* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pituitary Unit - rci.rutgers.edu
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Kallmann syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
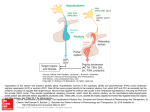
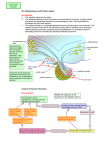
Hypothalamic – Pituitary Unit 11 HYPOTHALAMUS AND ANTERIOR PITUITARY • Introduction to communication, “story lines”, “reflex arc” models, neuroendocrinology, hierarchies, integration, endopathologies. • Hypothalamic - pituitary axis, neurohypophyseal neuronal pathway, posterior pituitary function. Neurovascular hypothesis, hypothalamic and hypophysiotropic neurohormones to the anterior pituitary, experiments. Harris and portal vessels, Halaz and Hypothalamic Hypophysiotropic Area, neuroendocrine transducer cells and AP function. Assessing in vivo and in vitro hypophysiotropic hormone release. • Neuroendocrine control, hierarchies, integrators. Inputs to neuroendocrine transducer cells and their effects on AP hormones. ME as a neuroendocrine integration site, other neuroendocrine integration sites. • Neurohormones (GnRH, TRH, GHRH, SS, CRH, DA). Hypothalamic – Pituitary Unit ANT, POST, AND INTERMEDIARY PITUITARY, & PINEAL • Introduction to hypothalamus, pituitary and pineal function. • Posterior pituitary hormones (OT, AVP) and their secretion, function and regulation. Countercurrent mechanism and the effect of AVP on collecting ducts. Mechanism of action and control of AVP secretion: osmotic stimulation, baroregulation, additional cellular actions. AVP pathologies: hypothalamic / nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (DI), SIADH, gene mutation in familial DI. • Anterior pituitary melanotropic hormones (ßEND, MSH) and their secretion, function and regulation. MSH effects on pigmentation and food intake, species variability, regulation, rhytms, receptors, mechanism of action. ßEND central and peripheral effects, action mechanism. • Pineal hormones (melatonin) and their secretion, function and regulation. Melatonin: biosynthesis, N-acetyl transferase activity and rhytms, light - dark cycle, physiological functions, sleep, behavioral rhythmicity, reproduction, thermoregulation. Page 1 10 Hypothalamic Pituitary Unit Hypothalamus – Ant. Pituitary Hypophysiotropic neurohormones’ main effect is to control anterior pituitary hormone secretion Page 2 Hypothalamus – Ant. Pituitary CS E2 P4 receptor Cortisol. receptor LHRH N TC gonadal hierarchy S CS E AP CS T3 receptor CRH adrenal hierarchy AP TRH thyroid hierarchy AP gonad adrenal thyroid E2 / P4 cortisol T3 / T4 Hypothalamus – Ant. Pituitary The median eminence an hypothalamic integration center Hypophysiotropic neurohormones’ main effect is to control anterior pituitary hormone secretion Page 3 Hypothalamus – Ant. Pituitary • anatomy, embryology, and hierarchies (gonadal, thyroid, GH, adrenal, Prl, intermedin). GnRH: structure, gene expression, receptor, secretion, action, Kallman syndrome, clinical use. TRH: structure, receptor, secreting GnRH cells, regulation, actions, clinical use. GHRH: structure, receptor, secretion, patophysiology, clinical use. SRIF: structure, receptor, secretion, analogs. CRH: structure, receptors, regulation,LH / FSH secretion and patophysiology, clinical use. DA: synthesis and DA neurons, regulation of Prl, receptors, hyperprolactinemia and D2R P4, T, E2 agonists. gases as neural messengers (neurohormones). Hypophysiotropic neurohormones • • • • • • • TRH GRH SS CRH DA VIP MSH - RF 5HT TSH GH ACTH Prl MSH T3, T4 IGFs cortisol Hypophysiotropic neurohormones’ main effect is to control anterior pituitary hormone secretion Hypothalamus – Ant. Pituitary POMC, MSH, ßEND, ACTH, INTERMEDIARY PITUITARY Page 4 Hypothalamus – Ant. Pituitary Melanocortin receptors MC-1, pigmentation MC-2, adrenal function MC-3, cardiovascular MC-4, energy homeostasis MC-5, exocrine secretion Alpha MSH on different subtypes of the MC recepto Hypothalamus – Post. Pituitary AVP main effect is antidiuresis but the “driving force” is the kidney medullary countercurrent mechanism Page 5 Hypothalamus – Post. Pituitary AVP main effect is antidiuresis but the “driving force” is the kidney medullary countercurrent mechanism Hypothalamic Pituitary Unit Page 6 Hypothalamic Pituitary Unit structure a) b) Which, increase or decrease? function How do you know? c) Parts to total? d) Two feedbacks and an absolute requirement? Next week question Page 7