* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fundamentals of Management 4e.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
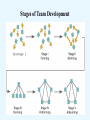
FS10321: Business Management Week #6: Chapter 8: Individual & Group Behavior 1 Team Project • Correction: Deadline is September 5th. • Assignments: Week 4: Week 5: Week 6: Week 7: Week 9: Teams announced Accounts must be created and shown to instructor! Turn in team name, target market, product concepts, initial marketing plan. At least one product must be available on CafePress.com Demonstrate your store in class Final write-up due (details to come!) 2 Team Papers/Presentations – Week 9! • • • • • • Target market Final marketing plan Product descriptions Artwork Promotional materials used Description of what happened – See next slide 3 Description of What Happened • In terms of topics from class – – – – – – Team Formation Team Structure Planning Procedure Managing Change Motivating etc 4 Chapter 8 Foundations of Individual and Group Behavior 5 The Organization as an Iceberg Metaphor EXHIBIT 8.1 6 Organizational Behavior (OB) • The study of the actions of people at work • Individual behaviors – this chapter – Personality, perception, learning, and motivation • Group behaviors – next chapter – Norms, roles, team-building, and conflict 7 OB Issues • Employee productivity – Efficiency and effectiveness • Absenteeism – Employees missing work • Turnover – Employees quitting • Organizational citizenship – Employees working to better the organization 8 Attitudes • Judgments/beliefs re:objects, people, events • Job-related Attitudes – Job satisfaction – Job involvement: how much employee… • Identifies with job • Actively participates in it • Considers job performance important for self-worth 9 Does Attitude Matter • Matter of debate for many years • Companies tried to make a caring environment – Hoped it would make more productive employees • Some argue that productivity is not raised • But, happier employees are likelier to show up • Best to focus on improving productivity itself 10 Personality • Combination of psychological traits – Characterize that person • Does personality predict behavior? 11 Personality Models • Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) – Identifies 16 personality types – Four dimensions of personality • Big Five model – Five-factor personality model 12 Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) • Extroversion versus introversion (EI) – (I) Ideas – vs. (E) Environment • Sensing versus intuitive (SN) – (S) Gathered information – Vs. (N) internal ideas 13 MBTI Continued • Thinking versus feeling (TF) – (T) Analyze information – Vs. (F) Values and beliefs • Judging versus perceiving (JP). – (J) Task completion oriented – Vs. (P) information seeking 14 Myers-Briggs Types – Examples • ESFJ – Warmhearted, cooperative – Want to be appreciated for: • Who they are • What they contribute • INTP – – – – Seek logical explanations Theoretical and abstract Skeptical, sometimes critical Analytical 15 Big Five Model of Personality Factors • Extroversion – How sociable, talkative, assertive • Agreeableness – How good-natured, cooperative, trusting • Conscientiousness – How responsible, dependable, persistent, achievementoriented • Emotional stability – How calm, enthusiastic, secure • Openness to experience – How imaginative, artistically sensitive, intellectual 16 Emotional intelligence (EI) • Non-cognitive skills, capabilities, competencies • Influence how others cope with environmental demands & pressures • Found to be very important factor for success – Multiple studies 17 Dimensions of EI: • Self-awareness of one’s feelings • Self-management of one’s own emotions • Self-motivation in face of setbacks • Empathy for others’ feelings • Social skills to handle others’ emotions 18 Perceptual Challenges: What Do You See? 19 Perceptual Challenges: What Do You See? EXHIBIT 8.5 20 Perceptual Challenges: What Do You See? EXHIBIT 8.5 21 Perception • Organizing & interpreting sensory input • Gives meaning to one’s environment • Judgment 22 Influences on Perception • Personal characteristics – – – – – – Attitudes Personality Motives Interests Past experiences Expectations • Target characteristics – Closeness/similarity to other things – Context – Other situational factors. 23 Distortions in Judging Others • Selectivity – Only look at part of picture • Assumed similarity – Assume others are like you • Stereotyping – Assumptions about a group • Halo effect – Impression formed on basis of a single trait • Self-fulfilling prophecy – People behave in ways consistent with expectations 24 Be Careful • Don’t misperceive others • Others may misperceive you/company 25 Shaping Behavior • Shaping behavior – Systematically reinforce each successive step – Moves individual closer to a desired behavior • Four ways in which to shape behavior: – – – – Positive reinforcement Negative reinforcement Punishment Extinction (eliminate rewards) 26 Foundations Of Group Behavior • Group – Two or more interacting and interdependent individuals – Come together to achieve particular objectives • Role – Set of expected behavior patterns – Attributed to someone in a given position/social unit • Norms – Acceptable standards • E.g. dress – Shared and enforced by the members of group 27 Foundations Of Group Behavior • Status – A prestige position or rank – May be informally conferred • Due to education, age, skill, or experience. – Anything can have status if others admire it. 28 Reasons Why People Join Groups • • • • • • Security Status Self-esteem Affiliation Power Goal achievement EXHIBIT 8.8 29 Solomon Asch and Group Conformity 30 Chapter 9 Understanding Work Teams 31 The Popularity Of Teams • Teams typically outperform individuals – When tasks require multiple: • Skills • Judgment • Experience • Better way to utilize individual talents • Flexibility & responsiveness is essential – Changing environment 32 Empowered teams • Increase job satisfaction and morale • Enhance employee involvement • Promote workforce diversity 33 Stages of Team Development 34 The Stages Of Team Development • Stage 1: Forming – Uncertainty about purpose, structure, and leadership • Stage 2: Storming • Stage 4: Performing – Fully functional and accepted structure • Stage 5: Adjourning – Team disbands – Conflict among members • Stage 3: Norming – Relationships develop – Cohesiveness begins 35 High-performing Team Characteristics • • • • • Unified commitment Good communication Mutual trust Effective leadership External support • • • • Internal support Negotiating skills Relevant skills Clear goals 36 Challenges to Creating Team Players • Resistance to teams • Individualistic national culture • High value/significant rewards for individual achievement. 37 Shaping Team Behavior • Proper selection – Both technical skills & interpersonal skills • Employee training – Involve employees in learning team behaviors • Reward appropriate team behaviors – Encourage cooperative efforts • Rather than competitive ones 38 Diversity & Teams • Fresh & multiple perspectives help team: – Identify creative or unique solutions – Avoid weak alternatives • Difficulty of working together may make it harder to: – Unify a diverse team – Reach agreements • Value of diversity increases with cohesiveness – Though diversity’s advantages dissipate with time 39