* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10th ed.
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geoprofessions wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
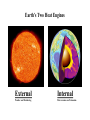
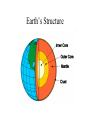
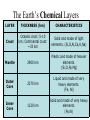
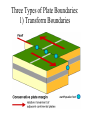
Welcome to Geology! Warm-up for 8/7/15 1) Why do people study geology? 2) What are some topics we might study? Video Clip • http://archives.aapg.org/k12resources/Geo scienceExplained.cfm WHAT IS D.E. GEOLOGY? High School & Maricopa Community College Credit Four Classes: Semester 1: a) Physical Geology Lecture (3cr) b) Physical Geology Lab (1cr) Semester 2: c) Historical Geology Lecture (3cr) d) Historical Geology Lab (1cr) Credit transfers to ASU, UofA, and NAU. TOPICS COVERED SEMESTER 1 -Minerals and Rocks -Topographic Maps -Landforms -Groundwater -Internal Processes -Geologic Structures -Geologic Hazards -Economic Geology TOPICS COVERED SEMESTER 2 -Formation of planets. -Fossil identification. -Paleoenvironments. -Stratigraphy. -Plate Tectonics. -Reconstructing Earth history. GRADING PVCC REGISTRATION • Registration deadline is August 27. • Payment deadline is Sept 16 ($351). Warmup • How might Dual Enrollment expectations differ from the expectations in a regular classroom? Classroom Procedures • 1) Class begins with a Warmup. Write the date, question, and your response. • 2) Quiet symbol: Classroom Procedures • 3) Take care of personal needs before coming to class (4 passes for sign-outs). • 4) Leave your food and drink outside. • 5) Cell phone policy. • 6) Pick up graded papers in back of room. • 7) Bell to bell learning. INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is Geology Important? Warmup: Continue listing ways in which GEOLOGY relates to this image. Welcome to Geology! How might a DE class differ from a high school class? 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) What is Physical Geology? • Physical Geology is the study of – 1) the materials that make up the Earth, – 2) the changes that occur inside the Earth and on Earth’s surface, and – 3) the forces behind these changes. WHAT IS PHYSICAL GEOLOGY? • Geology is an interdisciplinary science (based on chemistry, physics, and biology). CHEMISTRY PHYSICS Geology BIOLOGY • Geology is an applied science, influencing almost every aspect of our life. Reasons to Study Geology 1) To Obtain Natural Resources. For each American, we annually mine 22,000 pounds of mineral resources: -Stone -Sand -Gravel -Limestone -Clay -Salt -Metals such as Iron, Aluminum, Copper, Lead, Zinc, Manganese. And 17,000 pounds of energy resources: - Petroleum - Coal - Natural gas - Uranium Most of these physical and energy resources are nonrenewable. They take thousands or millions of years to form and concentrate). Warmup 8 /12 • Without looking at your notes, • Sketch a Pencil, and list the ways geology relates to your pencil. 2) To Protect the Environment - Geologists study the movement of contaminants in soil and groundwater. 3) To Understand Geologic Hazards -Some parts of the world are more geologically active than others. -We can live in these areas if we understand the threats. Flooding of the Mississippi River in 1993 resulted in 47 fatalities. In Washington State, Mount St. Helens erupted in 1980. There were 57 direct fatalities (and 7 incidental fatalities). The low death rate is a direct result of predictions and warnings by the USGS. 4) To appreciate our surroundings. AZ REPUBLIC HEADLINES 8/12/14 The Earth's Four Systems The Earth's Four Systems The “spheres” interact. For example, CO2 in the atmosphere is controlled by the biosphere (plants absorb CO2 and animals emit it), the geosphere (volcanoes release CO2), and the hydrosphere (the ocean absorbs CO2 and incorporates it into limestone as the mineral calcite, CaCO3). Warmup 8/14 Sketch the internal structure of the Earth. Earth’s Two Heat Engines External Internal Weather and Weathering Plate tectonics and Volcanism Earth’s Structure The Earth’s Chemical Layers LAYER THICKNESS (km) CHARACTERISTICS Crust Oceanic crust: 5-10 km; Continental crust: ~33 km Solid and made of light elements. (Si,O,Al,Ca,K,Na) 2900 km Plastic and made of heavier elements. (Si,O,Fe,Mg) 2270 km Liquid and made of very heavy elements. (Fe, Ni) 1220 km Solid and made of very heavy elements. (Fe,Ni) Mantle Outer Core Inner Core The Earth’s Mechanical Layers 1) Lithosphere: A cool, solid, rigid layer made of crust (oceanic and continental) and the uppermost part of the mantle. Tectonics “plates” are made of lithosphere. 2) Asthenosphere: A hot, weak, plastic layer in the upper mantle. Tectonic plates "float" on the plastic asthenosphere. Important Note! • The continents are not plates. • Continents “ride” upon plates, just like luggage rides on a conveyer belt. Warmup 8/15 Tell whether each process is linked to the external or internal heat engine (or neither): Mountain building Meteorite impacts Tsunamis Winds Tornados Sinkholes Earthquakes Weathering Flowing rivers Tides Rain Plate tectonics Continental Drift • Continental Drift is a hypothesis proposed by German scientist Alfred Wegener in 1920’s to explain the puzzlelike “fit of continents”, and the matching of rock and fossil types across oceans. • The hypothesis was largely rejected because the “driving mechanism” was unknown. Unifying Theme # 3: Plate Tectonics The theory of Plate Tectonics was proposed in the late 1960s, largely in response to a new understanding of seafloor geology. The theory describes lithosphere as being broken into plates that move slowly on top of the plastic aesthenosphere. This motion is driven by convection in the mantle (hot buoyant magma rises and cooler, more dense magma sinks). Warmup • What is the difference between “continental drift” and “plate tectonics”? • What do continental drift and plate tectonics help us to understand? The Plates and Plate Boundaries There are 12 main lithosphere plates. Much geology happens at the boundaries between these plates! Three Types of Plate Boundaries: 1) Transform Boundaries 2) Divergent Boundaries 3) Convergent Boundaries Geologic Time The best estimate for Earth's age is ~4.6 billion years (same as age of our Solar System, as indicated by meteorites). Historically, there has been much debate over "how fast" geology happens with two different camps of thought: CatastrophismUniformitarianism- Today we know that many geologic processes occur gradually over millions of years (such events are often imperceptible over the span of a human lifetime), whereas some geologic events happen within seconds. Geologic Time Define: CatastrophismUniformitarianism- Some Benchmark Events in Earth History • The first life forms (bacteria) developed ~3.5 billion years ago (bya). • Complex life forms first became abundant about 544 million years ago (mya). • Reptiles became abundant ~230 mya. • Dinosaurs went extinct (along with many other organisms) ~65 mya. • Humans have lived for ~0.5 - 3 million years.