* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nature of Matter
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
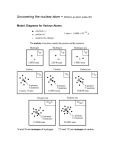
Chapter # 2 – The Chemistry of Life I. The Nature of Matter -Life depends on Chemistry….Chemical reactions in our body keep us alive & all things are made of chemical compounds. A. Atoms – atomos (unable to be cut) Atom – the basic unit of matter. The atom contains 3 subatomic particles 1. Protons – positively charged particles. 2. Neutrons – particles with no charge. 3. Electrons – negatively charged particles that are constantly in motion outside of the nucleus. Atomic Nuclei -Protons + Neutrons = the nucleus Nucleus – the center of the atom which contains the protons & the neutrons. -Atoms are neutral because they have equal numbers of protons & electrons. -Atomic mass = # protons + # neutrons B. Elements & Isotopes Element – a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom. -Over 100 elements are known, but only about 24 are found in living organisms. -Elements are represented by symbols, Ex : C = Carbon, H = Hydrogen, etc. -An element’s atomic number = # protons in an atom of the element. Atomic mass – # protons = # neutrons. Isotopes Isotopes – atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons, Ex : C12,C13, C14 -Are identified by mass number. -Because they have the same # of electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. Radioactive Isotopes Radioactive isotopes – isotopes with unstable nuclei that break down at a constant rate over time. -Used to date specimens, treat cancer, & kill bacteria. C. Chemical Compounds Compound – a substance formed by the chemical combination of 2 or more elements in definite proportions. -The composition of compounds is shown as a chemical formula, Ex : Water is made of 2 hydrogen atoms & 1 oxygen atom. Its chemical formula is H2O. D. Chemical Bonds -Atoms in compounds are held together by chemical bonds. -Bonding happens between electrons that surround atomic nuclei. Electrons that are available to bond are called valence electrons. 2 Major Types of Bonds 1. Ionic – when 1 or more electrons are transferred from 1 atom to another. 2. Covalent – when electrons are shared between atoms. In Ionic bonding : Ions – are positively or negatively charged atoms. Atoms become ions if they : 1. Lose electrons = become positive (cation). 2. Gain electrons = become negative (anion). Types of Covalent Bonds : 1. Single bond – when atoms share 2 electrons (1 pair of electrons). 2. Double bond – when atoms share 4 electrons (2 pairs of electrons). 3. Triple bond – when atoms share 6 electrons (3 pairs of electrons). Molecules & van der Waals forces -Atoms are joined together by covalent bonds, to form molecules – the smallest unit of most compounds. -Electron sharing isn’t always equal. van der Waals forces – a slight attraction that develops between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules.