* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OF LIFE
Survey
Document related concepts
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
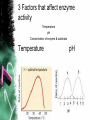
• Living and nonliving things are all made of elements. • It is the way that atoms combine that give every element a different characteristic. • Of the naturally occurring elements on earth, only 25 are essential to living organisms. • The elements Sulfur, Phosphorus, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon, and Hydrogen (SPONCH) are the main components of living matter. • Atoms are the building blocks of every element and all matter. ATOMIC STRUCTURE • The center of an atom is called the nucleus. • Inside the nucleus are positively charged particles called protons. • There are also particles with no charge, called neutrons. • Outside the nucleus are negatively charged particles called electrons. •Each atom has equal number of protons & electrons. No net charge. ISOTOPES • Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. • These atoms are called isotopes. • Isotopes are useful to scientists because they break down & their radiation is detectable, and can be used as a diagnostic tools. Ex. Iodine. COMPOUNDS AND BONDING • A compound is a substance composed of 2 or more different elements combined. • When elements combine they do so to gain stability. • They can share electrons with another element or compound and give away electrons Covalent Bonds • When 2 atoms share electrons. • Most compounds in organisms covalent bonds. • A molecule is a group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. Ex. H2O ** The electrons travel in the orbitals of both atoms involved. Ionic Bonds • When atoms gain or lose electrons it becomes an ion. • The attractive force between 2 ions of opposite charge is called an ionic bond. Ex. NaCl: Sodium Chloride Van der waals forces • Some atoms have a stronger attraction for electrons that others. This means a higher electronegativity. • Even when sharing is equal, the movement of electrons can create forces of slight positive or negative charges. • When molecules are close together, a slight attraction can develop between oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules. • These attractions are called Van der waals forces. • They are not as strong as ionic or covalent bonds but can hold molecules together CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OF LIFE •1 Inorganic compound & •4 Major organic compounds found in living things WATER • MOST IMPORTANT OF ALL INORGANIC COMPOUNDS • 2 Hs & 1O PROPERTIES: • COHESION • ADHESION • CAPILLARY ACTION • Cohesion- An attraction between water molecules. • Adhesion- An attraction between water and a different substance. • Capillary action is an adhesion between water and tubes. (ex. Roots in plants) • Polarity- The oxygen end of a water molecule is slightly negative because O has stronger attraction for electrons. •A molecule that has unequally distributed charges is called a polar molecule. Therefore water is considered polar covalent. FYI: WATER facts • RESISTS TEMPERATURE CHANGES • EXPANDS WHEN IT FREEZES • HELD TOGETHER BY H BONDS DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS VS. HYDROLYSIS • WATER IS REMOVED WHEN SYNTHESIZING (BUILDING) A MOLECULE • WATER IS ADDED TO HYDROLYZE (BREAK DOWN) A MOLECULE Solutions and Suspensions • A mixture is a material composed of 2 or more elements or compounds that are physically mixed together but not chemically combined. • A type of mixture is a solution. • In solutions, all the components are evenly distributed. The solute is the substance that is solid and the solvent is the liquid in which the solute dissolves. • Some materials don’t dissolve in water but separate into pieces that do not settle out. • Mixtures of water and non dissolved materials are known as suspensions. • Human blood is an example of both a solution and suspension. Acids, Bases, and pH • Water can react to form ions. This happens to about 1 water molecule in 550 mllion. WaterHydrogen+ + Hydroxide- • Equal numbers of positive and negative ions are produced which makes water neutral. • The pH scale indicates the concentration of H+ ions. The scale ranges from 0-14. Pure water has a pH of 7. • Each step on the pH scale is a factor of 10. • 1.5 Stomach acid; 2.5 lemon juice; 4.5 Acid rain. • 6 normal rainfall; 8.5 sea water; 10 Soap; 12.5 bleach • Solutions with a pH below 7 on the scale are acids. They have higher concentrations of H+ ions in solution. • Solutions with a pH above 7 are called bases because they have more OH- ions that H+ • A buffer is a weak acid or base that can react with strong acids or bases to cause sudden changes in pH. Carbon Compounds •Carbon atoms have 4 free electrons that can join with electrons from another atom to form a strong covalent bond. •Carbon can also bond with other carbon atoms to form long chains. These carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double, or triple covalent bonds. • Macromolecules are giant molecules made from thousands of smaller molecules. Smaller units called monomers join together to form polymers. This is called polymerization. • The millions of carbon containing compounds are classified into four groups of organic compounds: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. CARBOHYDRATES • Sugars & Starches • Energy Rich • Also used for storage purposes • Contains C, H, O • 1:2:1 ratio of C:H:O • End in –ose • Ex. Glucose C6H12O6 • Simple sugars are monosaccharides like glucose, galactose, and fructose. • The large carbs formed from monosaccharides are either disaccharides or polysaccharides or starches. • Animal starch is glycogen and plants have starch that they store or use in their structure, like cellulose LIPIDS • Contain mostly C, H, O • H ratio is larger than 2:1 • 3 Fatty Acids & 1 Glycerol • Saturated: No double bonds • Unsaturated: Double or Triple Bonds • Stored energy NUCLEIC ACIDS • Contain H,O,N,C,P • Compose of strands of nucleotides • Store and transmit genetic information. • 2 kinds:(DNA) and (RNA) • RNA contains the sugar ribose • DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose. PROTEINS • Contain C, H, O, N, and possibly S. • Composed of Amino Acids: amino group; carboxyl grp; -R grp • Ex. Enzymes, Hormones, Hb, Insulin, Structural Proteins • 1. 2. 3. 4. Proteins can have up to 4 levels or organization The sequence of amino acids in a protein chain (primary) The amino acids in a chain twist like a helix or bend like a pleat (Secondary) The chain itself is folded (Tertiary) van der waals and H bonds help to form globular proteins. A protein that is assembled from 2 or more separate chain (Quaternary) Chemical Reactions • Take place when bonds are formed and broken. REMEMBER: All the chemical reactions that occur within an organism are called metabolism. • Substances that undergo the reaction are called reactants, and the substances that form are called products. • In chemical equations atoms are neither created or destroyed, just rearranged. • A chemical equation is written so that the same numbers of atoms of each element appear on both sides of the arrow. 2H2 + O22 H20 • Chemical reactions can absorb energy or release energy. • The energy released is usually in the form of heat. ENZYMES • The energy that is needed to get a reaction started is called activation energy. • Enzymes decrease activation energy. • Complex proteins • Increase the rates (speed) of reactions. Biological catalyst. • End in -ase • Substances in the reactions are called substrates • LOCK & KEY (Enzyme-Substrate Complex) SPECIFIC • Named after reaction is catalyzes. • Ex. To speed up the breakdown of Maltose the enzyme Maltase is used. Enzyme movie clip 3 Factors that affect enzyme activity Temperature pH Concentration of enzyme & substrate Temperature pH Concentration of enzyme & substrate