* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural selection
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
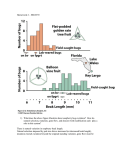
NATURAL SELECTION, SEXUAL SELECTION & ARTIFICIAL SELECTION WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT NATURAL SELECTION? DEFINITION • Natural selection: is one of the basic mechanisms of evolution, it is the process in nature by which, according to Darwin's theory of evolution, only the organisms best adapted to their environment tend to survive and transmit their genetic characters in increasing numbers to succeeding generations while those less adapted tend to be eliminated. TYPES OF NATURAL SELECTION • Stabilizing Selection: occurs when natural selection favors the intermediate states of continuous variation (results in a decrease of a population genetic variance). Over time, the intermediate states become more common and each extreme variation will become less common or lost. TYPES NATURAL SELECTION CONT.. • Directional selection: occurs when natural selection favors one extreme of continuous variation (Effect: there is a shift in genetic variance of the population for a different phenotype). Over time, the favored extreme will become more common and the other extreme will be less common or lost. TYPES NATURAL SELECTION CONT… • Disruptive/Diversifying selection: occurs when natural selection favors both extremes of continuous variation (increases genetic variance when natural selection selects for two or more extreme phenotypes that each have specific advantages). Over time, the two extreme variations will become more common and the intermediate states will be less common or lost. Disruptive selection can lead to two new species. EXAMPLE OF NATURAL SELECTION WHAT TYPE OF NATURAL SELECTION IS THIS? SEXUAL SELECTION ARTIFICIAL SELECTION