* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geo rev 1 (intro)
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
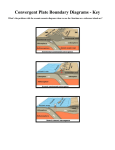
Climate Change and CO2 Sequestration Fundamentals of Geology Importance of Geology to Climate & CCS Earth’s climate record is stored in rocks Subsurface sequestration sites require geologic knowledge: Reservoir Seal Trap geometry Reaction of CO2-rich solutions with minerals may impact long-term carbon storage What is geology? The study of the planet Earth –– the materials of which it is made, the processes [series of actions that produce change] that act on these materials, the products formed, and the history of the planet and its life forms since its origin (AGI Glossary of Geology). Scientific method Every physical event has a physical explanation Hypotheses (tentative explanations) are proposed Theories are hypotheses that are confirmed by others and widely accepted No explanation is immune to question Principle of uniformitarianism Geologic processes in operation today have worked in much the same way over geologic time. The present is the key to the past Origin of the Earth Nebular hypothesis: Solar system originated from a rotating cloud of gases and dust. (Immanuel Kant, 1755) Nebular Hypothesis • Contraction of rotating cloud • Most matter concentrated at center • Accretion of planets Origin of the Earth Differentiation: Heat of impacts and radioactive decay causes melting and differentiation of Earth Plate tectonics The Earth science revolution of the 1960s Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) German meteorologist and geophysicist Proposed continental drift hypothesis in 1915 Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Hypothesized that continent arranged in super continent 200 my ago Plate tectonics The Earth science revolution of the 1960s Crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere Driving force for plate motion Plate tectonics The Earth science revolution of the 1960s Crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere Driving force for plate motion Plate margins (where all the action is) Divergent Margin Divergent Margin Divergent Margin, Iceland Divergent and Convergent Margins Convergent Margin Convergent Margin Convergent Margin Continental Collision Continental Collision Transform Margin Transform Margins Transform Margins Transform Margins Continental drift Continental configurations for past 750 my