* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Theories of Human Development
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of autism wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
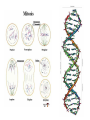
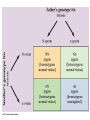
Hereditary Influences on Development Chapter 3 The Genetic Code Chromosomes – Rodlike – Store and transmit genetic information – Matching pairs – 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs… Comprised of deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA Gametes/Sex Cells Sperm, ovum Contain only 23 chromosomes Formed through meiosis “Regular” body cells mitosis Sex cells meiosis Crossing over Multiple Offspring Identical/monozygotic twins Fraternal/dizygotic twins Patterns of Genetic Influence Phenotype Genotype Can have same phenotype but different genotypes…why? How Are Genes Expressed? Simple dominant-recessive inheritance – Each different form of a gene is called an allele – Alleles alike = homozygous Alleles different = heterozygous How Are Genes Expressed? Dominant-recessive Examples of Dominant-Recessive Genes Dominant Traits Recessive Traits Eye color brown eyes grey, green, hazel, blue Vision farsightedness normal vision normal vision normal vision normal vision nearsightedness night blindness color blindness* Hair dark hair non-red hair curly hair full head of hair widow’s peak blonde, light, red hair red hair straight hair baldness* normal hairline *sex-linked characteristic Examples of Dominant-Recessive Genes Dominant Traits Recessive Traits Facial features dimples unattached earlobes freckles broad lips no dimples attached earlobes no freckles thin lips Appendages extra digits fused digits short digits fingers lack 1 joint limb dwarfing clubbed thumb double-jointedness normal normal normal normal normal normal normal number digits digits joints proportion thumb joints Examples of Dominant-Recessive Genes Dominant Traits Other immunity to poison ivy normal pigmented skin normal blood clotting normal hearing Recessive Traits susceptibility to poison ivy albinism hemophilia* congenital deafness normal hearing and speaking deaf mutism normal – no PKU phenylketonuria (PKU) *sex-linked characteristic How Are Genes Expressed? If heterozygous, can pass on a recessive allele to children – Carriers Phenylketonuria (PKU) How Are Genes Expressed? Sex-linked inheritance Codominance Polygenic inheritance Hereditary Disorders Chromosomal abnormalities Hereditary Disorders Autosomal abnormalities – Most frequent is Down syndrome (trisomy 21) – Mental retardation – Distinctive physical features Mutations Detecting Hereditary Disorders Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Ultrasound Know the procedures, advantages, and disadvantages of each… Genetic-Environmental Interactions Reaction range Range of Reaction Canalization Heredity restricts development of some characteristics Examples = babbling, motor development Behavioral Genetics The scientific study of how genotype interacts with the environment to determine behavioral attributes such as intelligence, personality, and mental health Methods of studying hereditary influences – Selective breeding – Family studies Twin studies Adoption studies Behavioral Genetics Twin studies – Identical/fraternal reared together – Adoption studies – Identical twins reared apart Calculate concordance rates Heritability coefficient Behavioral Genetics Heritability coefficient (H) = (r identical – r fraternal) X 2 Environmental influences – Nonshared environmental influences (NSE) 1 – r identical twins reared together – Shared environment influences 1 - (H + NSE) Behavioral Genetics Anxiety scale score – Monozygotic twins: r = .78 – Dizygotic twins: r = .51 – Heritability: 2(.78-.51) 2(.27) .54 – Nonshared: 1 - .78 = .22 – Shared: 1 – (.54 + .22) 1 - .76 = .24 Behavioral Genetics Favorite color – Monozygotic twins: r = .26 – Dizygotic twins: r = .23 – Heritability: 2(.26-.23) 2(.03) .06 – Nonshared: 1 - .26 = .74 – Shared: 1 – (.06 + .74) 1 - .80 = .20 Molecular Genetics To discover the precise locations of genes that determine an individual’s susceptibility to various diseases and other aspects of health and well-being Genome = complete set of instructions for making an organism Human Genome Project