* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download endocrinesystemshort
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
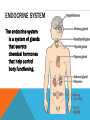
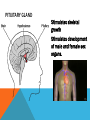
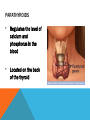
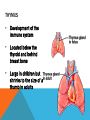
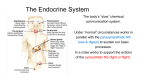
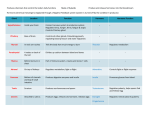
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The endocrine system is a system of glands that secrete chemical hormones that help control body functioning. ENDOCRINE GLANDS A tissue or group of tissues that makes and releases chemicals is called a gland. The chemical product of an endocrine glands is called a hormone. Endocrine glands produce and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. HORMONES Hormones are the chemical product of endocrine glands. Hormones turn on, turn off, speed up, or slow down the activities of different organs and tissues. TARGET CELLS Target cells are cells that recognize the hormone’s chemical structure. A hormone interacts only with specific target cells the way a key fits into a lock. Hormones travel through the bloodstream until they find their “lock” or particular cell type. NEGATIVE-FEEDBACK MECHANISM Endocrines systems method of regulating the level of hormones in the blood. HYPOTHALAMUS A part of the brain that regulates the activities of the pituitary gland. Located in the lower central part of the brain. Links the nervous system and endocrine systems and controls the pituitary gland PITUITARY GLAND Stimulates skeletal growth Stimulates development of male and female sex organs. THYROID GLAND • Produces Thyroxine to increase the body’s metabolism. • Maintains the level of calcium and phosphorus in the blood. PARATHYROIDS • Regulates the level of calcium and phosphorus in the blood • Located on the back of the thyroid THYMUS • Development of the immune system • Located below the thyroid and behind breast bone • Large in children but shrinks to the size of a thumb in adults ADRENAL GLANDS Increases heart and breathing rate, raises blood pressure Produce Epinephrine and norepinephrine Located on the top of each kidney PANCREAS • Produces insulin • Regulates the amount of sugar in the blood. OVARIES • Produces female sex characteristics • Located on both sides of the uterus below the opening of the fallopian tube. • Contain the egg cells necessary for reproduction. • Produce estrogen and progesterone TESTES Produces male sex characteristics Located in the scrotum Produce testosterone and sperm