* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Requirements to achieve the Intended Learning Outcomes
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Specialty drugs in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
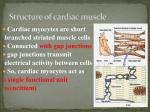
COLLEGE OF MEDICINE CVS - 322 BLOCK (Girls) Table for the guidelines/ Requirements to achieve the Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO’s) 2015 1 CVS 322 Block Educational Framework (Week 1) Requirement to achieve the ILO’s The intended learning outcomes Describe the gross anatomy of the mediastinum. Discuss the gross anatomy of the pericardium, external and internal features of the heart. Describe the development of the heart. Define mediastinum. Enlist the divisions of mediastinum. Describe the boundaries and contents of mediastinum. Define pericardium. Differentiate between fibrous and serous pericardium. Define pericardial sinuses. Identify the borders and surfaces of the heart. Describe the structure of the heart List the chambers of the heart. Describe the internal features of right atrium. Describe the internal features of the right ventricle. Discuss internal features of the left atrium. Discuss the internal features of the left ventricle. Differentiate between right and left ventricles. Define conducting system of the heart. Describe the formation and position of the heart tube. Explain the mechanism of formation of the cardiac loop. Discuss the development of sinus venosus. Explain how cardiac septa are formed. Describe the septum formation in the common atrium. Discuss the septum formation in the Atrioventricular canal. Discuss the septum formation in the truncus arteriosus and Conus Cordis. Describe the septum formation in the ventricle. 2 Correlate the structural anatomy of the heart with its function. Enlist the structure, synthesis, regulation and excretion of cholesterol. Illustrate the structure, types and separation of lipoprotein as complex lipids. Explain the metabolism of Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL. Enlist diseases related to abnormal lipoprotein metabolism. Describe the chambers and valves of the heart. Recognize the layers of the heart wall. Describe the functions of valves and papillary muscles. Understand how heart is working as syncytium. Differentiate between systemic and pulmonary circulation. Define cholesterol as the most important animal steroid. Know the structure of cholesterol. Discuss the synthesis of cholesterol. Identify the regulation of cholesterol. Describe the excretion of cholesterol. Define hypercholesterolemia. Describe lipoproteins as complex lipids. Understand the structure of lipoproteins. Point out to types and separation of lipoprotein. Know chylomicrons metabolism. Explain VLDL metabolism. Discuss LDL structure and metabolism. Describe HDL structure and metabolism. Know the function of HDL. Define HDL as a good cholesterol carrier. Recognize the diseases related to abnormal lipoprotein metabolism. 3 CVS 322 Block Educational Framework (Week 2) Requirement to achieve the ILO’s The intended learning outcomes Discuss the conductive system of the heart. Enlist the arteries, veins and nerves supplying the heart. Describe the phases of cardiac cycle. Explain heart sounds. Describe the development of the heart. Describe the development of the aortic arches Identify the components of conducting system of heart . Know the sequence of conduction of impulse in the heart Recognize the concept associated with pacemaker Appreciate the role of ANS in controlling rate of generation and conduction of impulse Recognize the difference between A.P of SA Node and ventricular muscle fiber Enlist the arteries and veins supplying heart. Describe the origin and branches of the right and left coronary arteries. Define coronary artery anastomosis. Describe the arterial supply of the conducting system of heart. Discuss the venous drainage and nerve supply of the heart. To know about different phases of cardiac cycle To understand the volume, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To emphasize the inter-relationship between all these changes To know the event that leads to the heart sounds Recognize the relationship of heart sounds with events of cardiac cycle Describe the formation and position of the heart tube. Explain the mechanism of formation of the cardiac loop. Discuss the development of sinus venosus. Explain how cardiac septa are formed. Describe the septum formation in the common atrium. Discuss the septum formation in the atrioventricular canal. Discuss the septum formation in the truncus arteriosus and Conus Cordis. Describe the septum formation in the ventricle. Describe the formation of the aortic arches. 