* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ion
List of phenyltropanes wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
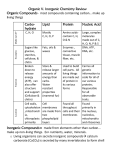
Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ion Introductory of Chemistry English 100-1 Semester 2.1 The Atomic Theory 2.1 The Atomic Theory Law of multiple proportions If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. Law of conservation of mass Matter can be neither created nor destroyed. 2.2 Structure of the Atom Radiation Radioactivity Cathode ray Alpha (a) ray Beta (b) ray Gamma (g) ray 輻射,放射 放射性 陰極射線 Cathode Ray Tube Rays 2.2 The Structure of the Atom Atom* Electron* Proton* Nucleus* Neutron* 原子 電子 質子 原子核 中子 Protons and Neutrons Electron cloud Proton Neutron Mass and Charge of Subatomic Particles 2.3 Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes Atomic number Mass Number Isotopes 原子數 質量數 同位素 Isotopes 2.4 The Periodic Table 週期 Periods Groups (Families) Metal* Nonmetal Metalloid transition metal Alkali metals Alkaline earth metals Halogens* Noble gases (rare gases) 表 週期表中之週期 週期表中之族 金屬 非金屬 準金屬 過渡金屬 鹼金屬 鹼土族 鹵素 鈍氣 (稀有氣體) The Periodic Table 2.5 Molecules and Ions Diatomic molecule Polyatomic molecule Cation Anion Ionic compound Monatomic ions Polyatomic ions 雙原子分子 多原子分子 陽離子 陰離子 離子化合物 單原子離子 多原子離子 Diatomic Molecules Monatomic Ions 2.6 Chemical Formulas 分子式 Molecular formula 分子模型 Molecular Model 結構式 Structural formula 經驗式 Empirical formula Formula of ionic Compound 離子化合物公式 Molecular and Structural Formula Naming Compound Naming Compounds I. Ionic Compounds cation + anions Potassium Bromide Zinc Iodide Aluminum Oxide Lithium hydroxide Potassium cyanide KBr ZnI2 Al2O3 LiOH KCN Transition metal with different charge Manganese (II) oxide MnO Manganese (III) oxide Mn2O3 Manganese (IV) oxide MnO2 Mn2+ Mn3+ Mn4+ Naming Compounds II. Molecular compounds First element + second element-ide Hydrogen chloride HCl Hydrogen bromide HBr Silicon carbide SiC Naming Compounds II. Using Greek prefixes to denote the number of atoms of each element Carbon monoxide Carbon dioxide Sulfur dioxide Sulfur trioxide Nitrogen dioxide Dinitrogen tetroxide CO CO2 SO2 SO3 NO2 N 2O 4 Greek Prfixes Naming Compounds III. Exceptions to the use of Greek prefixes are molecular compounds containing hydrogen. Diborane Methane Silane Ammonia Phosphine Water Hydrogen sulfide B2H6 CH4 SiH4 NH3 PH3 H 2O H 2S Naming Compounds IV. Acid An acid is a substances that yields hydrogen ions H+ when dissolved in water. Naming Compounds IV. Acids Acids that contain hydrogen, oxygen, and other element are called oxoacids. Carbonic acid Chloric acid Nitric acid Phosphoric acid Sulfuric acid H2CO3 HClO3 HNO3 H3NO4 H2SO4 Naming Compounds IV. Acids Oxoacids have the same central atom but a different number of O atoms. Addition of one O atom “ – ic” acid “per … – ic” acid HClO3 HClO4 Chloric acid perchloric acid Naming Compounds IV. Acids Oxoacids have the same central atom but a different number of O atoms. Removal of one O atom “ – ic” acid “ – ous” acid HNO3 HNO2 nitric acid nitrous acid Naming Compounds IV. Acids Oxoacids have the same central atom but a different number of O atoms. Removal of two O atom “ – ic” acid “hypo … – ous” acid HBrO3 HBrO bromic acid hypobromous acid Naming Compounds IV. Acids Oxoanions: anions of oxoacids When all the H ion are removed from “– ic” acid “ – ic” acid “– ate” H2CO3 CO32- carbonic acid carbonate Naming Compounds IV. Acid and Bases Oxoanions: anions of oxoacids When all the H ion are removed from “– ous” acid “ – ous” acid “– ite” H2CO3 CO32- carbonic acid carbonate Naming Compounds IV. Acids Oxoanions: anions of oxoacids Removal of hydrogen Phosphoric acid Hydrogen phosphate Dihydrogen phosphate Phosphate H3PO4 _ H2PO4 2_ HPO4 3_ PO4 Naming Compounds V. Bases A base can be described as_a substance that yields hydroxide ion (OH ) when dissolved in water. Sodium hydroxide Potassium hydroxide Barium hydroxide Ammonia NaOH KOH Ba(OH)2 NH3 Naming Compounds VI. Hydrates (水合物) Hydrates are compounds that have a specific number of water molecules attached to them. Barium chloride dihydrate BaCl2·2H2O Lithium chloride monohydrate LiCl·H2O Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate MgSO4·7H2O Naming Compounds VI. Introduction to Organic Compounds 碳水化合物 Hydrocarbon 烷類 Alkanes 直鏈烷類 Straight chain alkanes Methane Ethane Propane Butane 甲烷 乙烷 丙烷 丁烷 CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 Straight-chain Alkane Naming Compounds VI. Introduction to Organic Compounds 官能基 Functional group 氫氧基 hydroxyl group 胺基 amino group 羧基 carboxyl group Functional Groups hydroxyl group amino group CH3OH CH3NH2 Methanol Methylamine carboxyl group CH3COOH Acetic acid