* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download organ - Amper
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
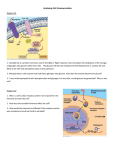
Biologie člověka úvod Orgány, orgánové soustavy Hierarchické uspořádání živočišného těla Atoms Organelle Smooth muscle cell Molecule 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. Cardiovascular system Heart Blood vessels 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules. Smooth muscle tissue 3 Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells. Blood vessel (organ) Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue Epithelial tissue 4 Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues. 6 Organismal level The human organism is made up of many organ systems. 5 Organ system level Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely. Figure 1.1 Atoms Molecule 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. Atomy Molekuly Figure 1.1, step 1 Atoms Organelle Smooth muscle cell Molecule 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules. Buněčné organely Buňky Figure 1.1, step 2 Atoms Organelle Smooth muscle cell Molecule 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules. Smooth muscle tissue 3 Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells. Tkáně Figure 1.1, step 3 Atoms Organelle Smooth muscle cell Molecule 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules. Smooth muscle tissue 3 Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells. Blood vessel (organ) Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue Epithelial tissue 4 Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues. Orgány Figure 1.1, step 4 Atoms Organelle Smooth muscle cell Molecule 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. Cardiovascular system Heart Blood vessels 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules. Smooth muscle tissue 3 Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells. Blood vessel (organ) Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue Epithelial tissue 4 Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues. Orgánové soustavy 5 Organ system level Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely. Figure 1.1, step 5 Atoms Organelle Smooth muscle cell Molecule 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. Cardiovascular system Heart Blood vessels 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules. Smooth muscle tissue 3 Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells. Blood vessel (organ) Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue Epithelial tissue 4 Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues. 6 Organismal level The human organism is made up of many organ systems. Organismus 5 Organ system level Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely. Figure 1.1, step 6 Orgánové soustavy Hair Skin Nails Soustava tělního pokryvu (a) Integumentary System Forms the external body covering, and protects deeper tissues from injury. Synthesizes vitamin D, and houses cutaneous (pain, pressure, etc.) receptors and sweat and oil glands. Figure 1.3a Kosterní soustava Bones Joint (b) Skeletal System Protects and supports body organs, and provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement. Blood cells are formed within bones. Bones store minerals. Figure 1.3b Skeletal muscles Svalová soustava (c) Muscular System Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture, and produces heat. Figure 1.3c Brain Nervová soustava Spinal cord Nerves (d) Nervous System As the fast-acting control system of the body, it responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands. Figure 1.3d Pineal gland Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Thymus Soustava žláz s vnitřní sekrecí Adrenal gland Pancreas Testis Ovary (e) Endocrine System Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells. Figure 1.3e Heart Oběhová soustava Blood vessels (f) Cardiovascular System Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, etc. The heart pumps blood. Figure 1.3f Red bone marrow Thymus Lymphatic vessels Thoracic duct Imunitní systém Spleen Lymph nodes (g) Lymphatic System/Immunity Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood. Disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream. Houses white blood cells (lymphocytes) involved in immunity. The immune response mounts the attack against foreign substances within the body. Figure 1.3g Nasal cavity Pharynx Larynx Trachea Lung Bronchus Dýchací soustava (h) Respiratory System Keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. The gaseous exchanges occur through the walls of the air sacs of the lungs. Figure 1.3h Oral cavity Esophagus Trávicí soustava Liver Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus (i) Digestive System Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells. Indigestible foodstuffs are eliminated as feces. Figure 1.3i Kidney Ureter Vylučovací soustava Urinary bladder Urethra (j) Urinary System Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water, electrolyte and acid-base balance of the blood. Figure 1.3j Pohlavní (rozmnožovací) soustava Mammary glands (in breasts) Prostate gland Ovary Penis Testis Scrotum Ductus deferens Uterus Vagina Uterine tube (l) Female Reproductive System (k) Male Reproductive System Overall function is production of offspring. Testes produce sperm and male sex hormone, and male ducts and glands aid in delivery of sperm to the female reproductive tract. Ovaries produce eggs and female sex hormones. The remaining female structures serve as sites for fertilization and development of the fetus. Mammary glands of female breasts produce milk to nourish the newborn. Figure 1.3k-l Digestive system Takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and eliminates unabsorbed matter (feces) Respiratory system Takes in oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide Food O2 CO2 Cardiovascular system Via the blood, distributes oxygen and nutrients to all body cells and delivers wastes and carbon dioxide to disposal organs Blood CO2 O2 Heart Nutrients Interstitial fluid Urinary system Eliminates nitrogenous wastes and excess ions Nutrients and wastes pass between blood and cells via the interstitial fluid Integumentary system Feces Protects the body as a whole Urine from the external environment Figure 1.2 Homeostáza = stálost vnitřního prostředí (fyziologická stabilita organismu) 3 Input: Information sent along afferent pathway to control center. 2 Receptor detects change. Receptor 4 Output: Control Center Afferent Efferent pathway pathway 1 Stimulus produces change in variable. BALANCE Information sent along efferent pathway to effector. Effector 5 Response of effector feeds back to reduce the effect of stimulus and returns variable to homeostatic level. Figure 1.4 1 Stimulus produces change in variable. BALANCE Figure 1.4, step 1 2 Receptor detects change. Receptor 1 Stimulus produces change in variable. BALANCE Figure 1.4, step 2 3 Input: Information sent along afferent pathway to control center. 2 Receptor detects change. Receptor Control Center Afferent pathway 1 Stimulus produces change in variable. BALANCE Figure 1.4, step 3 3 Input: Information sent along afferent pathway to control center. 2 Receptor detects change. Receptor 4 Output: Control Center Afferent Efferent pathway pathway Information sent along efferent pathway to effector. Effector 1 Stimulus produces change in variable. BALANCE Figure 1.4, step 4 3 Input: Information sent along afferent pathway to control center. 2 Receptor detects change. Receptor 4 Output: Control Center Afferent Efferent pathway pathway 1 Stimulus produces change in variable. BALANCE Information sent along efferent pathway to effector. Effector 5 Response of effector feeds back to reduce the effect of stimulus and returns variable to homeostatic level. Figure 1.4, step 5 Control Center (thermoregulatory center in brain) Information sent along the afferent pathway to control center Afferent pathway Information sent along the efferent pathway to effectors Efferent pathway Receptors Temperature-sensitive cells in skin and brain Effectors Sweat glands Sweat glands activated Response Evaporation of sweat Body temperature falls; stimulus ends Stimulus Body temperature rises BALANCE Stimulus Response Body temperature rises; stimulus ends Body temperature falls Receptors Temperature-sensitive cells in skin and brain Effectors Skeletal muscles Shivering begins Efferent pathway Information sent along the efferent pathway to effectors Afferent pathway Control Center (thermoregulatory center in brain) Information sent along the afferent pathway to control center Figure 1.5