4 and venous system of the heart and discuss their congenital anomalies. Enlist the derivatives of aortic arches. Discuss the development of venous system of the heart. Differentiate between fetal and neonatal circulation. Discuss the congenital anomalies of the aortic arches. 5 CVS 322 Block Educational Framework (Week 3) Requirement to achieve the ILO’s The intended learning outcomes Discuss the congenital anomalies of the heart. Analyze and calculate the Electro- Cardiogram (ECG) and illustrate its significance. Delineate the surface and radiological anatomy of the heart. Differentiate the microbial agents of myocarditis according to microscopic features, cultural characteristics, pathogenesis, virulence, and role of immunity in tissue destruction. Identify the causative agents of parasitic and viral myocarditis. Define the clinical presentation of Myocarditis. Describe microscopic picture, pathogenesis and complications Discuss the congenital anomalies related to the heart development. Identify the concept of ECG leads. Describe basic components of ECG. Relate each components of ECG with the electrical event in the heart. Understand the concept of QRS axis. Analyze the ECG and calculate the heart rate and cardiac axis. Know the importance of ST segment in IHD and MI. Apply knowledge of analyzing ECG on interpretation of sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, AF, IHD, MI, heart block. Delineate the surface anatomy of the heart and valves. Explain the radiological anatomy of the heart. Enlist the causative agents of myocarditis. Correlate the microbial antigenic cross-reactivity with the mechanism of myocardium inflammation. Differentiate the microbial agents of myocarditis according to microscopic features, port of entry, cultural characteristics, virulence, pathogenesis, role of immunity in inflammation. Summarize the clinical presentations that associated with parasitic, viral, and bacterial Myocarditis. Understanding the definition of arteriosclerosis specially 6 of atherosclerotic plaque formation. Discuss risk factors and pathogenesis of ischemic heart diseases. Describe morphologic changes, diagnose and complications of myocardial infarction. Discuss oxidative stress and atherosclerosis. Explain biochemical markers of myocardial infarction and related heart diseases. atherosclerosis. Knowing the risk factors, gross morphology, and common sites of atherosclerosis. Recognizing the microscopic picture of atherosclerosis plaque. Being aware of the complications of atherosclerosis. Defining ischemic heart disease. Being aware of the risk factors of IHD. Understanding the pathogenesis of IHD. Recognizing definition, cause and types of angina pectoris. Understanding the definition, causes and common sites of the myocardial infarction. Knowing the morphological features of myocardial infarction. Understanding the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (clinical picture, laboratory findings). Being aware of the complications of myocardial infarction. Define oxidative stress. Know Reactive Oxygen species (ROS). Understand antioxidant mechanisms. Identify molecular and vascular effects of ROS. Recognize Nitric Oxide and their role in oxidative stress. Define oxidative stress and pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Define myocardial infarction. Detect time-course of plasma enzyme changes. Explain Creatine kinase (CK), Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and Aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Define Myoglobin. Discuss cardiac troponins I and T and mention other markers related to heart diseases. 7 CVS 322 Block Educational Framework (Week 4) Requirement to achieve the ILO’s The intended learning outcomes Explain different mechanisms and actions of antihypertensive drugs. Describe antihypertensive drugs according to their route of administration, indications, drug interactions and contraindications. List the site of action of antihypertensive drugs Explain the molecular mechanism of action of each class of antihypertensive drugs Explain the hemodynamic mechanism of action of each class of antihypertensive drugs. Describe the hemodynamic actions of antihypertensive drugs. Describe the main non-vascular actions of antihypertensive drugs. Describe the routes of administration and the elimination processes of antihypertensive drugs. Describe the main adverse effects of antihypertensive drugs. Describe the clinically important drug interactions among antihypertensive drugs and between antihypertensive drugs and other drugs. Describe the main contraindications of antihypertensive drugs. Describe the use of antihypertensive drugs in mild, moderate and severe essential hypertension. Outline the strategy of the individualized sequential therapy of hypertension. Describe the use of antihypertensive drugs in case of hypertensive emergencies. Explain the choice of the appropriate antihypertensive drug in patients with concomitant diseases. Describe the use of some antihypertensive drugs in other cardiovascular disorders (heart failure, myocardial infarction, etc.) and other non-vascular disorders. 