* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mdr and xdr tuberculosis
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
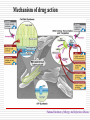
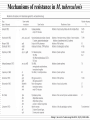
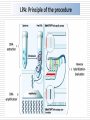
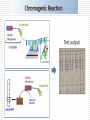
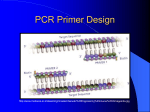
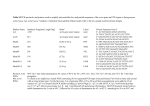
MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOSIS MUHAMMAD MUNTAZIR SHAH 11-ARID-2287 Ph.D. Scholar (Biochemistry) Tuberculosis Tuberculosis has been present in the human population since antiquity 1882 - Robert Koch discovered Mycobacterium tuberculosis Tuberculosis in Humans Treatment of Tuberculosis First Line Drugs Rifampicin Ethambutol Pyrazinamide Isoniazid Streptomycin (injectable) Second Line Drugs Flouroquinolones: Ciprofloxacin,Ofloxacin,Levofloxacin,Gatifloxacin Aminoglycosides: Kanamycin ,Amikacin (Injectable) Cyclic Peptide : Capreomycin (Injectable) Ethionamide : Ethionamide and Protionamide 4 Mechanism of drug action National Institute of Allergy And Infectious Disease Drug-Resistant TB Mono-resistant Resistant to any one TB treatment drug Poly-resistant Resistant to at least any 2 TB drugs (but not both isoniazid and rifampin) Multidrug resistant (MDR TB) Resistant to at least isoniazid and rifampin, the 2 best first-line TB treatment drugs Extensively drug resistant (XDR TB) MDR PLUS resistant to any fluoroquinolone AND at least 1 of the 3 injectable second-line drugs (e.g., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin) Mechanisms of resistance in M. tuberculosis Zhang Y, et al. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2015; 19(11):1276-1289. TB Diagnosis: WHO Recommended Technology Xpert MTB/RIF Assay Principle Single-use disposable GeneXpert cartridges that hold the PCR reagents and host the PCR process. The Xpert MTB/RIF assay uses 3 specific primers and 5 unique molecular probes to ensure a high degree of specificity. Assay targets the rpoB gene, which is critical for identifying mutations associated with rifampicin resistance. Molecular Beacon Technology Molecular beacon is a short segment of single-stranded DNA composed of: Target specific sequence Stem Fluorescent dye Quencher Molecular Beacon Technology Molecular Beacon Target Fluorescence No Fluorescence No Target = No Fluorescence Internal Controls Sample processing control (SPC) to control for adequate processing of the target bacteria and to monitor the presence of inhibitor(s) in the PCR reaction. The Probe Check Control (PCC) verifies reagent rehydration, PCR tube filling in the cartridge, probe integrity, and dye stability. How GeneXpert Work GenoType MTBDRsl Ver2.0 Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification: LAMP Notomi et al. 2000, developed LAMP-auto cycling technique Utilizes a polymerase with strand displacing property Works under isothermal condition 60-65C Results visualized directly, no post amplification procedure needed Less time-60 min. 10 to 100 times more than PCR Enzyme – Heart of the LAMP Bst polymerase Isolated from Bacillus stearothermophilus Optimum temperature for activity 63 C Bsm polymerase Isolated from Bacillus smithii Optimum temperature for activity 60 C Phi29 DNA polymerase Bacillus subtilis phage phi29 Primers F3 also called Forward outer Primer major role during strand displacement – Strand displacing primer B3 also called backward outer Primer major role during strand displacement – Strand displacing primer FIP (Forward Inner Primer) function in loop formation BIP (Backward Inner Primer) function in loop formation LAMP Principle Properties PCR LAMP Denaturation Required for separation of strands, enabling primer binding Denaturation step is not a mandate Temperature Usually employs 3 steps as Works under a constant temperature denaturation, annealing and extension, usually between 60-65 C working at different temperature and timing Time required Take 2-3 hour based on the different parameters 60 min usually Post amplification Need agarose gel electrophoresis or DNA binding dyes like SYBR green or any material indicator like calcien or HNB results can be interpreted visually Sensitivity Can detect up to nanogram level of DNA Can detect up to femtogram level of DNA Instrument Needs sophisticated instrument in order to maintain different temperature within a given time Water bath can serve the purpose Impurities Impurities can hinder the PCR reaction Impurities won’t hinder the reaction (Kaneko et al., 2007: Francois et al., 2011) THANKS