* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom of the NIle - Pleasantville High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Memphis, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Khnumhotep and Niankhkhnum wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian technology wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian religion wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
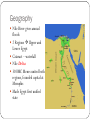
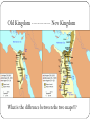
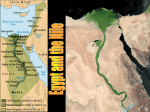
Kingdom of the Nile Aim: To discuss the history of ancient Egypt and explain why it thrived Geography Nile River gives annual floods 2 Regions Upper and Lower Egypt Cataract – waterfall Nile Delta 3100BC Menes united both regions, founded capital at Memphis Made Egypt first unified state Geography “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile” – Herodotus Why is the river so important???? 1) Deposited rich layer of silt (soil) used for farming 2) Used for transportation 3) Trade routes “If the Nile smiles, the Earth is joyous!” Old Kingdom 2700 -2200 BC Pharaohs organized strong central government King Menes unites Upper and Lower Egypt Created (dynasty) ruling family Built capital at Memphis Human and divine Bureaucracy Vizier chief minister Instructions of theVizier Ptah-hotep Great Pyramids of Giza King Menes Middle Kingdom 2050- 1800 BC What happened to the Old Kingdom!???!! Power struggles, bad crops and $$$ of pyramids led to decline Middle Kingdom formed! Draining projects formed new farm land Hyksos horse drawn chariots for customs and beliefs (CULTURAL DIFFUSION) Invasion of the Hyksos New Kingdom 1550- 1100 BC Drove out Hyksos, New Kingdom formed Reached from Syria to Euphrates Hatshepsut (female ruler) Encouraged trade Rames II built statues in his honor Fought Hittites and signed first peace treaty Old Kingdom ------------- New Kingdom What is the difference between the two maps??? Egyptian Civilization Religions Shapes Egypt Lord of the Gods AMON- RE Pharaohs believed their rule stretched from this great god Osiris,Isis and Set god of the underworld God of the Nile Isis goddess, taught how to spin cloth, weave and care Akhenaton tried to worship god Aton Nobles and people refused to switch View of Afterlife Proof to Osiris Mummification Across lake of fire to Osiris Embalming Weighed heart against Preservation of dead feather of truth Happy Field of Food Book of the Dead: spells charms and formulas bodies Buried everything one would need Valley of the Kings King Tut (son in law of Akheton) Discovered in 1922 He was a minor king Society pharaoh Government officials and high priests • served gods and goddesses Merchants, scribes, artisans Peasants who worked the land • Trade offered chance to move up, more business for artisans • Women held higher positions legally than others • Most were farmers, irrigates field, prepares equipment, built palaces Advances in Learning Written hieroglyphics Papyrus Rosetta Stone Greek/ Hieroglyphics Medical advances Astronomy Accurate calendar Arts and Literature Paintings in tombs and temples Gods and pharaohs larger than other figures Sphinx (early pharaoh as lionman) Tale of Sinuhe