* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5. Evolution and extinction of biological population by Dr Snigdhadip
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
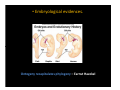
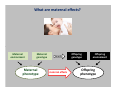
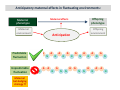
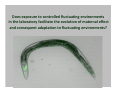
Evolution to the rescue Snigdhadip Dey École normale supérieure, Paris Maison de l’inde, 3rd July 2015 Sketch of the talk • What is evolution? • Charles Darwin and his theory of evolution by natural selection. • Practical applicability of evolutionary research. • Causes and consequences of species extinction. • My research. Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Evolution by Natural Selection What Darwin did? • Proposed a theory on how evolution works by natural selection. • Gathered plenty of evidences to support his theory. Darwin´s voyage • Invited to travel around the globe as a naturalist (1831-1836). Darwin´s voyage Darwin´s research • Darwin found many unique species in Galapagos. • Each island had its own species of tortoises and birds that were distinctly different from other islands. • Studied fossils to find evidences that living creatures changed over time • Embryological evidences. Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny – Earnst Haeckel How does natural selection work? Darwinian vs Lamarckian giraffe Why do you need evolutionary ideas?? Evolutionary medicine: Antibiotic resistance Understanding how antibiotic resistance evolves Agriculture: • Improving the quality of crop and livestock by artificial selection. • Understanding the evolution of pesticide resistance. Fishery : • How does selective harvesting affect the future of fisheries? • Improving the quality and yield via artificial selection. Conservation Biology: Adaptive potential to withstand global change. More efficient Drug designing The tree of life Species Extinction : unfortunate facts • According to the fossil record, 2-4% of the species that have ever lived survive today. • Rapid loss of species in recent time is estimated to be between 1000 and 10,000 times higher than the “background” or expected natural extinction rate. International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) How does extinction affect ? • Loss of biodiversity results in disruption of the balance of the ecosystem (water cycling, soil formation and retention, resistance against invasive species, plant pollination, climate regulation and pollution control. • The monetary value of goods and services provided by ecosystems is estimated to amount to some 33 trillion dollars per year – nearly twice the global production resulting from human activities. (IUCN) Major threats to biodiversity • Habitat destruction and degradation • Over-exploitation (extraction, hunting, fishing etc.) • Pollution Can populations adapt to these threats? • Disease • Global climate change (IUCN) Real-time evolution in the laboratory!! Artificial speciation in the laboratory!! • One of the first to carry out a controlled evolution experiment was William Dallinger. • During the course of a seven year-long (1880– 1886) experiment, Dallinger slowly increased the temperature from 60 °F to 158 °F. Dodd (1989) My voyage so far….. Dr. Amitabh Joshi Dr. Henrique Teotónio How do populations adapt to fluctuating environments? What are maternal effects? Maternal environment Maternal genotype Maternal phenotype Heredity maternal effects Offspring genotype Offspring environment Offspring phenotype Anticipatory maternal effects in fluctuating environments: Maternal effects Maternal phenotype Maternal environment Predictable fluctuation Unpredictable fluctuation Maternal bet-hedging strategy ?? Offspring phenotype Offspring environment Anticipation N N A A N A A N N A A N A N N N A A A N N A N N A A N N A A A N N Does exposure to controlled fluctuating environments in the laboratory facilitate the evolution of maternal effect and consequent adaptation to fluctuating environments? Design of the experiment A = Anoxia stress N = Normoxia Predictable N A N A N A N A N A A N N A N A N ......... (60 generations) Unpredictable N N A A N A N N A A N N A N A A N ...... (60 generations) de novo evolution of anticipatory maternal effect Predictable Unpredictable Mother A N Offspring A A How does the maternal effect work? The hypothesis Mother N Offspring Glycogen allocation in the eggs Better performance in A Evolution of anticipatory glycogen provisioning Predictable A N Mother Perspective: is evolution of maternal effect favourable in fluctuating environments in general? Maternal effects improve future performance of the populations in an array of fluctuating environments. Conclusions Populations exposed to predictably fluctuating environments adapted by evolving maternal effects. While the ones exposed to unpredictably fluctuating environment failed to do so. The maternal protection from anoxic stress is due to an adaptive glycogen provisioning to the oocytes. We have evolved so much that we are studying evolution!! But have we evolved enough to save ourselves from extinction? Thank you