8 Discuss prostaglandins and related compounds. Identify the nature of prostaglandins and related compounds. Demonstrate if prostaglandins are true hormones. Describe cyclooxygenase and their role in synthesis of PG. Overview of synthesis of leukotriene. Discuss the role of PG in platelet homeostasis. 9 CVS 322 Block Educational Framework (Week 5) Requirement to achieve the ILO’s The intended learning outcomes Define and discuss cardiac output and factors affecting it and the venous return. Enlist the arteries and veins supplying the head and neck. Discuss the hemodynamics of the heart and enlist factors affecting peripheral resistance. Define and describe the terms COP, stroke volume, EDV, ESV the ejection fraction. Describe factors affecting cardiac output and venous return. Recognize the effect of sympathetic and parasympathetic ANS on heart rate and COP. Identify Frank starling law. Understand the principle of measuring the COP (Fick principle, dye dilution method). Apply the physiological knowledge of factors affecting COP on conditions causing low COP and high COP . Enlist the major arteries supplying head and neck. Understand how common carotid arteries take origin. Enlist important relations of common carotid arteries. Describe the relations and branches of external carotid artery. Describe the relations and branches of subclavian artery. Enlist the major veins supplying head and neck. Discuss the formation of external and internal jugular veins. Describe the tributaries of external and internal jugular veins. Discuss the pattern and physics of blood flow in vascular system. Define the term resístanse& pressure in the blood vessels. Describe laminar and turbulent blood flow. Explain factors affecting the peripheral resistance. 10 Enlist the arteries and veins supplying the upper limb. Explain different mechanisms and actions of antianginal drugs. Describe antianginal drugs according to their route of administration, time course, drug interactions and contraindications. Discuss the use of antianginal drugs in different types of angina, myocardial infarction and other disorders. Appreciate the typical functional features of different types of vessels in vascular tree. Describe axillary artery and its relations. Enlist the branches of axillary artery. Discuss the arterial anastomosis around the shoulder joint. Describe brachial artery, its relations and branches. Discuss the arterial anastomosis around the elbow joint. Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar arches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Discuss the superficial veins of the upper limb. Describe the formation of axillary vein. Explain the molecular mechanism of action of antianginal drugs. Explain the hemodynamic mechanism of action of antianginal drugs. Outline the significance of the difference between exertional angina and vasospastic angina in relation to the therapeutic activity of antianginal drugs. Describe the cardiac actions of antianginal drugs. Describe the peripheral vascular actions of antianginal drugs. List other actions of antianginal drugs. Outline the problem of tolerance development to nitrates. Describe the routes of administration and the elimination processes of antianginal drugs. Outline the time course of antianginal activity in relation to the administration routes. Describe the main adverse effects of antianginal drugs. Describe the clinically important drug interactions among antianginal drugs and 11 between antianginal drugs and other drugs. Outline the main contraindications of antianginal drugs. Describe the use of antianginal drugs in exertional and vasospastic angina. Describe the use of antianginal drugs in unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction. Explain why the combination of nitrates with beta-blockers (or calcium channels blockers) may be more effective that either alone. Outline the use of some antianginal drugs in other disorders (i.e amyl nitrite in cyanide poisoning, nicardipine in subarachnoid hemorrhage, etc). IMAGING Discuss dietary fat, dietary factors and the incidence of coronary heart. Enlist dietary recommendations for cardiovascular fitness. Discuss, physiological mechanism that play important homeostatic role in regulation blood pressure. Identify dietary fat and the incidence of coronary heart. Define saturated fats. Explain unsaturated fats. Know the Mediterranean Diet. Understand dietary factors and blood cholesterol levels. Detect dietary recommendations for cardiovascular fitness. Identify the factors affecting the mean arterial pressure. To understand the concepts of different regulatory mechanism that play major role in control of blood pressure. Recognize the importance of the baroreceptors and Renin - Angiotensin – Aldosterone Mechanism. To know the normal value of BP (systolic, diastolic and pulse pressure). Learn the Use of sphygmomanometer. Recognize the effect of posture and exercise on BP. Apply the basic physiological knowledge in in understanding the hypotension and hypertension. 