* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mrs. G`s History Class
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
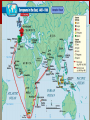
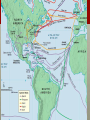
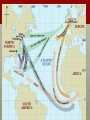
The Age of exploration & conquest The Spread of the West 1400-1700s Europeans explore the east …. Reasons for Exploration: •Renaissance encourages adventure and exploration •Crusades created contact with ‘outside’ world •Marco Polo’s excursion to China (1275) •Expanded possibilities for Europeans •Before this time did not have the means nor the will to explore Reason’s for Exploration “To serve God and His Majesty, to give light to those who were in darkness and to grow rich as all men desire to do” -Bartolomeu Diaz NEW SOURCES OF WEALTH Renaissance increased the size of the middle class. Europeans got a taste of spices and luxury goods (Asia) • Nutmeg, ginger, cinnamon, pepper • Demand was greater than supply=expensive prices The rest of Europe wanted a piece of the PROFIT to cut out Italians and Muslims who controlled the land routes The only option was to find a route by sea Spread of Christianity Desire to spread Christianity also motivated Europeans to Explore Crusades created hostility between Christians and Muslims Europeans felt they had a sacred duty to fight and convert non-Christians throughout the world Improvements in technology • 1400s Caravel created • Sturdier than older ships • Can sail against the wind with triangular sails from Muslims Navigational Techniques • Astrolabe (Muslims) • Magnetic Compass (Chinese) • Improved Maps Portugal leads the way Prince Henry the Navigator • Son of Portugal’s King & obsessed with exploring • Conquered Ceuta in N. Africa • Witnessed wealth of other places • Wanted to reach treasures in the East and spread faith • Never actually sailed but founded navigational school • Mapmakers, instrument makers, shipbuilders, etc. By 1460, Portugal has many trading posts in Africa • Springboard to further explorations Portugal leads the way Reaching Asia Bartolomeu Dias • 1488 reached the Southern tip of Africa • Proved that you could get around Africa by sea Vasco da Gama • 1498 reached the port of Calicut in India • Amazed by spices, rare silks and precious gems • Filled their ships and cargo worth 60X cost of the voyage • FOUND A DIRECT SEA ROUTE TO INDIA Spain Joins in Christopher Columbus • 1492 convinces Isabella and Ferdinand of Spain to finance his trip • Reaches San Salvador and claims for Spain The voyages of columbus Columbus got his money from Spain’s monarchs Ferdinand and Isabella • Sailed with three ships • Nina, Pinta, and Santa Maria • Arrive to ‘San Salvador’ October 12, 1492 • Result of near mutiny aboard his ships • Mistakenly calls inhabitants los indios • Columbus interested in gold and land possessions • When he returned people were enthralled with his tale • Funded for three more journeys and became an empire builder. Other explorers 1500: Pedro Alvares Cabral • Brazil and claims for Portugal 1501: Amerigo Vespucci • Claimed not part of Asia but a “new” world. • 1507 German mapmaker named the new continent ‘America’ in honor of Vespucci Spanish explorer Vasco Balboa • Crossed Isthmus of Panama viewed Pacific Ocean 1519 Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan • • • • Circumnavigated the world 250 men, 5 ships Died in Philippines, crew carried on back to Spain Only 18 men and 1 ship returned home Rivalry between Portugal and Spain Pope Alexander VI keeps peace • Treaty of Tordesillas • Everything East=Portugal • Everything West=Spain • Why wasn’t the rest of Europe involved in the initial discovery of the west? Trading empires in the Indian ocean Vasco da Gama’s trip opened up sea route to India • Led to mad scramble and violence between European powers and land’s inhabitants Portugal establishes trading empire • Removed Muslims from Spice trade (w/cannons) • Establish fort at Hormuz (control Persian Gulf and Arabian Sea) • Find strategic points to take over to control spice trade • Portuguese charged 1/5 the price of Arab and Italian merchant. Why could they charge a cheaper price? • The cheaper price allowed more people to buy/experience spices and materials from the Far East Other nations Join in the fun By 1600 Dutch owned 20,000 ships (largest in world) English and Dutch challenged Portugal’s control and then fought each other. Both created East India Company (controls trade throughout Asia) Dutch win the land eventually • Established trading headquarters on Java • Seized Malacca from Portugal • Amsterdam becomes commercial center Mercantilism The theory and system of political economy prevailing in Europe after the decline of feudalism, based on national policies of accumulating bullion, establishing colonies and a merchant marine, and developing industry and mining to attain a favorable balance of trade. • What does this mean???? Mercantilism • Mercantilism=country’s power depends mainly on its wealth • Goal of every