* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
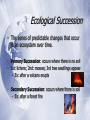
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
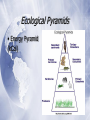
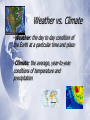
The Biosphere Chapter 3 What is Ecology? Ecology •The study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms their environment. Biosphere All parts of the Earth where life can exist (land, water and air). Biotic vs. Abiotic Biotic: the living factors in an ecosystem Abiotic: the nonliving factors in an ecosystem Levels of Organization Ecosystem: interactions among the community and abiotic factors Community: group of interacting populations Population: group of one species living in the same place at the same time Energy, Producers, and Consumers Autotrophs • An organism that can make its own food. • Use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. • Also called producers. Heterotrophs • An organism that has to get its food from others. • Also called consumers. Types of Heterotrophs Herbivores: eat only plants Carnivores: eat only meat Omnivores: eat both plants and meat Detritovores: break down dead material; decomposers Scavengers: eat dead animals Energy Flow in Ecosystems Feeding Relationships • Food chains: less complex • Food webs: show all eating relationships in an ecosystem. BETTER! Trophic Levels • Each step in a food chain. • As you move up trophic levels, 90% of the energy is lost. Ecological Pyramids • Energy Pyramid (kCal) Cycles of Matter The Water Cycle Nutrient Chemicals an organism needs to sustain life. Carbon Nitrogen Phosphorous Limiting nutrient: the nutrient whose supply limits productivity of producers Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Phosphorous Cycle Ecosystems & Communities Chapter 4 Niches & Community Interactions Niche • Everything an organism does to survive. • All physical and biological conditions. • What it eats, where it lives (habitat), how it avoids predators, etc. Competition Occurs when two organisms want the same resource at the same time. Competitive Exclusion Principle: No two species can occupy the same niche at the same time. Predation • An interaction where one organism captures and feeds on another organism. • Predator: the “killer” • Prey: the “killed” Keystone Species A species that exerts strong control on the structure of a community so that changes to its population causes dramatic changes Ex: sea otters Symbiosis • Any relationship in which two species live closely together. • Mutualism: both species benefit • Ex: bees and flowers • Commensalism: one species benefits while the other is not affected • Ex: barnacles on a whale • Parasitism: one species benefits, while the other is harmed • Ex: tapeworms- YUK! Examples of Symbiosis Succession Ecological Succession • The series of predictable changes that occur in an ecosystem over time. • Primary Succession: occurs where there is no soil • 1st: lichens; 2nd: mosses; 3rd tree seedlings appear • Ex: after a volcano erupts • Secondary Succession: occurs where there is soil • Ex: after a forest fire Climate Weather vs. Climate •Weather: the day to day condition of the Earth at a particular time and place •Climate: the average, year-to-year conditions of temperature and precipitation Effect of Latitude on Climate • The tilt of the Earth creates climate zones based on latitude: • Polar • Temperate • Tropical Heat Transport in the Biosphere • Unequal heating of the Earth drives winds and ocean currents. • Air and water near the equator heats and rises. Ozone Layer • Layer of the Earth’s atmosphere (13-20 km above Earth) containing ozone (O3). • Absorbs 93-99% of UV light. The Greenhouse Effect • Natural situation where gases trap the sun’s heat energy in the atmosphere. • Maintains our climate. (Earth would be 30 ºC cooler without it.) Humans in the Biosphere Carrying Capacity The maximum number of individuals of a particular species that a particular environment can support. Resources Renewable Resource: can be replaced by a healthy ecosystem Ex: trees, wind Nonrenewable Resource: can’t be replenished by natural processes in a reasonable amount of time Ex: fossil fuels Biological Magnification Increasing concentration of a harmful substance in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain Biodiversity All of the organisms in the biosphere Ecological hot spot: a place where significant numbers of species and habitats are in immediate danger of extinction Conservation “wise use” studying the loss of biodiversity & ways it can be prevented Ecological footprint The total area of functioning land and water ecosystems needed to provide resources and absorb the wastes of an individual or population. Used to calculate the biosphere’s carrying capacity for humans.