* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
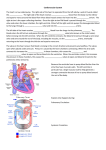
The Cardiovascular System Name____________________ per___ I. Vessels A. Artery Strong elastic vessel that takes blood ________ form heart Under __________________ 3 layers: 1.________________endothelium, 2.________________smooth muscle, 3.________________connective tissue B. Arteriole Smaller arteries with smooth muscle Help control flow of blood by _______________&______________ Layers of vessel get _________ as they approach ____________ C. Capillary Smallest diameter ~_____________ Diffusion of ___________, gases& waste between blood system & cells Can _______ or __________ depending on blood flow needed to area D. Venule Merge to form________________ Start path back to ______________ E. Vein Returns blood to heart _______________ pressure ___________ walls, __________ muscle but ___________ diameter than arteries Valves ___________ back flow of blood Skeletal muscles help blood flow toward ______________ Blood reservoir: 1.veins ______________ to increase blood pressure in times of blood loss 2.Can maintain normal pressure with up to _____% loss of blood volume. II. The Heart A. General characteristics Involuntary, _______________ muscle Located between the lungs, behind sternum in ________________ 14cm x 9cm ( about the size of your ________) Specialized muscular pump( 2 in 1) Right side is “____________________” Left side is “ ____________________” The _________ is located at second rib(top) The___________ is located at the 5th intercostals space, left of sternum heart extends down and to the left ( base to apex) B. Heart coverings pericardium has _________ layers 1. ______________pericardium- outermost sac around heart; tough/dense tissue 2. ______________ pericardium: inner lining of fibrous pericardium 3. _______________pericardium: inner most layer; directly attached to heart. C. Heart Wall _______________: outmost layer of the heart( AKA visceral pericardium) ________________: middle layer: actual cardiac muscle ________________: inner most layer; lines chambers, covers all internal structures. D. Heart Chambers Atria: 1. _____________________ 2. thin walls 3.______________blood returning to the heart from body 4. pushes blood into __________________ 5._____________: small earlike appendages attached to atria 6.interatrial septum:_______________ atria 7.________________: remains of old foramen in fetal heart. Ventricles 1. _________ lower chambers 2. _____________________________________ 3. force blood out of heart to lungs or body 4. _______________ muscles attach to valves 5. interventricular septum: _______________________ B. Valves Atrioventricular valves (AV) 1. Have ______________ that point downward into ventricle. 2. force blood 1 direction 3. close to stop _________________of blood 4. _____________of valves give “lubb-dubb” sound to heart 5. attached by __________________ to papillary muscles a. ___________________ valve( 3 cusps) i. between R. Atrium & R. ventricle b. ____________________ valve( 2 cusps) i. ( mitral valve) ii. between L. Atria & L. ventricle Semilunar (SL) Valves 1. Pulmonary valve: between R. ventricle & pulmonary artery 2. Aortic (semilunar) valve: between L. Ventricle & Aorta Blood flow through heart Deoxygenated side 1. from body via __________________ & superior vena cava 2.__________________________ 3.________________________ valve 4.____________________________ 5.___________________________________ valve 6. Pulmonary trunk 7.____________________________________ 8. to lungs Oxygenated side 1. from lungs via ______________________________veins 2. ______________________ 3. ___________________valve 4. Left ventricle 5.______________________ valve 6. ______________________ 7. ________________________ Coronary Circulation 1. Coronary arteries branch off ___________ a. give _________________ blood to heart 2. Coronary sinus (vein) a. ________________apex & base b. lies in coronary sulcus c. empties into right _______________ D. Heart Conduction System muscles has inherent ability to _________________ muscle cells together contract to cell with the ________________ rhythm coordinates contraction so atria go 1st then ventricles 1. _________________________________ (SA) a. “pacemaker” b. wall of right atrium c. atrial contraction or systole d. stimulates AV node 2. Atrioventricular node a. relays signals to ventricles b. bundle