* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulation - Heart 13 slides
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
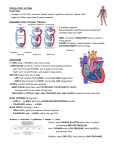
Aim: How does blood travel through the human heart? Where does this sound come from? Weird Science Fact The heart will continue to beat for several minutes after removal from the body due to its own internal electrical system. How does the circulatory system help maintain homeostasis? Arteries, capillaries, and veins help to transport nutrients and oxygen TOWARD the body cells, while taking carbon dioxide and other wastes AWAY from body cells. What are some characteristics of arteries, capillaries, and veins? Structure Of The Heart • The heart is a MUSCULAR pump with FOUR CHAMBERS. • Two Atria: Upper, THIN walled chambers that receive blood from the body. • Two Ventricles: Lower, THICK walled chambers that force blood into arteries. • Valves: Which prevent the backflow of blood • Septum: separates right and left sides. Superior Vena Cava Pulmonary Veins Aorta Right Atrium Right Ventricle Pulmonary Artery Left Atrium Septum Left Ventricle Inferior Vena Cava Path Of Blood Through The Heart Body Aorta Left Ventricle Vena Cave Right Atria Right Ventricle Pulmonary Left Atria Artery Pulmonary Lungs Veins Types Of Circulation 1 - PULMONARY CIRCULATION: -Blood travels from RIGHT side of heart to the lungs and back to Left side of heart. Pulmonary Circulation LUNGS LUNGS • Pulmonary Artery: DEOXYGENATED blood leaves the heart from the R. ventricle travels through this vessel to the lungs. • Lungs: OXYGENATED blood now reenters the L. atria through the Pulmonary Veins. Types Of Circulation 2 - SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION: Blood travels from the LEFT side of the heart to the rest of the body (to deliver oxygen and nutrients) and back to heart.. Systemic Circulation BODY BODY • OXYGENATED blood is pumped from the L. Ventricle through the AORTA to the rest of the body. • After oxygen is removed by body tissue, the DEOXYGENATED blood re-enters the R. atria through the S. & I. Vena Cava. Types of Circulation: 3 - Coronary Circulation: Responsible for delivering blood to the heart tissue so it can have the oxygen & nutrients to pump. Why is the septum important? • It separates oxygen POOR blood (right side of the heart) from oxygen RICH blood (left side of the heart). SEPTUM Regulation of the Heartbeat: A specific region of the heart muscle located in the RA sets the rate at which it contracts (pacemaker). Systole: 1-5 The pacemaker is influenced by both the nervous and endocrine systems. Heart Cycle: Diastole: 6 1) RA & LA contract 2) RV & LV fill with blood 3) RA & LA relax 4) RV & LV contract 5) Blood enters aorta & PA 6) Entire heart is relaxed (allows for heart to refill with blood). Blood Disorders Blood Pressure: (Hypertension) The force or pressure developed by the heart, which acts to pump blood through the circulatory system. Blood Pressure Two Distinct pressures that are measured!! Systolic: A measure of the maximum force or pressure developed in the arteries when the heart contracts Diastolic: A measure of the lowest pressure, which occur in the arteries during cardiac relaxation. Blood Pressure High Blood Pressure: Continuous elevation of blood pressure above the normal range. Ex. 140/90 Blood Pressure • Sphygmomanometer: An instrument used to measure blood pressure. • Stethoscope: An instrument used to listen to the sounds of the heart, or listen to the flow of blood through the vessels when measuring the blood pressure.