* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atom
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
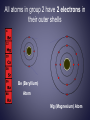
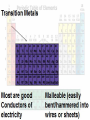
The Periodic Table of elements Elements in Earth’s Crust What are people made of? Classic Greek Mendeleev- First Periodic Table ( 1869) • Grouped by atomic mass & chemical properties. • Blank spaces were left to add predicted elements Mendeleev’s Periodic Table Mosley 1914- Modern P.T. • Atomic # • Similar property elements ended up next to each other •Periodic Law Periodic Law Repetition of physical & chemical properties due ↑ atomic # Modern Periodic Table Elements are arranged: Vertically into Groups Horizontally Into Periods Why? If you looked at an atom of each element in a group, you would see… Same # valence electrons. All atoms in group 2 have 2 electrons in their outer shells Be (Beryllium) Atom Mg (Magnesium) Atom If you looked at an atom from each element in a period you would see… All atoms in Period 4 have 4 Energy Levels 4th Shell K (Potassium) Kr (Krypton) Atom Atom Fe (Iron) Atom Shells = Ring= Orbit = E Level Periodic Patterns Element’s chemical behavior is determined by: its e- config Each Group has distinct properties Alkali Metals • 1 valence e-: ns1 • Most reactive metals • Always bonded with another element. Alkaline Earth Metals • 2 valence e-: ns2 • Never found free in nature • Found in rocks/ earth’s crust How many things can you think of that have Transition Metals in them? Hydrogen • In a class of its own • Gas @ room temp. Group 13: 3 valence eGroup 14: 4 valence eGroup 15: 5 valence eGroup 16: 6 valence e- ns2np1 ns2np2 ns2np3 ns2np4 Interesting facts • Carbon element of life • Nitrogen 78% atmosphere • Oxygen the most abundant element in earth’s crust Halogen • • • • 7 valence electrons ns2 np5 Most active non-metals. Never found free in nature Poisonous Noble Gases • • • • • Very stable 8 valence electrons ns2np6 Colorless gases Un reactive (inert) World’s running out of He Properties of Metals 1. Conductors of heat and electricity 2. Luster: shiny. 3. Ductile: stretched into thin wires 4. Malleable: pounded into thin sheets Properties of Metalloids • Metalloids :metal-like • Can be shiny or dull • Conduct heat/electricity better than non-metals but not as well as metals. • They are ductile and malleable. What are metalloids used for? Properties of Non-Metals • Not: ductile, malleable, shiny, or conductor • Brittle and break easily ELEMENT SONG Element Game