* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outline 19
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
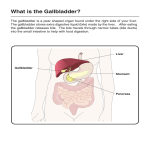
Lecture 19 Digestive System General Anatomy Divisions o Digestive ________________ Muscular tube extending from the mouth to the anus Includes the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine o Accessory organs The teeth, tongue, salivary glands, ____________, gallbladder, and pancreas Walls of the digestive tract o Layers __________________ – innermost layer that lines the lumen Epithelium – simple columnar in most of the tract Lamina propria – loose connective tissue layer Muscularis mucosa – thin layer of smooth muscle Submucosa – loose connective tissue Contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, a nerve plexus, and __________________ glands Muscularis externa – Consists of two layers of smooth muscle near the outer surface _____________________ layer – consists of the inner layer which encircles the tract Longitudinal layer – consists of the outer layer which runs the length of the intestine Serosa – consists of a thin layer of areolar tissue topped by a simple squamous mesothelium Relationship to the Peritoneum The peritoneum is a __________________ membrane that lines the peritoneal cavity of the abdomen and covers the mesenteries and viscera o Organs that are within the peritoneal cavity are intraperitoneal o Organs dorsal to the peritoneum are _________________________ The mesenteries are serous membranes the bind the intestines together and suspend them from the abdominal wall The lesser omentum is a membrane that extends from the stomach to the liver The ______________________ omentum is a membrane that extends from the stomach and loosely covers the intestines like an apron o It extends down the abdomen and then turns back on itself and passes upward, forming a pouch The Mouth through the Esophagus The oral cavity – the mouth o The cheeks –the ______________________ limits of the mouth 1 o The tongue – the muscular organ that aids in food intake, detects food, manipulates food, and initiates swallowing o The __________________ – the wall that separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity (it allows us to breathe through the nose while chewing) Hard palate – supported by palatine process of the maxillae and palatine bones Soft palate – posterior to the hard palate, composed of muscle, but no bone o The teeth – _______________________ dentition – Our teeth don’t all have the same shape Incisors – chisel-like cutting teeth used to bite off a piece of food Canines – pointed teeth that act to puncture and shred food o Act as weapons in many mammals Premolars and Molars – have broad surfaces for ___________________ and grinding Diphyodont dentition – We have ____________ sets of teeth in a lifetime Deciduous teeth – baby teeth erupt from the age of 6 to 30 months Permanent teeth – replace deciduous teeth between 6 and 25 years of age Teeth layers – Alveolus – tooth socket Periodontal ligament – ____________________ fibers that anchor the tooth Cementum – outermost layer of the root Dentin – hard yellowish tissue deep in the tooth _____________________- – outermost layer of the crown (above the root) Pulp cavity – space within the tooth containing loose connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves The salivary glands o Parotid gland – anterior and inferior to the ear Over the ____________________ muscle Largest of the salivary glands o Submandibular gland – medial to the margin of the mandible o Sublingual gland – located in the __________________ of the mouth The pharynx o Regions covered in lecture 17 o Has constrictors that push food to the _________________________ The esophagus o Straight muscular tube dorsal to the trachea, leading to the stomach o Mucosa has esophageal glands that secrete lubricating mucus 2 The Stomach Muscular sac in the upper left region of the abdominal cavity just below the ______________________ Functions o It stores food (expanding from 50 ml to up to 4 L) o It mechanically breaks up food particles o It begins ___________________ digestion, producing a mixture of semidigested food called chyme Curvatures: o Lesser curvature – short distance between esophagus and intestines o _______________________ curvature – longest distance between esophagus and intestines Regions: o Cardia– small area within about 3 cm of the esophagus o Fundus – dome-shaped portion superior to the esophageal attachment o _________________ – the largest portion of the stomach o Pylorus –funnel-shaped portion that connects to the intestines Microscopic anatomy: o Innermost layer (mucosa) has simple columnar glandular epithelium o The mucosa has depressions called gastric ___________ o Surrounding the gastric pits are gastric ______________ of various types Mucous cells secrete mucus _________________ cells