* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Integrated Land and Water Management
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
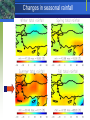
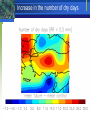
Integrated Approaches to Land and Water Management Lessons from Turkey Global Perspectives on Watershed Management First generation (1970s and 80s): top down, engineered solutions, little consultation Second generation (1990s): community participation, local involvement, working from menus of options …. What’s the next generation? Experience in Turkey Eastern Anatolia Watershed Rehabilitation Project, now closed, was a classic second generation project which had significant positive impacts. Poverty and Forests in Turkey Second project (Anatolia Watershed Rehabilitation Project) was a second generation ‘plus’ project ….. What was the ‘plus’? Significant differences from the previous project 1. Institutions: widened involvement of public sector institutions (MEF and MARA: TÜGEM,OGM, ORKÖY, KKGM, AGM, SPAs, and CYGM) Significant differences from the previous project 2. Very strong focus on service delivery: to poor communities in upland catchments Significant differences from the previous project 3. Linkages: between upstream and downstream interests Upstream interests: jobs, income generation, access to resources (forests, pastures, irrigation) [High poverty rates] Significant differences from the previous project 3. Linkages: between upstream and downstream interests Downstream interests: livestock improvement, manure management, crop productivity [Lower poverty rates] Adding to the menu of options Capitalizing on local interests in animal health and hygiene Introducing integrating manure management systems which return compost to crops/pastures Reducing and controlling water pollution into the Black Sea Reducing nitrate levels in groundwater Manure management measures Some lessons Centrality of community institutions in decision making Organizing multiple government institutions to focus on service delivery in poor communities (convening power of the Bank) Impact of introducing marginal technical improvements for managing manure Animal hygiene Local hygiene Nitrate pollution reduction Access to composted manure What about climate change? Warming is already evident (3ºC over last 50 years in western Mediterranean) Winter precipitation since 1950 has decreased by about 20 percent Projected impacts on Turkey of global 2ºC temperature rise include: changes in seasonal rainfall more dry days per year outcome will have impacts on agriculture Changes in seasonal rainfall Increase in the number of dry days The challenges Scaling up: 65 percent of total rural land is degraded. Current operation is a ‘micropilot,’ covering 28 microcatchments. As many as 2000 could use similar treatment Poor understanding of impacts on hydrology – increasingly critical to have this understanding as climate change impacts are felt Medium term challenge of mitigating climate change impacts