* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The atmosphere! - Studentportalen
Water vapor wikipedia , lookup
Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Space weather wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Solar irradiance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change wikipedia , lookup
Surface weather analysis wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
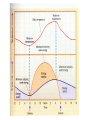
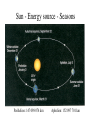
The atmosphere! -! Climate variations" Pär Holmgren" www.parholmgren.se" Dept. of Earth Sciences" Meteorology" ”The knowledge about what is in the air.”" The physics and chemistry of the atmosphere." The atmosphere" Radiation budget" General circulation" Greenhouse effect" Weather vs climate" What’s the difference?" What is weather?" What is climate?" Climate" Mark Twain: Climate is what we expect, weather is what we get." The Blue Planet! Water is a unique in our solar system" •" 71 percent of the Earth is covered by water and only 29 percent is landmass.# Earth's atmosphere# •" •" •" •" •" •" Nitrogen 78.081%" Oxygen 20.945%" Argon 0.934%" Carbon dioxide 0.038%" Water vapor >1%" Other 0.002%" Atmosphere" •" No definite boundary between the atmosphere and ”outer space”. It slowly becomes thinner and fades into space. # •" Three quarters of the atmosphere's mass is within 11 km of the planetary surface. # •" An altitude of 120$km marks a boundary where atmospheric effects become noticeable during re-entry of spacecrafts . # Temperature and layers# •" Troposphere: From the Greek word ”tropos” meaning to turn or mix. The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere; it begins at the surface and extends to between 7#km at the poles and 17#km at the equator, with some seasonal variation due to weather factors. The troposphere contains approximately 75% of the atmosphere's mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols." •" This is where we find the ”weather”!! Temperature and layers# Stratosphere: From the Latin word "stratus" meaning a spreading out. The stratosphere extends from the troposphere to about 50#km. Temperature increases with height." The stratosphere contains the ozone layer, the part of the Earth's atmosphere which contains relatively high concentrations of ozone. The ozone layer is mainly located in the lower portion of the stratosphere, from approximately 15 to 35#km above Earth's surface, though the thickness varies seasonally and geographically." Temperature and layers# •" Exosphere: from 500 – 1000#km up to 10,000#km, free-moving particles that may migrate into and out of the magnetosphere or the solar wind." •" Ionosphere: ionized by solar radiation and contains auroras. It affects radio propagation to distant places on the Earth. It is located within in the thermosphere." •" Thermosphere: from 80 – 85#km to 640 km, temperature increasing with height" •" Mesosphere: From Greek word “meso” meaning middle. The mesosphere extends from about 50#km to 80 or 85#km. Temperature decreasing with height." Troposphere - Convection# •" The troposphere has a great deal of vertical mixing due to solar heating at the surface, or convection. This is the main source for most of the weather! The heating warms bubbles of air, which makes them less dense so they rise. When a bubble of warm air rises the pressure upon it decreases so it expands, and the temperature decreases. As the temperature decreases, water vapor in the air may condense or solidify, creating clouds and precipitation. The condensation releases energy “latent heat” - that further uplifts the air bubble.! Radiation budget" •" It represents the balance between# •" The incoming energy (short wave) from the Sun and# •" The outgoing thermal (longwave) and reflected energy from the Earth. # Sun - Energy source - Seasons" Perihelion: 147 098 074 km Aphelion: 152 097 701 km " The general circulation" The worldwide system of winds, which transports warm air from the equator where solar heating is greatest towards the higher latitudes, is called the general circulation of the atmosphere, and it gives rise to the Earth's climate zones."