* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is an isotope?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
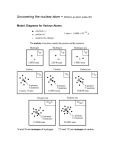
Oct 17 & Oct 20 QUIZ – LoC List #4 Quiz starts 2 minutes after bell ring You have 4 minutes! Warm-up#5: Summarize the contributions to the Atomic Theory Scientist Experimental Design Democritus -------------- Conclusion/ Contribution Hypothesized model -------------- Niels Bohr -------------- Quiz over history of atomic theory next time! Draw what you think an atom looks like • Draw a model of an atom on the front of a sticky note and put your name on the back. Then stick it on the white board. • The Atom Reviews of Atoms • All matter is made up of elements (e.g. carbon, hydrogen, etc.). • The smallest part of an element is called an atom. • Atom of different elements contain different numbers of protons • The mass of an atom is almost entirely due to the number of protons and neutrons Parts of Atoms - Subatomic Particles Atom consists of two parts: The nucleus which contains: • Protons • Neutrons Orbiting Electrons What are their charges? Ions The Atom (reminder) The atom consists of two parts: 1. The nucleus which contains: protons neutrons 2. Orbiting electrons Ions have charges! Charge: 0 -1 +1 Ions’ charges come from changes in ELECTRONS only! Isotopes What is an isotope? Number of protons for an atom of a specific element never changes. Number of neutrons can change. Two atoms with equal protons but different neutrons are called isotopes of each other. All atoms in existence are isotopes! Some isotopes are just more common than others. Isotopes Atoms with equal protons but different number of neutrons What do you notice that the isotopes have in common? What varies? Isotope Notation Mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons X Z A Element symbol Atomic number = number of protons Isotope Notation Write isotope notation for each isotope of hydrogen below: 1 1 H 2 1 H 3 1 H Hyphen Notation • Write out the name of the element, then add a hyphen (-), then the mass number. • Write the hyphen notation for the three isotopes of hydrogen. Isotope Notation Hyphen Notation 1 1 H hydrogen-1 2 1 H hydrogen-2 3 1 H hydrogen-3 Summary • If protons vary, the identity of the element changes • oxygen has 8 protons; fluorine has 9 protons • If neutrons vary, mass number changes and we have different isotopes • sulfur-32 has 16 neutrons; sulfur-33 has 17 neutrons • If electrons vary, charge changes and we have different ions • iron can lose two electrons to become Fe+2; iron can also lose three electrons to form Fe+3 • All atoms are isotopes; isotopes can also become ions Petri Dish Atoms Activity • Draw a card – same number in same group • You will work on 2 petri dishes at a time • You must complete the chart for at least 6 petri dishes • You will return the pair of petri dishes to the box when you are finished and get 2 new ones. • Isotope notation looks like this: Mass number of this atom Atomic number of this atom 40 19 K +1 Ion charge, if it is not zero Symbol of this element • Quiz: Atomic Theory History—be ready!! • Page 4: top half • Sapling Practice Assignment due Monday night • Sapling #1 due next Friday night Homework