secrete hydrochloric acid Chief cells secrete pepsinogen The small intestine Gross anatomy o Regions: Duodenum – first 10 inches Begins at the pyloric valve, forms an arc around the head of the ________________________ Internally, it has spiral ridges called circular folds that cause the chyme to move slowly and cause more contact with the mucosa It receives and mixes the stomach contents, pancreatic juice (from the pancreas), and _______________ (from the gall bladder and liver) Jejunum – next 8 feet Begins at the dudenojejunal flexure Has large, tall, closely-spaced circular folds It has relatively __________________ and muscular walls and a rich blood supply Ileum – last 12 feet of small intestine (note the spelling - not “ilium”) It has __________________, less-muscular walls than the jejunum 3 It has prominent lymphatic nodules in clusters called Peyer patches It is connected to the first part of the large intestine (the cecum) at the ileocecal valve Microscopic anatomy o To increase surface area there are three kinds of folds or projections ____________________ folds - spiral ridges that slow the path of food and increase surface area by a factor of 2 or 3 Villi – finger-shaped projections about .5 to 1 mm high that give the mucosa a ___________________ appearance (like a terrycloth towel) The increase surface area by a factor of 10 Microvilli – Each cell of a villus has a fuzzy brush border of microvilli and 1 m high This wrinkling of the cell membrane increases the surface area by a factor of ___________ The Large Intestine The large intestine is about 6 feet long and 2.5 inches in __________________ (it’s larger in diameter than the small intestine) Regions: o ___________________ Blind pouch at the beginning of the large intestine that connects to the ileum (at the ileocecal valve) Attached to the cecum is the appendix – a blind tube about 5 cm long It contains lymphocytes and plays an important role in the immune system In herbivorous vertebrates, the cecum and appendix are filled with _________________ that digest plant fiber o Colon Ascending Colon – extends up on the right side of the abdominal cavity Transverse Colon – extends from right to left ___________________ Colon – extends down the left side of the abdominal cavity Sigmoid Colon – S-shaped portion that directs waste medially and downward Other Structures – Taneae coli are distinct muscle bands that run the length of the large intestine Haustra are a series of bulges in the walls of the intestine Epiploic appendages are small but numerous fat-filled pouches that are attached superficially to the taeniae coli o ____________________ Sends waste downward through the pelvic cavity (about 15 cm) 4 o Anal Canal The last 3 cm of the rectum Secretes extra mucus which lubricates the canal during defecation Accessory Glands of Digestion The liver o Reddish brown organ under the diaphragm o In addition to performing other functions, it produces _____________ Bile is a fluid containing minerals, cholesterol, neutral fats, phospholipids, and bile acids Bile emulsifies fat to improve fat digestion o Gross Anatomy It has four lobes _______________ lobe – Superior and largest lobe Left lobe – Superior lobe; smaller than right lobe Caudate lobe – Inferior lobe, posterior (near vena cava) ________________ lobe – Inferior lobe, anterior, 4-sided (near gall bladder) o Microscopic Anatomy The interior of the liver contains hepatic lobules Each lobule contains a central vein passing through its core The lobule consists of plates of cells called hepatocytes The plates have blood-filled chambers called hepatic sinusoids The ______________________ secrete bile into bile canaliculi Bile canaliculi lead to bile ductules Bile ductules lead to hepatic ducts Bile moves towards the periphery of the lobule Blood flows into the liver from two sources: Hepatic _______________ vein Hepatic artery Blood flows from these sources from the periphery into the hepatic sinusoids The hepatocytes process the blood, and the blood collects in the _______________ vein in the center of the lobule Blood from the central veins converges in the hepatic veins which empty into the inferior vena cava The gallbladder and bile passages o The liver produces bile, which then travels to the gallbladder o The gallbladder is a pear-shaped sac on the underside of the liver It stores and concentrates bile o The neck of the gallbladder leads to the _________________ duct o The cystic duct combines with the common bile duct to carry bile to the duodenum through the common bile duct The Pancreas o Ninety percent of the pancreas is exocrine tissue o This tissue has a system of branching ducts The finest branches end in sacs of secretory cells called acini 5 The smaller ducts converge on a main _______________________ duct The pancreatic duct runs lengthwise through the pancreas and joins the bile duct at the duodenum 6