* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploration Continued
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
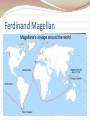
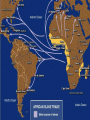
Use YOUR brain How many explorers can you list? Think even harder- Can you list what they discovered? I dare you to name what country they represented! Warm-up 1. What would make a person want to voyage out away from their home to search for new lands (think about the time period). SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa and Asia. For Glory, God, Gold The three G’s of exploration; Glory God and Gold The desire to grow rich and to spread Christianity, coupled with advances in sailing technology, spurred an age of European exploration. Through overseas exploration, merchants and traders hoped ultimately to benefit from what had become a profitable business in Europe: the trade of spices and other luxury goods from Asia. Pocahontas video Improved Technology The main problem was that European ships could not sail against the wind. The Caravel Triangular Sails Astrolabe-was a brass circle with carefully adjusted rings marked off in degrees. Using the rings to sight the stars, a sea captain could calculate latitude, or how far north or south of the equator the ship was. This was invented by the Muslims. Compass Chinese invention China Ming Dynasty -Rules for nearly 300 yrs -Brought peace and stability to China Zheng He 1405-1433 -The purpose of his voyages was to impress the world with the power and splendor of Ming China, they also wanted to expand China’s tribute system. -Southeast Asia -India -Africa Portugal leads the way in Europe The leader in developing and applying these sailing innovations was Portugal. Portugal took the lead in overseas exploration in part due to strong government support. The first to explore the east in the Indian Ocean They eventually travel south and explore the western side of Africa. Gold Ivory Slaves In 1492 Columbus sailed the ocean blue Determined to find a sea route to India by sailing west In October Columbus landed in the Caribbean, he thought it was the East indies This is going to start conflicts between Portugal and Spain Columbus Day video In Early 1493 Columbus returned back to Spain. The monarchs agreed to fund 3 more voyages to the America. He journeyed no longer as an explorer but now as an empire builder. Columbian exchange – gifts exchanged by the Old World and the New World. Europe gets Tomatoes Corn Potatoes Squash Chocolate Tobacco • America gets – – – – Slavery Smallpox Conquest Horses Vasco de Gama Portuguese explorer Began exploring the east African coast 1498 reached the port of Calicut in SW India Da Gama and his crew were amazed by the spices, rare silks, and precious gems that filled Calicut’s (in India) shops. Their cargo was worth 60 times more than the cost of their voyage First to find a direct sea route to India from Europe (around the southern tip of Africa) Ferdinand Magellan In 1519 Magellan led the boldest voyage yet Originally had just wanted to check out the pacific ocean Had 270 men and 5 ships He and his men were the first people to circumnavigate, or sail around the world. James Cook 1769-1770 British Explorer First European contact with the Australian coastline First to circumnavigate New Zealand Superior cartographer and navigator •Charts maps of the Pacific •Discovers Hawaii, refers to them as the Sandwich islands Samuel de Champlain 1608 •He sails for France •Quebec is the first French settlement in the Americas. It is in Canada. •Sent Jesuit missionaries to convert people to Christianity •Traded with the natives blankets, furs and wine for animal skins •He established the fur trade Founded Quebec Spanish invasions! Conquistadors: Spanish conquerors. Given the right by Spain to hunt for treasure. keep 1/5 of all treasure found. Conquer or die! Cortes lands in Mexico. Burns his ships. Befriends native tribes. Met by emissaries of the Aztecs. Cortes asks if they have any gold. They say lots. “Bring it to us, for I and my companions suffer from a disease of the heart that can only be cured by gold.” What treasures be there? El Dorado: legendary 7 cities of gold in the Americas. Hernando Cortes – Spanish conquistador who landed in Mexico in 1519 C.E. Has an army of 500 men, 16 horses and 14 cannon. Francisco Pizarro Conquered the Incan Empire They captured the Incan King. The king offered to fill a room once with gold and twice with silver for his release. They take him up on his ransom- but then kill him as soon as he gives them all the gold and silver Mercantilism Became a national policy Definition: states power depended on it’s wealth 1. Gold & Silver = wealth of nation (bullion) Remember before land=power, then $=power, now gold= power 2. Export more than it imports – balance of trade 3. Colonies – both the sources of raw materials as well as vital markets for finished goods Positives Negatives “Mother-countries” were self Spain and Portugal will go sufficient There was a mass exchange of goods and raw materials Nations were prospering and in turn building colonial empires and expanding to new territories Introduction to new products from all over the world into decline because they did not build extensive manufacturing industries within their countries Tariffs and Taxes The “mother-countries” are seeing all the wealth, not the colonies; they don’t treat colonies fairly Atlantic slave trade Triangle Trade Ships sailed the legs of a triangle formed by Europe, Africa and the Americas. Leaving from Europe: Knives, swords, guns, cloth and rum Leaving from Africa: slaves Sold for money that was used to buy sugar, molasses, cotton, and tobacco