of His (AV bundle) to Purkinje Fibers c. ventricle contraction or systole E. Cardiac Cycle Complete cycle of atrial & ventricular contractions 1. Atrial pressure> ventricular: A-V valves open a. Blood flows into ______________ 2. Atria Contracts: pushes blood into ventricles 3. Increase pressure in ventricles > atrium, contraction a. ___________ valve close b. ____________________muscles contract to hold valves open 4. Atria relaxation: blood flows into chamber a. Semilunar valves (SLV) open: blood forced into______________ 5. Ventricles relax: SLV _____________ a. When ventricular pressure< atrial pressure: A-V _______ b. Brief time when both atria & ventricles are _______________ C. Electrocardiogram(ECG) Record of electrical change in myocardium during cardiac cycle 1. P-Wave: ________________________________ of ventricles a. Leads to _________________ contraction b. ___________ node triggered 2. Q-R-S Complex: depolarization of _________________________ a. Leads to ventricular contraction b. Atria ___________________________________ 3. T-Wave: repolarization of ___________________________ 4. P-Q interval: time for cardiac impulse to travel from _____node through___ node 5. A-V bundle injury: Increase ______________ complex a. Takes ________________to spread impulse through ventricles b. May be caused by_________________ blood flow c. Artificial pacemaker can restore G. Heart Sounds Lubb-Dubb 1.Lubb- ________________________ contraction; ____________valves close a. 5th intercostals space @ nipple line i. Left side=__________________ ii. Right side=_________________ 2.Dubb- Ventricular ; SL Valves close a. 2nd intercostals space H. Heart Action _____________________ (CO): blood pushed / minute ~5,250ml/min or 5.25 L/min. _____________________(SV): how much blood pushed /beat ~70ml/min ______________________( HR): how fast heart beats/min ~ 75 bpm 1. CO = SV x HR 2. ____________________ law of the heart: explains how CO changes with levels of exercise & blood flow I Blood Pressure Force against walls of blood vessels 1 _____________________ Pressure: Ventricular systole a. Forced blood into pulmonary trunk & aorta increase arterial pressure b. Normal ~______mmHg 2 _____________________ Pressure: ventricular diastole a. Ventricles relax, pressure decreases b. Normal ~80 mmHg 3. Measuring Pressure a. __________________ over ____________________ b. Normal _________________mmHg c. Use Sphyg/mo/ma/no/meter ( BP cuff) & stethoscope to hear Korotkoff sounds 4. Pulse a. Distention & recoil of _____________ wall near surface b. Normal ~_____________ in adults, 80-140 in children c. Adult above 100 bpm : ____________________ d. Adult below 60 bpm: ____________________ Influences on Pressure 1. Blood ___________________: increased viscosity= increased pressure a. _____________________/ anemia 2. Blood volume_ ~5L or 8% of body weight a. Hemorrhage/ dehydration= __________________volume 3. Resistance to flow: dilation/ constriction of vessels, a. ______________________ resistance( PR) is friction of blood cells against wall of vessel b. change in __________________ of vessels 4. Heart action: a. Co = _____ x _____ b. BP= _____ x ______ Regulation of BP 1. Nervous system a. Adjusts _____ & PR b. ____________________ control over SA node c. Vasomotor reflex center: constricts/ dilates vessels d. Baroreceptors: _______________________________ e. Chemoreceptors: _____________________________ 2. Hormonal controls a. Epinepherine/Norepinepherine i. _______________________ CO & PR ii. Arteriole vasoconstriction b. Atrial natriuretic factor i. Secreted by _____________ ii. Reduce blood _______________, decrease BP iii. Does so via ____________________ c. Antidiuretic hormone i. Increase blood volume, increasing ________ ii. Kidneys conserve __________________ 3. Kidney’s a. Maintain long term ________ controls i. Regulate water ________________ rate b. Release of Renin i. Triggers angiotensin: _______________________ ii. Triggers aldosterone: reabsorb ________________ follows iii. Increases BP by increasing BV & PR J. Capillary exchange Movement of fluid is caused by 2 forces 1. _________________pressure a. pushes fluid out of vessel b. higher at artery end 2. __________________ pressure a. movement of fluid into vessel b. higher at venous end 3. some fluid goes into lymph system B. Circulation Pulmonary circulation 1. to/from lungs Systemic circulation 1. to/from body