* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Making Sense of Addiction Behaviors Larry Tyler, M.Ed., LADC, CCS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
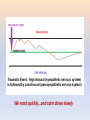
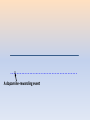
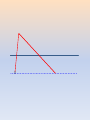
Making Sense of Addiction Behaviors Making Sense of Addiction Behaviors Larry CCSCCS LarryTyler, Tyler,M.Ed., M.Ed.,LADC, LADC, As a result of attending this lecture, participants will… • Have a better understanding of how drug use generates antisocial behavior • Learn how changes in the limbic system create drug cravings, tolerance and relapse • Recognize common patterns of behavior in early recovery • Understand the therapeutic strategies that are used in treatment programs “Why Do Drug Addicts Do What They Do?” Why do they start using drugs again after they’ve gotten through their withdrawal? Don’t they care about their children? If they claim to hate themselves, then why are they so selfish? Why do they deny things that are obviously true? Why is their behavior even worse when they get sober? What makes us tick: •The brain attempts to keep the body in balance (homeostasis) •The brain is elastic and resilient…but only to a point •The brain reacts quickly…but counter-reacts slowly afterward Traumatic Event: High Arousal (sympathetic nervous system) Is followed by Low Arousal (parasympathetic nervous system) We react quickly…and calm down slowly What makes us tick: •The limbic system “flags” outside stimuli, labels emotions and stores memories •The brain releases neurotransmitters (epinephrine, dopamine, endorphins, etc.) to flag events •The prefrontal cortex produces conscious thoughts; planning, contemplating, deciding What is happiness? What we call pleasure, and rightly so, is the absence of all pain -Cicero Pleasure is never as pleasant as we expected it to be and pain is always more painful. The pain in the world always outweighs the pleasure. If you don't believe it, compare the respective feelings of two animals, one of which is eating the other. -Schopenhauer What is happiness? The brain’s basic function: Homeostasis Dopamine is our reward for enjoyable experiences Pleasure is meant to be brief We all try to extend pleasure THE HEDONIC SET POINT (The level at which we are aware of pleasure) What is happiness? •The hedonic set point is the threshold at which the brain recognizes pleasure and reacts to it •Dopamine: The “reward neurotransmitter” (“That feels good, better than I expected…I’ll do it again.”) •Dopamine depletion: A subnormal release of dopamine (This feels horrible…How can I stop this from happening to me?”) ------------------------------------------ Normal Level of Dopamine Release - - -X- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - A dopamine-rewarding event - - -X- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -X- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -X- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -X- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -X- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -X- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - What Goes Up… What Goes Up… Must Come Down What Goes Up… Must Come Down Why won’t the brain just let us be happy all the time??? The Brain Flags Pleasurable Experiences So We Will Remember Them And Return To Them… But It Doesn’t Intend Pleasure To Be Permanent The Brain Cannot Tolerate Chaos •Homeostasis requires balance, order, consistency •When the brain can’t makes sense of something, it confabulates •It struggles to make the illogical logical •Every time we recall an event, we bring forth the memory, and return it to the hippocampus altered •Our values are important to us. When we breach our values, we struggle to justify our behavior WHAT DOES THIS THIS SAY? How does the limbic system handle the “invasion” of drugs into our body? • • • • Tolerance Craving Withdrawal Relapse (All triggered by the limbic system) How does the limbic system handle the “invasion” of drugs into our body? • • • • Tolerance Craving Withdrawal Relapse (All triggered by the limbic system) What do drugs teach us? • • • • Greed Instant gratification Subservience (You’ll be punished if caught) Hopelessness What do drugs teach us? • • • • Greed Instant Gratification Subservience (You’ll be punished if caught) Hopelessness Treatment is deliberately designed to counter the lessons taught by drugs by emphasizing • • • • Positive social interaction Delayed gratification Thoughtfulness and constructive planning Hope Replacing Dopamine as a teacher Counteracting these antisocial traits and behaviors: • • • • • • Manipulation Lying Irresponsibility Lack of empathy Burying/concealing shame Blaming Treatment attempts to reverse everything the brain learned in addiction: Reactivate the prefrontal cortex Learn/re-learn coping skills Become a social animal Develop self respect Early Recovery Post-acute Withdrawal Syndrome Revolt of the Limbic System Physical Withdrawal is Acute… Psychological Effects are Prolonged The Challenges of Recovery • Everything you know and do has to change • The speed of positive results is going to slow way down • The road back to everything that is “familiar and comfortable” (i.e., relapse) is quick and easy. As a result of attending this lecture, participants will… • Have a better understanding of how drug use generates antisocial behavior • Learn how changes in the limbic system create drug cravings, tolerance and relapse • Recognize common patterns of behavior in early recovery • Understand the therapeutic strategies that are used in treatment programs