12 CVS 322 Block Educational Framework (Week 6) Requirement to achieve the ILO’s The intended learning outcomes Describe the clinical feature, pathogenesis and diagnosis of rheumatic heart disease. Describe regulation and factors affecting coronary circulation. Discuss factors affecting capillary circulation and mention lymph formation. Defining and mentioning types of non-infective endocarditis. Understanding the definition and pathogenesis of acute rheumatic fever. Being aware of the clinical features and diagnosis of rheumatic fever. Describing the cardiac lesions in rheumatic heart disease. Understanding the pathology of libman-sack endocarditis and non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis. Mentioning the types of infective endocarditis, causative organisms, risk factors and complications. Review the functional anatomy of coronary circulation Recognize the importance of phasic changes in coronary blood flow Describe the factors affecting the coronary blood flow Recognize the clinical significance (IHD) Define capillary circulation. Recognize the importance of Mechanisms for control of blood flow to the various organs Understand factors affecting capillary circulation. Identify Starling forces acting on capillary. Appreciate the role of lymphatic. Apply the physiological knowledge of microcirculation in understanding the causes 13 of edema. Define intravascular infections considering Endarteritis, phlebitis, endocarditis, bacteremia, septicemia, and septic shock. Define the causative agents of intravascular infections. Discuss endocarditis with regard to microbial virulence, pathogenesis, role of immunity involved in cardiac valves vegetation and tissue destruction. Discuss bacteremia and septicemia considering the immune response stimulation, the immunity induced complications, and laboratory diagnosis. Describe the different actions, main therapeutic uses and guidelines for the use of cardiac glycosides in heart failure. Discuss digitalis toxicity according to the dose, different manifestations, risk factors and therapy. Define intravascular infections considering Endarteritis, phlebitis, endocarditis, bacteremia, septicemia, and septic shock. Define the most common causative agents of different types of endocarditis Describe the cardiac valves vegetation and granuloma. Identify the role of microbial virulence and immunity in formation of cardiac vegetation. Recognize the port of entry of microbes to bloodstream. Define the role of systemic inflammatory response in establishment of septic shock and multi-organs dysfunction. Enlist some causative agents of bacteremia, and septicemia. Define the laboratory methods used for differential diagnosis of bacteremia and septicemia. Explain the molecular mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides. Explain the cardiac mechanism of action of beta-receptor agonists Explain the mechanism of action of phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Describe the actions of cardiac glycosides on various parameters of cardiac activity (contractility, automaticity, conduction, refractoriness). Describe the electrophysiological action of cardiac glycosides on normal and abnormal myocardial tissue Describe the main effects of cardiac glycosides on the ECG. Contrast the direct and autonomic actions of cardiac glycosides upon the heart. Describe the hemodynamic actions of cardiac glycosides in the failing heart. Describe the extra-cardiac actions of cardiac glycosides. Describe the cardiac actions of beta-agonists and of phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Describe the routes of administration, oral bioavailability and elimination processes 14 Describe the microscopic structure of the heart. Explain definition, types and pathogenesis of different types of vasculitis. of digoxin. List the main drugs that can alter the pharmacokinetics of digoxin. Explain the concept of loading dose and maintenance dose in chronic digitalis therapy. Describe the cardiac and extra-cardiac manifestations of digitalis toxicity. List the main factors that can increase the risk of digitalis toxicity. Outline the general guidelines for the therapy of digitalis toxicity. Describe the clinically important drug interactions between digoxin and other drugs. Describe the main contraindications of digoxin. Describe the main adverse effects of beta-agonists and of phosphodiesterase