* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Back Round to Judaism
Self-hating Jew wikipedia , lookup
Orthodox Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Supersessionism wikipedia , lookup
Homosexuality and Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Invention of the Jewish People wikipedia , lookup
History of the Jews in Gdańsk wikipedia , lookup
The Reform Jewish cantorate during the 19th century wikipedia , lookup
Hamburg Temple disputes wikipedia , lookup
Jewish military history wikipedia , lookup
Interfaith marriage in Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Origins of Rabbinic Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Jewish religious movements wikipedia , lookup
Back Round to Judaism
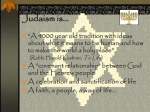
Judaism is one of the oldest religions still existing today. It began as the religion of the small nation of the Hebrews,
and through thousands of years of suffering, persecution, dispersion, and occasional victory, has continued to be a
profoundly influential religion and culture. Today, 14 million people identify themselves as Jewish. Modern Judaism is
a complex phenomenon that incorporates both a nation and a religion, and often combines strict adherence to ritual
laws with a more liberal attitude towards religious belief.
Growth of Judaism
The period of Christian hegemony in 5th-century Palestine, Jews flourished in Babylonia, spread
westward to medieval Spain, north and east to Europe, while continually adjusting their cultural
bearings.
As religious and social conditions worsened for the Jews in Palestine under the control of
Christian Rome, the center of Jewish life was transferred from the land of Israel to Babylonia,
the seat of the new Muslim empire. During this period of Muslim rule from the 7th-13th
centuries, Jews encountered Greek philosophy, medicine, physics, astronomy, and mathematics.
They also studied the Quran, Muslim poetry, philology, biography, history, and mysticism,
illustrating a linguistic, philosophical, and religious synthesis that is best described as "JudeoArabic culture." Yet this synthesis not only occurred in the elite, intellectual realm, but also at
the popular level in the sense that most Jews were indistinguishable from their Muslim neighbors
in terms of names, dress, and language.
Worldwide Jewish Birth Rates
Art and Architecture of Judaism
It's the Alhambra of Granada, a Moorish palatine city in Spain. But the famous lion’s
fountain was originally from a Jewish palace of the city. It came from the palace of the
Jewish poet and visir Ibn Nagrela, in the 11st century. Ke know it due to a text from the
poet Ibn Gabirol: the 12 lions are the 12 tribes from Israel and two of them have a triangle
in their forehead symbolizing the chosen tribes of Judá and Levi.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yyh8bzQnOr4&feature=player_detailpage
Western Wall Judaism’s most sacred site.
THE spread of Judaism
At numerous points in the history of Judaism, Jews were taken into captivity by other nations.
The people spread, so their beliefs also spread. Generally speaking, throughout history Judaism
hasn't really spread per se. Rather it has survived and grown naturally through childbirth. This
due to fact that Judaism doesn't proselytize and the small numbers of converts throughout history
have been minimal. Keep in mind that during most of history, in most places, converting to
Judaism was a capital offence, punishable by death or losing all your possessions. Generally
speaking most Jews are descendents of Jews. Only in recent years has conversion to Judaism
picked up a bit, relatively to previous generations.
History and Spread
Jewish civilization after the exodus prospered in the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, originally headed by
powerful kings like Saul, David and Solomon, who built the first great temple in Jerusalem. In 586 BCE,
the Babylonians overran Jerusalem, taking many captives into exile and destroying the temple. A second
temple was built when the Jews returned about 538 BCE, to be destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE. This
destruction was decisive for the future of Judaism, replacing a sacrificial religion based around a temple
with a tradition of studying and learning centered around local synagogues.
By around 100CE, the canon of the Hebrew Bible was fixed. Between 200 and 700 CE, scholars compiled
the Mishna, the definitive code of Jewish law. The Talmud (written interpretation of the scriptures) was
compiled and the rules for the Jewish calendar were laid down. These scriptures and teachings were the
basis of the religious worship that was practiced around the world during the Jewish Diaspora (exile).
Influences of Judaism
In modernity, Judaism has successfully met the challenges accompanying emancipation, assimilation,
and anti-Semitism, by redefining itself as a multiplicity of cultures based on the triad: God, Torah, and
Israel.
The total number of Jews worldwide is difficult to assess because the definition of "who is a
Jew" is problematic; not all Jews identify themselves as Jewish, and some who identify as Jewish
are not considered so by other Jews. According to the Jewish Year Book (1901), the global
Jewish population in 1900 was around 11 million. The latest available data is from the World
Jewish Population Survey of 2002 and the Jewish Year Calendar (2005). In 2002, according to
the Jewish Population Survey, there were 13.3 million Jews around the world. The Jewish Year
Calendar cites 14.6 million. Jewish population growth is currently near zero percent, with 0.3%
growth from 2000 to 2001.
More pics
Scenes from the Book of Esther decorate the Dura-Europos synagogue dating from 244 CE
The Western Wall in Jerusalem is a remnant of the wall encircling the Second Temple. The Temple
Mount is the holiest site in Judaism.
Judaism has spread to all corners of the world. Seen here is a synagogue in downtown Mumbai.
Other info if needed
Date founded
c. 1300 BC
Place founded
Mesopotamia
Founder
Abraham
Adherents
14 million
Main location
Israel, Europe, and USA
Original language
Hebrew
Spiritual leader
Rabbi (Rebbe in Hasidism)
Place of worship
synagogue ("temple" in Reform Judaism)
Day of worship
Saturdays
Theism
monotheism
Ultimate reality
One God (YHWH)
Human nature
Created good
Purpose of life
Obedience to God
How to live
Obey the law and atone for sin
Afterlife
Views vary: Gan Eden, Gehinnom, nonexistence, or reincarnation