* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Approaches Hand gestures
Reinforcement wikipedia , lookup
Observational learning wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral economics wikipedia , lookup
Professional practice of behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
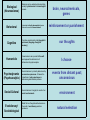
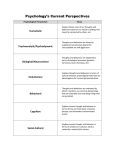
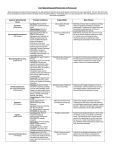
Unit 1: History, Approaches & Research Methods Today’s Topic: the APPROACHES the psychological APPROACHES hand gestures can help us to remember the psychological approaches PSYCHOANALYTIC / PSYCHODYNAMIC Ideas put forth by Sigmund Freud and other Neo-Freudians. Focuses on the ideas that: • your early childhood plays a huge role in shaping your personality. • childhood traumas and experiences create unconscious drives and conflicts that impact individual personalities. PSYCHOANALYTIC / PSYCHODYNAMIC – point behind you -- way back • “My past, my unconscious, determines my behavior” COGNITIVIST • Focuses on mental processes (how we encode, process, store, and retrieve information). • Believe that behavior is partially governed by the ways we think and interpret the world. COGNITIVIST – point to forehead • “How I think determines my behavior” HUMANISTIC • Focuses on an individual’s free will and potential for growth. • Believes that behavior is determined by each person’s capacity to choose how to think and act which is dictated by their perceptions of the world. HUMANISTIC – point to self • “I choose how I behave” NEUROSCIENCE /BIOLOGICAL • Focuses on the belief that behavior is governed by physiological responses like changes in brain chemistry, brain structure, nervous system, etc. NEUROSCIENCE /BIOLOGICAL -pinky finger • We are only starting to know just how much our brain, genes, hormones… determine our behavior. BEHAVIORAL Focuses on: • the importance of the external environment in shaping behavior. A behavior’s frequency is largely a result of rewards and punishments. • the study of learning. • experimental testing that is observable. BEHAVIORAL – middle finger • “My observable behaviors are reinforced or punished and this is what determines my behavior.” SOCIO-CULTURAL • Focuses on how behaviors and mental processes vary amongst the different cultures of the world • This is a more recent approach that came about as people in different places came into contact with each other more often (globalism) • Used to understand and predict SOCIO-CULTURAL – make “the world” gesture • “My culture and social environment determines my behavior “ EVOLUTIONARY • believe that people change or perpetuate (continue) behavior in order improve their chance to survive (and therefore reproduce) • Based on Charles Darwin’s theory of “survival of the fittest” (Natural Selection) EVOLUTIONARY – opposable thumbs • Our behaviors are the result of our innate need to reproduce Biological (Neuroscience) Behavioral Cognitive Humanistic Behavior can be understood by describing underlying biochemical and neurological causes. Interested in directly observable behaviors that are the result of external stimuli. Cognitive psychologists study thoughts & processes (language, thought & memory). Views behavior as a product of free will and opposed the determinism of behaviorism & psychoanalysis. brain, neurochemicals, genes reinforcement or punishment our thoughts I choose Psychodynamic (Psychoanalytic) Human behavior is primarily determined by unconscious processes. Stresses the importance of early experiences in determining later behavior patterns. events from distant past; unconscious Social-Cultural Human behavior is largely the result of our social environments. environment Belief that our thoughts and behaviors are the result of evolutionary selection pressures. natural selection Evolutionary/ Sociobiological