inhibitors. List the main therapeutic uses of cardiac glycosides. Outline the guidelines for the use of cardiac glycosides in heart failure. Describe the role of other inotropic drugs, beta-blockers, diuretics and drugs affecting the renin- angiotensin system, in the therapy of acute and chronic heart failure. Explain the histological features of cardiac muscle. Differentiate between histological features of artery, vein and capillary. Understanding the definition of vasculitis. Recognizing the types of vasculitis. Identifying the pathogenesis of immune mediated vasculitis. . Recognizing the pathological features of giant cell arteritis. Recognizing the pathological features of takayasu arteritis. Recognizing the pathological features of polyarteritis nodosa. Recognizing the pathological features of Kawasaki disease. Recognizing the pathological features of microscopic polyangitis. 15 Recognizing the pathological features of Wagner's granulomatosis. Recognizing the pathological features of thromboangitis obliterans. 16 CVS 322 Block Educational Framework (Week 7) Requirement to achieve the ILO’s The intended learning outcomes Enlist the arteries and veins supplying the lower limb. Explain definition, types, and changes occurring during of shock and body response to different types of shock. Explain Rickettsial diseases considering microbiologic aspects, virulence, pathogenesis, and clinical presentation of these diseases. Define the laboratory methods used in diagnosis of Describe femoral artery and its relations. Enlist the branches of femoral artery. Define the trochanteric and cruciate anastomosis. Describe popliteal artery, its relations and branches. Discuss the arterial anastomosis around the knee joint. Discuss the anterior tibial artery, its relations and branches. Define dorsalis pedis artery. Discuss the posterior tibial artery, its relations and branches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Describe the formation of great saphenous vein and enlist its tributaries. Discuss the formation of small saphenous vein and enlist its tributaries. Describe the formation of popliteal vein and femoral veins. Define shock. Recognize types of shock – haemorrhagic, anaphylactic, septic, and cardiogenic. Understand the shock by discussing changes occurring in haemorrhagic shock. Explain compensatory response of body to shock. Identify the concept of irreversible (unresponsive) shock. Define Rickettsia species according to microbiologic aspects, virulence, pathogenesis, and clinical presentation of these diseases. Discriminate the laboratory methods used for diagnosis of Rickettsial diseases. 17 Rickettsial infections. Discuss Arboviruses according to port of entry, mode of transmission, classification, properties, pathogenesis and tissue destruction. Define the methods used in prevention and control of arboviruses infection. Enlist the clinical presentations associated with Arboviruses infections. hemorrhagic fever. Classify hemorrhagic fever viruses according to Baltimore classification system. Define the port of entry, vector, and properties of Arboviruses. Describe the pathogenesis and clinical presentation of Arboviruses infection. Explain the molecular mechanism of action of antiarrhythmic drugs. Explain the effects of antiarrhythmic drugs on the different phases of action potential. Describe the actions of antiarrhythmic drugs on various parameters of cardiac activity (automaticity, conduction, refractoriness). Describe the electrophysiological actions of antiarrhythmic drugs on normal and abnormal myocardial tissue. Describe the main effects of antiarrhythmic drugs on the ECG. Describe the relevant extracardiac actions of antiarrhythmic drugs. Describe the routes of administration and the elimination processes of selected antiarrhythmic drugs. Describe the main adverse effects of antiarrhythmic drugs. Describe the clinically important drug interactions among antiarrhythmic drugs and between antiarrhythmic drugs and other drugs. Describe the main contraindications of antiarrhythmic drugs. Describe the use of antiarrhythmic drugs in the acute treatment and in the chronic control of supraventricular arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation and flutter, supraventricular tachycardias, etc). Describe the use of antiarrhythmic drugs in the acute treatment and in the Explain different mechanisms and actions of antiarrhythmic drugs. Describe antiarrhythmic drugs according to their route of administration, drug interactions and contraindications. Discuss the use of antiarrhythmic drugs in different types of arrhythmias. Enlist different types of Arboviruses that associated with establishment of 18 chronic control of ventricular arrhythmias (ventricular ectopic beats, ventricular tachycardias, ventricular fibrillation, etc). 19