nation to become as rich as possible • Countries increase wealth in two ways • Obtain as much gold and silver as possible • Establish favorable balance of trade • Sold more goods than it bought • Limit imports • The goal is only be importing raw materials that cannot be grown or found in home country • Countries want to be self-sufficient • Hip Hughes Video- Mercantilism Triangular Trade • Slaves became part of a transatlantic trading network known as the Triangular Trade. Europe: Transport manufactured goods to west coast of Africa (guns, clothes, etc.) Africa: Slaves and gold to West Indies and Americas Americas: Raw materials to Europe (sugar, coffee, tobacco, cotton) Consequences of Slave Trade • Africa • Cultures lost generations of fittest and most able members • Families torn apart • Introduced guns to the continent • Americas • • • • Contributed huge amount of labor Experience in agriculture Brought culture (art, music, religion, food) Substantial populations of African-Americans The Columbian Exchange • Columbian Exchange= the global transfer of foods, plants, animals, ideas, technology, and disease during the colonization of the Americas. • Lots of new animals, and plants shifted throughout the world, and expanded with trade. Columbian Exchange • Exchange from the Americas to Europe, Asia, Africa • Most important crops corn and potatoes • Inexpensive to grow and nutritious • Both crops became important part of diet throughout world. • Helped people live longer =significant role in boosting world population Global Trade • Colonial empires influenced Europe, besides just food • New wealth and overseas trade has huge impact • Creates new businesses and trade practices in Europe • Capitalism=economic system based on private ownership and the investment of resources for profit • Individuals, not only government, have wealth • Merchants, because of trade, become wealthy • Increase in nation’s money supply • Inflation • (more money so the money is less valuable) • Costs of good increases significantly Joint-Stock Companies • Joint-Stock Companies= kind of like a modern day corporation • • • • Investors buy shares of stock in a company All reap benefits of profits Share risk of investment 1500-1600s Joint-Stock Companies for American colonization The truth about Columbus Columbus was not the first European to reach America. Who was? The meaning of Columbus’s voyage is highly contested. On the one hand, it is witness to the tremendous vitality and verve of late medieval and early modern Europe - which was on the verge of acquiring a world hegemony. On the other hand, the direct result of this and later voyages was the virtual extermination, by ill-treatment and disease, of the vast majority of the Native inhabitants, and the enormous growth of the transatlantic slave trade. Crash Course History: The Columbus Exchange http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HQPA5oNpfM4 Conquering the Aztecs and Incas Hernan Cortez, 1519 • Montezuma, thinking Cortez a God, gives the Spanish some gold • Spanish not satisfied and wage war on the Aztecs Francisco Pizzaro, 1532 • Kidnapped Incan ruler • While protected by a force of about 30,000 • Inca paid ransom for the return of their leader • Spanish strangled Incan king anyway • Pizzaro captured Incan capital Cuzco from demoralized Incans Conquistador’s success The Conquistadors were so successful for several reasons. Though they were typically outnumbered, they had several advantages on their side. 1. Superior weaponry • Guns and cannons vs. bow and arrows 2. Enlisting help of smaller native groups • Cortez found groups that didn’t approve of Aztec sacrifices 3. Disease • Measles, mumps, smallpox, etc. Spain’s pattern of conquest Breeding the natives out • Most peninsulares (settlers) were men and they had relationships with native women • = Mestizo (mixed Spanish and Native Americans) • Caste System http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UdxdXfDLaNs Oppressed native peoples with Encomienda • System where natives farmed, ranched or mined for Spanish landlords. • Landlords received rights to the natives’ labor from Spanish authorities • Worked laborers to death often, though they promised to treat them well. • Mines were especially dangerous Bartolome de Las Casas Article 1. Write down any vocabulary that is unfamiliar to you 2. Who was Bartolome de Las Casas? 3. Why did he come to the New World? 4. What were the two sides in the “debate” sponsored by the King of Spain? 5. Analysis (1-2) paragraphs: Do you think that history could have developed any differently? Could the old world and new have collided peacefully? Use evidence to support your opinion. European Nations settle N. America Spain was very successful in the Americas England, France, and Netherlands want to join in. European countries ignore the Treaty of Tordesillas Want to find a North West Passage to Pacific Ocean • Shorter route to Asia= more profitable • Never find route • Establish colonies in N. America instead