* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introducing DOTUR, a Computer Program for Defining Operational
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Multilocus sequence typing wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
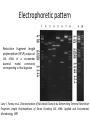
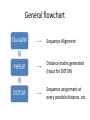
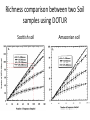
Introducing DOTUR, a Computer Program for Defining Operational Taxonomic Units and Estimating Species Richness Patric D. Schloss and Jo Handelsman Department of Plant Pathology, University of Wisconsin-Madison APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2005 Presenter: Mingjie Wang The Schloss Lab http://schloss.micro.umass.edu/ What is in there Statistical approaches for quantifying and comparing the number and composition of lineages in microbial communities are lacking. (species richness) Species richness estimation • Based on 16S rRNA gene sequences • Grouped as Operational taxonomic units (OTUs)/(Phylotypes) • Defined by Electrophoretic pattern DNA sequence Nucleotide sequence: 97%, 95%, 80% OTU determined by DNA sequence Phlip L. Bond. et al. Bacterial Community Structures of Phosphate-Removing and NonPhosphate-Removing Activated Sludges from Sequencing Batch Reactors. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 1995 Electrophoretic pattern Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis of 16S rDNA of a six-member bacterial model community corresponding to HhaI digestion Larry J. Forney et al. Characterization of Microbial Diversity by Determining Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms of Genes Encoding 16S rRNA. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 1997 General flowchart ClustalW Sequence Alignment PHYLIP Distance matrix generated (input for DOTUR) DOTUR Sequence assignment at every possible distance. etc. Clustering algorithms • Nearest neighbor (NN): Each of the sequences within an OTU are at most X% distant from the most similar sequence in the OTU • Furthest neighbor (FN): All of the sequences within an OTU are at most X% distant from all of the other sequences within the OTU • Average neighbor (AN): A middle ground between the other two algorithms DOTUR makes appropriate sequence assignment • NN: nearest neighbor assignment algorithm • AN: average neighbor assignment algorithm • FN: furthest neighbor assignment algorithm • n1: no. of singletons; • n2: no. of doubletons; etc. Lineage-through-time plots by DOTUR Application of DOTUR • Construction of rarefaction and collector’s curves, Shannon’s and Simpson’s diversity index, ACE, and Chao1, Jackknife, and Bootstrap richness estimators Rarefaction curves Richness comparison between two Soil samples using DOTUR Scottish soil Amazonian soil Richness comparison between two soil samples using DOTUR • Result: The number of observed OTUs from the Amazonian soil falls within the 95 confidence interval (CI) of the Scottish soil with 98 sequences sampled • Conclusion: The two samples have the same level of richness. Application of DOTUR to the Sargasso Sea metagenome sequence 16S rDNA rpoB gene Question • What is the expected number of OTUs in a microbial community? • How to determine the minimum number of sequences to estimate the overall OTUs? Chao1 richness estimation • DOTUR could give the full bias corrected Chao1 richness estimates as described by Chao and modified by Colwell (http://viceroy.eeb.uconn.edu/estimates) Construction of collector’s curves using Chao1 richness estimator 16S rDNA rpoB gene Summary • DOTUR assigns sequences accurately and consistently to OTUs for every distance level. • DOTUR can be used to tell the relative richness between two communities by generating rarefaction curves. • DOTUR can be used to compare different phylogenetic anchors for measuring richness. Summary (cont.) • DOTUR can generate collector’s curves that help determine the minimum number of sequences to estimate the overall OTUs.