continued Jewish State ends around 70 A.D. Romans Africa, Asia, and Europe. The Holocaust 1939-45) +6 Million killed Jewish State 1948 Modern Di-jew-sion 6 5 2 1 1 million million million million million in in in in in USA Israel Europe Asia Latin America Denominations Orthodox Jews (traditional)- largest 200 and 700 A.D. Talmud Progressive Judaism (liberal and reform) 19th Century Europe adapts Judaism to contemporary living critical of Talmudic fundamentalism scientific research on the Bible. Conservative Judaism American Cross between Orthodox and Reform Changes Assyrians settled in Samaria Superstitions Worship Yahweh Jewish acculturated to Persian religion procreation, agricultural, and economic activities Lost 10 tribes Changes After Babylonian Diaspora: Some left to Judea Babylonian Jews reconstructed religion Sacrifice Meditation+Prayer Hereditary Priest Rabbi (study and piety) Differences in Practices In America, mainly Ashkenazi Conservative In Israel: Orthodox is only legally recognized movement 50% Secular 15%-20% Ultra-Orthodox Rest are traditionally observant Secular Jews of Israel observe some traditional practices Rare among American Reform and secular Differences in Practices In the UK: Mainly Reform Same prayer book as the American Conservative Yiddish: Ashkenazi Never a part of Sephardic Culture Hebrew and English Russian, French, and Spanish Affect on the Cultural Landscapes All western law can be partly traced to the Torah, especially the 10 Commandments. Today’s laws for women’s rights were originally maintained in Jewish culture. The emphasis on educa?on has long been held as the highest goal towards godliness. Excep?ng pigs, many foods that westerners abstain from directly result from Jewish kosher law. Conflict Holocaust: Mass targeting of Jewish people Jews against Muslims in Palestine: Territory Battle over Jerusalem Judaism and Cultural Landscape The Romans destroyed their capital, Jerusalem, around A.D. 70. There is no predominant design of their synagogues, but all have an ark containing the Five Books of Moses known as the Torah. The most symbolic landscape is the Western Wall at the edge of the temple mount in Jerusalem. The Jewish faith has about 18 million adherents, but the distribution of Jews proves that Judaism is indeed a world religion. A tradi?onal synagogue in Liver Pool A modern, LEED-‐cer?fied, “green” synagogue (Illinois) Bibliography Works Cited “The Diaspora.” Jewish Virtual Library. N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Jan. 2011. <http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/ History/Diaspora.html>. “Judaism.” ABC.net. ABC, 2010. Web. 13 Jan. 2011. <http://www.abc.net.au/religion/stories/s796551.htm>. “Judaism.” BBC. BBC, 7 Jan. 2009. Web. 13 Jan. 2011. <http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/judaism/history/ history_1.shtml>. “Judaism 101.” Judaism 101. N.p., 9 Dec. 2010. Web. 13 Jan. 2011. <http://www.jewfaq.org/index.htm>. Robinson, B A. “Judaism: Beliefs, Practices, JewishChristian Relations, News...” Religious Tolerance. Ontario Consultants, 2 Jan. 2009. Web. 13 Jan. 2011. <http://www.religioustolerance.org/judaism.htm>.