* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download central_nervous_system_overview_211
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
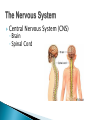
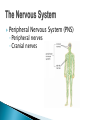
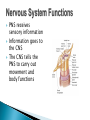
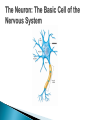
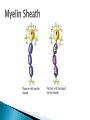
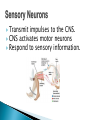
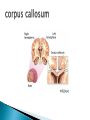
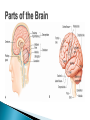
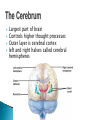
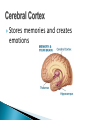
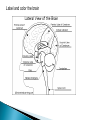
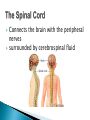
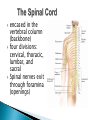
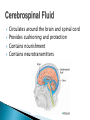
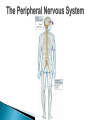
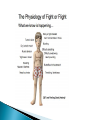
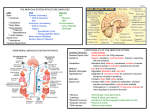
The Nervous System Lesson 1: An Overview Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to … List the functions of the nervous system. Identify and discuss the structures that make up the central nervous system. Explain how nerve impulses are transmitted. State the functions of the peripheral nervous system, the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system, and distinguish the differences between each. Explain the delicate balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Central Nervous System (CNS) ◦ Brain ◦ Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) ◦ Peripheral nerves ◦ Cranial nerves PNS receives sensory information Information goes to the CNS The CNS tells the PNS to carry out movement and body functions Control body’s functions impulse is transmitted from the neural cell body to muscle or organ Usually have several dendrites and only one axon. covered with fatty insulating substance myelin sheath Myelin increases the speed at which impulses are transmitted along the axon. Axons may be several feet long Dendrites resemble tree branches and are unsheathed Lack true dendrites, Sheathed resemble axons Motor Neuron Sensory Neuron Transmit impulses to the CNS. CNS activates motor neurons Respond to sensory information. located entirely within the CNS Work between sensory and motor neurons Myelinated sheaths ◦ inner sheath of myelin ◦ outer sheath of Schwann cells ◦ Schwann cells are needed for regenerating a damaged nerve Unmyelinated sheaths bundled unit of fibers Group of nerve fibers in CNS The spinal cord ◦ Afferent =ascend to the brain ◦ Efferent = descend from the brain The Brain largest nerve tract is corpus callosum joins the right and left hemispheres Solely comprised of the brain and spinal cord. Parts of the brain Largest mass of nervous tissue Three meninges: ◦ Pia Mater ◦ Arachnoid ◦ Dura Mater Controls body functions and movement specific areas of the brain Generates thought memory and emotion REPORT ON REPORTER Largest part of brain Controls higher thought processes Outer layer is cerebral cortex left and right halves called cerebral hemispheres has four lobes Stores memories and creates emotions Contains ◦ midbrain ◦ pons ◦ medulla oblongata (Connects brain [pons] to spinal cord) Relay information ◦ visual ◦ auditory Located in the back of the skull Second largest portion of the brain Coordinates voluntary and involuntary movement Adjusts muscles to maintain posture Label and color the brain Connects the brain with the peripheral nerves surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid encased in the vertebral column (backbone) four divisions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral Spinal nerves exit through foramina (openings) 1. What do you think is the purpose of cerebrospinal fluid? Circulates around the brain and spinal cord Provides cushioning and protection Contains nourishment Contains neurotransmitters http://www.raptorpharma.com/science_neur otrans.html 12 pairs of cranial nerves Olfactory – provides sense of smell Optic – provides vision Trigeminal –sensory input from the face Facial – controls the muscles of the face and scalp Vestibulocochlear–hearing and equilibrium Glossopharyngeal – provides general sense of taste Vagus – controls muscles of the digestive, slowing of heartbeat Pair up Different stations Responsible for controlling involuntary bodily functions divides ◦ sympathetic ◦ parasympathetic fight or flight ◦ increased alertness ◦ Increase metabolic rate the adrenal gland releases epinephrine that causes adrenaline rush conserve energy innervate the digestive system decrease in metabolism Decrease in bodily functions Impulses are transmitted between neurons via chemicals called neurotransmitters Anesthesiologist Neurologist Neurosurgeon Psychiatrist Psychologist