* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download study for circulatory system
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
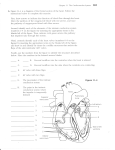
Circulatory System List the functions of the heart, the systemic circulation, and the pulmonary circulation. Heart = Pump for blood Systemic circulation = to all areas except lungs Pulmonary circulation = to lungs (alveoli – air sacs) Label the parts of the heart and coronary vessels, on both an external and an internal view. Trace blood from the vena cavae to the aorta, naming all the heart parts (both valves and chambers) encountered along this path. Name these structures on a heart. Path of Blood Through the Heart: Superior & Inferior Vena Cava Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Right Ventricle Pulmonic (=pulmonary semilunar) valve Pulmonary Trunk Pulmonary Circulation Pulmonary Veins Left Atrium Bicuspid (=Mitral) Valve Left Ventricle Aortic Semilunar Valve Aorta Describe the ECG (=EKG) tracing and explain the meaning of each wave. Explain what is measured on the horizontal axis and on the vertical axis. Briefly discuss information to be gathered from frequency, shape, and direction of the P, QRS, and T waves. R Isoelectric P Q S T Isoelectric line = baseline, reference line, horizontal axis = timing of events, frequency P wave = depolarization of atria QRS wave=depolarization of ventricles (repolarization of atria hidden within QRS wave) T wave = repolarization of ventricles Vertical axis = strength & direction of current Observed Interpretation # P waves Rate of atrial systole # QRS More P than QRS waves QRS without P Direction of wave reversed Irregular line without clear pattern Rate of ventricular systole Blocked conduction from atria to ventricles PVC, premature ventricular contraction; ectopic pacemaker active (damaged & unstable muscle) Current flowing around injured or scarred area of muscle Fibrillation; can occur in atria or ventricles; contractions fluttering, ineffective